Abstract
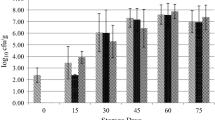
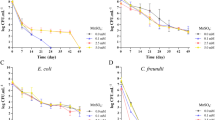
This study aimed to evaluate the use of nalidixic acid-adapted strains of three major Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and non-pathogenic E. coli for the use of radio frequency (RF) heating using phosphate buffer saline (PBS). The effectiveness of RF was evaluated on cocktails of various STEC serotypes (O157:H7, O26:H11, O111) and non-pathogenic E. coli at different endpoint temperatures (55, 60, and 65 °C). All strains were successfully adapted to nalidixic acid (Nal). In general, the results indicated that Nal-adapted strains were not significantly different from Nal-sensitive strains evaluated either before treatment or at the endpoint temperatures. Nal-adapted strains were, therefore, confirmed to be effective as marker organisms in studies involving the use of RF in buffer. Results also showed that the thermal inactivation of strains was more effective as the treatment temperature increased, particularly at 65 °C, which showed a 6.0 log CFU/ml reduction. The results of the present study serve as a baseline to study RF as a potential intervention technology for non-intact beef products.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awuah, G. B., Ramaswamy, H. S., Economides, A., & Mallikarjunan, K. (2005). Inactivation of Escherichia coli K-12 and Listeria innocua in milk using radio frequency (RF) heating. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 6, 396–402.
Aymerich, T., Picouet, P. A., & Monfort, J. M. (2008). Decontamination technologies for meat products. Meat Science, 78, 114–129.
Blackburn, C. W., & Davies, A. R. (1994). Development of antibiotic resistant strains fr the enumeration of foodborne pathogenic bacteria in stored foods. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 24, 125–136.
Blanco, M., Blanco, J. E., Mora, A., Dahbi, G., Alonso, M. P., Gonzalez, E. A., Bernardez, M. I., & Blanco, J. (2004). Serotypes, virulence genes and intimin types of Shiga toxin (verotoxin)-producing Escherichia coli isolates from cattle in Spain and identification of a new intimin variant gene (eae-xi). Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 42, 645–651.
Byrne, B., Lyng, J. G., Dunne, G., & Bolton, D. J. (2010). Radio frequency heating of comminuted meats—considerations in relation to microbial challenge studies. Food Control, 21, 125–131.
Datta, A., & Davidson, M. (2000). Microwave and radio frequency processing. Journal of Food Safety, 65, 32–41.
Fiore, A., Di-Monaco, R., Cavella, S., Visconti, A., Karneili, O., Bernhardt, S., & Foglinano, V. (2013). Chemical profile and sensory properties of different foods cooked by a new radiofrequency oven. Food Chemistry, 139, 515–520.
Gekeve, D. J., & Brunkhorst, C. (2008). Radio frequency electric fields inactivation of Escherichia coli in apple cider. Journal of Food Engineering, 85, 215–221.
Gill, A. O., Moza, L. F., & Barbut, S. (2009). Survival of bacteria in less than thorough cooked, brine-injected steaks. Food Control, 20, 501–507.
Guo, Q., Pisayena, P., Mittal, G. S., Si, W., & Gong, J. (2006). Efficacy of radio frequency cooking in the reduction of Escherichia coli and shelf stability of ground beef. Food Microbiology, 23, 112–118.
Ha, J., Rye, S., & Kang, D. (2013). Inactivation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in peanut butter cracker sandwiches by radio-frequency heating. Food Microbiology, 34, 145–150.
Heddleson, R. A., & Doores, S. (1994). Factors affecting microwave heating of foods and microwave induced destruction of foodborne pathogens—a review. Journal of Food Protection, 57(11), 1025–1037.
Jadeja, R., & Hung, Y. C. (2013). Influence of nalidixic acid adaptation on sensitivity of various shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli to EO water treatment. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 54, 298–301.
Jadeja, R., Hung, Y. C., & Bosilevac, J. M. (2013). Resistance of various shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli to electrolyzed oxidizing water. Food Control, 30, 530–584.
Ju, W., Shen, J., Li, Y., Toro, M. A., Zhao, S., Ayers, S., Naijar, M. B., & Meng, J. (2012). Non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in retail ground beef and pork in the Washinghton D. C. area. Food Microbiology, 32, 371–377.
Kirmaci, B., & Singh, R. (2012). Quality of chicken breast meat cooked in a pilot-scale radio frequency oven. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 14, 77–84.
Lyng, J. G., Zhang, L., & Brunton, N. (2005). A survey of the dielectric properties of meats and ingredients used in meat product manufacture. Meat Science, 69(4), 589–602.
Marshall, K. M., Niebuhr, S. E., Acuff, G. R., Lucia, L. M., & Dickson, J. S. (2005). Identification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 meat processing indicators for fresh meat through a comparison of the effects of selected antimicrobial interventions. Journal of Food Protection, 68(12), 2580–2586.
Nagaraj, G., Purohit, A., Harrison, M. A., Singh, R., Hung, Y. C., & Mohan, A. (2016). Radiofrequency pasteurization of inoculated ground beef homogenate. Food Control, 59, 59–67.
Niebuhr, S. E., Laury, A., Acuff, G. R., & Dickson, J. S. (2008). Evaluation of nonpathogenic surrogate bacteria as process validation indicators for Salmonella enterica for selected antimicrobial treatments, cold storage, and fermentation in meat. Journal of Food Protection, 71(4), 714–718.
Niemira, B. A. (2005). Nalidixic acid resistance increases sensitivity of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to ionizing radiation in solution and on green leat lettuce. Journal of Food Science, 70(2), M121–M124.
Niemira, B. A., Lonczynski, K. A., & Sommers, C. H. (2006). Radiation sensitivity of Salmonella isolates relaitve to resistance to ampicilin, chloramphenicol or gentamicin. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 75, 1080–1086.
Perez-Juan, M., Kondjoyan, A., Picouet, P., & Realini, C. (2012). Effect of marination and microwave heating on the quality of Semimembranosus and Semitendinosus muscles from Friesian mature cows. Meat Science, 92, 107–114.
Rincon, A. M., & Singh, R. K. (2016). Inactivation of Shiga toxin-producing and nonpathogenic Escherichia coli in non-intact steaks cooked in a radio frequency oven. Food Control, 62, 390–396.
Schlisselberg, D. B., Kler, E., Kalily, E., Kisluk, G., Karniel, O., & Yaron, S. (2013). Inactivation of foodborne pathogens in ground beef by cooking with highly controlled radio frequency energy. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 160, 219–226.
Sporing, S. B. (1999). Escherichia coli O157:H7 risk assessment for production and cooking of blade tenderized steaks. Master’s Thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas.
Statistical solutions LLC (2014). Available at http://www.statisticalsolutions.net/pssZtest_calc.php, Accessed on July, 2014.
Taormina, P. J., & Beuchat, L. R. (1999). Comparison of chemical treatments to eliminate enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 on alfalfa seeds. Journal of Food Protection, 62, 318–324.
U. S. Department of Agriculture, & Food Service and Inspection Service. (1999). Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in certain raw beef products. Federal Register, 77, 9888–9889.
U. S. Department of Agriculture, & Food Service and Inspection Service. (2011). Performance standards for the production of certain meat and poultry products. Federal Register, 64, 732–749.
Ukuku, D. O., Gekeve, D. J., Cooke, P., & Zhang, H. Q. (2008). Membrane damage and viability loss of Escherichia coli K-12 in apple juice treated with radio frequency electric field. Journal of Food Protection, 71(4), 684–690.
Yamamoto, S. A., & Harris, L. J. (2001). Phosphate buffer increases recovery of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from frozen apple juice. Journal of Food Protection, 9, 1315–1319.
Zhang, L., Lyng, J. G., & Brunon, N. P. (2007). The effect of fat, water and salt on the thermal and dielectric properties of meat batter and its temperature following microwave or radio frequency heating. Journal of Food Engineering, 80, 142–151.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Grant no. 2011-68003-30012 from the USDA National Institute of Food Agriculture, Food Safety: Food Processing Technologies to Destroy Food-borne Pathogens Program- (A4131). Special thanks are extended to Dr. Mark Harrison (Food Science and Technology, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia) for allowing the use of his lab for the completion of the present experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rincón, A.M., Singh, R.K. Effect of Radio Frequency Heating on Nalidixic Acid-Adapted Shiga Toxin-Producing and Non-pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains in Buffer. Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 1535–1541 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1740-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1740-z