Abstract
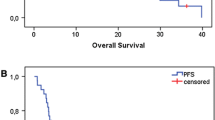
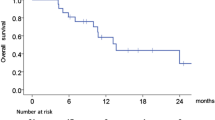
Platinum-based therapy is active in advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Patients with inoperable recurrent or metastatic HNSCC have a poor prognosis; many have difficulty tolerating cisplatin-based regimens. Oxaliplatin has antitumor activity without many of the toxicities of cisplatin. We conducted a phase I pilot study to investigate the dose limitation of oxaliplatin with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and cetuximab in patients with untreated recurrent or metastatic HNSCC. The planned dose escalation schedule included: dose level 1: oxaliplatin 100 mg/m2 day 1, 5-FU CIV 750 mg/m2/day over 96 h beginning day 1, and cetuximab 400 mg/m2 day 1 (then 250 mg/m2 weekly) every 21 days. Dose level 2: oxaliplatin 130 mg/m2 day 1, 5-FU CIV 1,000 mg/m2/day over 96 h beginning day 1, and the same dose and schedule of cetuximab. Seven patients were accrued at dose level 1 and three at dose level 2. Dose level 1 toxicity included grade 1–2 stomatitis, fatigue, acneiform rash, and anemia, and grade 1 nausea and transaminitis. Dose level 2 toxicity was unacceptable: 2 of 3 patients experienced grade 4 toxicities (stomatitis, diarrhea, and acute renal failure) requiring hospitalization with one treatment-related death. Accrual was therefore closed with dose level 1 considered the maximum tolerated dose. Observed responses were short-lived. The regimen of oxaliplatin 100 mg/m2 day 1, infusional 5-FU 750 mg/m2/day over 96 h beginning day 1, and cetuximab 400 mg/m2 day 1 (then 250 mg/m2 weekly), every 21 days, has manageable toxicity; these doses are recommended for phase II evaluation in the treatment for unresectable or metastatic HNSCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelstein DJ, Tan EH, Lavertu P. Treatment of head and neck cancer: the role of chemotherapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1996;24:97–116.
Jacobs C, Lyman G, Velez-Garcia E, et al. A phase III randomized study comparing cisplatin and fluorouracil as single agents and in combination for advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10:257–63.
Forastiere AA, Metch B, Schuller DE, et al. Randomized comparison of cisplatin plus fluorouracil and carboplatin plus fluorouracil versus methotrexate in advanced squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10:1245–51.
Clavel M, Vermorken JB, Cognetti F, et al. Randomized comparison of cisplatin, methotrexate, bleomycin and vincristine (CABO) versus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (CF) versus cisplatin (C) in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. A phase III study of the EORTC Head and Neck Cancer Cooperative Group. Ann Oncol. 1994;5:521–6.
Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1116–27.
Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, et al. Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:824–32.
Chung CH, Ely K, McGavran L, et al. Increased epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4170–6.
Temam S, Kawaguchi H, El-Naggar AK, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor copy number alterations correlate with poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2164–70.
Goldstein NI, Prewett M, Zuklys K, et al. Biological efficacy of a chimeric antibody to the epidermal growth factor receptor in a human tumor xenograft model. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:1311–8.
Li S, Schmitz KR, Jeffrey PD, et al. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:301–11.
Sato JD, Kawamoto T, Le AD, et al. Biological effects in vitro of monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal growth factor receptors. Mol Biol Med. 1983;1:511–29.
Patel D, Guo X, Ng S, et al. IgG isotype, glycosylation, and EGFR expression determine the induction of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in vitro by cetuximab. Hum Antibod. 2010;19:89–99.
Kimura H, Sakai K, Arao T, et al. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of cetuximab against tumor cells with wild-type or mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:1275–80.
Zhang W, Gordon M, Schultheis AM, et al. FCGR2A and FCGR3A polymorphisms associated with clinical outcome of epidermal growth factor receptor expressing metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with single-agent cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3712–8.
Vermorken JB, Trigo J, Hitt R, et al. Open-label, uncontrolled, multicenter phase II study to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of cetuximab as a single agent in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck who failed to respond to platinum-based therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2171–7.
Baselga J, Trigo JM, Bourhis J, et al. Phase II multicenter study of the antiepidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with platinum-refractory metastatic and/or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5569–77.
Herbst RS, Arquette M, Shin DM, et al. Phase II multicenter study of the epidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab and cisplatin for recurrent and refractory squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5578–87.
Fan Z, Baselga J, Masui H, Mendelsohn J. Antitumor effect of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies plus cis-diamminedichloroplatinum on well established A431 cell xenografts. Cancer Res. 1993;53:4637–42.
Reed E, Kohn KW. Platinum analogues. In: Chabner BA, Collins JM, editors. Cancer chemotherapy. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Co.; 1990. p. 465–90.
Al-Sarraf M. Head and neck cancer: chemotherapy concepts. Semin Oncol. 1988;15:70–85.
Legallicier B, Leclere C, Monteil C, Elkaz V, Morin JP, Fillastre JP. The cellular toxicity of two antitumoural agents derived from platinum, cisplatinum versus oxaliplatin, on cultures of tubular proximal cells. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1996;22:41–50.
Rixe O, Ortuzar W, Alvarez M, et al. Oxaliplatin, tetraplatin, cisplatin, and carboplatin: spectrum of activity in drug-resistant cell lines and in the cell lines of the National Cancer Institute’s Anticancer Drug Screen panel. Biochem Pharmacol. 1996;52:1855–65.
Fukuda M, Ohe Y, Kanzawa F, Oka M, Hara K, Saijo N. Evaluation of novel platinum complexes, inhibitors of topoisomerase I and II in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) sublines resistant to cisplatin. Anticancer Res. 1995;15:393–8.
Dunn TA, Schmoll HJ, Grunwald V, Bokemeyer C, Casper J. Comparative cytotoxicity of oxaliplatin and cisplatin in non-seminomatous germ cell cancer cell lines. Invest New Drugs. 1997;15:109–14.
Extra JM, Marty M, Brienza S, Misset JL. Pharmacokinetics and safety profile of oxaliplatin. Semin Oncol. 1998;25:13–22.
Woynarowski JM, Chapman WG, Napier C, Herzig MC, Juniewicz P. Sequence- and region-specificity of oxaliplatin adducts in naked and cellular DNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;54:770–7.
Degardin M, Cappelaere P, Krakowski I, Fargeot P, Cupissol D, Brienza S. Phase II trial of oxaliplatin (L-OHP) in advanced, recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1996;32B:278–9.
Debled M, Gervais R, Laguerre B et al. (2003) Phase II study of oxaliplatin (OXA) in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5FU) in first line treatment of locally advanced (LA) or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:509 (abstr 2049).
Tabernero J, Van Cutsem E, Díaz-Rubio E, et al. Phase II trial of cetuximab in combination with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5225–32.
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Makhson A, et al. Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin with and without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:663–71.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Sanofi-Aventis, Paris, France.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, J.I., Greene, J.B., Lau Clark, A. et al. Phase I pilot study of oxaliplatin, infusional 5-FU, and cetuximab in recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. Med Oncol 30, 358 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0358-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0358-x