Abstract
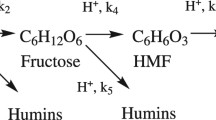
Rate-controlling mechanisms in the photo-degradation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) were studied applying kinetic and thermodynamic compensations. Aqueous solutions of HMF were prepared at a concentration of 100 mg L−1 and at pH values of 3, 3.4, 4, and 5. The UV irradiation of samples was performed in an installation consisting of a black chamber containing the reactor and a mid-pressure mercury lamp with emission wavelengths between 250 and 740 nm. Every sample was irradiated at 12, 25, 35, and 45 °C for 120 min, analyzing their HMF content each 10 min. The photo-degradation data fitted well to zero-order kinetic model, and the constant values were used to study whether the kinetic and thermodynamic compensation could be applied. The isokinetic temperature was very similar for kinetic compensation (TB = 278.0 K) and thermodynamic compensation (TB = 277.8 K). Applying the Leffler’s criterion, the HMF photo-degradation was entropically controlled, probably as a consequence of hydrophobic interactions. In order to check the entropical control, two experiments were repeated at pH 3 but avoiding agitation. As the new obtained kinetic constants were highly different from the values previously obtained using agitation, it can be concluded that the HMF photo-degradation is an entropy-controlled process and can be speeded up by changing non-thermal parameters, like agitation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C HMF :
-
HMF concentration (mg L−1)
- C HMF 0 :
-
Initial HMF concentration (mg L−1)
- E a :
-
Activation energy (J mol−1)
- ∆G B :
-
Change in Gibbs free energy at the isoequilibrium point (J mol−1)
- ∆H :
-
Change in enthalpy (J mol−1)
- h :
-
Planck’s constant (J s)
- HMF:
-
HMF molecule
- K B :
-
Boltzmann’s constant (J K−1)
- k eq :
-
Equilibrium kinetic constant (mol L−1 s−1)
- K 0 :
-
Frequency factor (mol L−1 s−1)
- k HMF :
-
Zero-order kinetic constant on the relation between C HMF and time (mol L−1 s−1)
- N:
-
Total number of treatments
- R:
-
Universal gas constant (J mol−1 K−1)
- ∆S :
-
Change in entropy (J mol−1 K−1)
- T :
-
Absolute temperature (K)
- T B :
-
Isokinetic temperature (K)
- T hm :
-
Harmonic mean temperature (K)
- t:
-
Time (s)
References
Aguilar, K., Garvin, A., Azuara, E., & Ibarz, A. (2015). Modelling of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural photo-degradation by UV irradiation. Influence of temperature and pH. Food Research International, 71, 165–173.
Albala-Hurtado, S., Veciana-Nogues, M. T., Marine-Font, A., & Vidal-Carou, M. C. (1998). Changes in furfural compounds during storage of infant milks. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 46(8), 2998–3003.
Azuara, E., & Beristain, C. I. (2006). Enthalpic and entropic mechanisms related to water sorption of yogurt. Drying Technology, 24(11), 1501–1507.
Azuara, E., & Beristain, C. I. (2007). Thermodynamic and kinetic study of water adsorption on whey protein. Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Quimica, 6(3), 359–365.
Barnes, R., Vogel, H., & Gordon, J. (1969). Temperature of compensation: significance for virus inactivation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.A.), 62, 263–270.
Beristain, C. I., García, H. S., & Azuara, E. (1996). Enthalpy-entropy compensation in food vapor adsorption. Journal of Food Engineering, 30(3), 405–415.
Beristain, C. I., Vernon-Carter, E. J., & Azuara, E. (2011). Thermodynamic and kinetic criteria to study the stability of dried foods. In M. A. Coneau (Ed.), New topics in food engineering (pp. 150–170). New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Chandler, D. (2002). Two faces of water. Nature, 417, 491.
Chodera, J. D., & Mobley, D. L. (2013). Entropy–enthalpy compensation: role and ramifications in biomolecular ligand recognition and design. Annual Review of Biophysics, 42(1), 1–19.
Codex Alimentarius Commission, Codex standard for honey, CODEX STAN 12–1981; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and the World Health Organization, Rome, Italy, 2001.
Delgado-Andrade, C., Rufián-Henares, J. A., & Morales, F. J. (2009). Hydroxymethylfurfural in commercial biscuits marketed in Spain. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, 48(1), 14–19.
Delgado-Andrade, C., Morales, F. J., Seiquer, I., & Pilar Navarro, M. (2010). Maillard reaction products profile and intake from Spanish typical dishes. Food Research International, 43(5), 1304–1311.
Escriche, I., Visquert, M., Carot, J. M., Domenech, E., & Fito, P. (2008). Effect of honey thermal conditions on hydroxymethylfurfural content prior to pasteurization. Food Science and Technology International, 14(5), 29–35.
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). (2004). Report of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on provisional findings on furan in food. EFSA Journal, 137, 1–20.
Falguera, V., Pagán, J., Garza, S., Garvín, A., & Ibarz, A. (2011a). Ultraviolet processing of liquid food: a review. Part 1: fundamental engineering aspects. Food Research International, 44, 1571–1579.
Falguera, V., Pagán, J., Garza, S., Garvín, A., & Ibarz, A. (2011b). Ultraviolet processing of liquid food: a review. Part 2: effects on microorganisms and on food components and properties. Food Research International, 44, 1580–1588.
Falguera, V., Pagán, J., Garza, S., Garvín, A., & Ibarz, A. (2012). Inactivation of polyphenol oxidase by ultraviolet irradiation: protective effect of melanins. Journal of Food Engineering, 110(2), 305–309.
Flores-Andrade, E., Beristain, C. I., Vernon-Carter, E. J., Gutiérrez, G. F., & Azuara, E. (2009). Enthalpy–entropy compensation and water transfer mechanism in osmotically dehydrated agar gel. Drying Technology, 27(9), 999–1009.
García, C. F., Moyano, P. C., & Pedreschi, F. (2008). Enthalpy-entropy compensation for water loss of vegetable tissues during air drying. Drying Technology, 26(12), 1563–1569.
Gökmen, V., & Senyuva, H. Z. (2006). Improved method for the determination of hydroxymethylfurfural in baby foods using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54(8), 2845–2849.
Ibarz, A., Casero, T., Miguelsanz, R., & Pagán, J. (1989). Cinéticas de formación de hidroximetilfurfural en concentrado de zumo de pera almacenado a diferentes temperaturas. Alimentaria, 199, 81–84.
Ibarz, A., Pagán, J., Panadés, R., & Garza, S. (2005). Photochemical destruction of color compounds in fruit juices. Journal of Food Engineering, 69(2), 155–160.
Ibarz, A., Garza, S., Garvín, A., & Pagán, J. (2008). Kinetics of peach clarified juice discoloration process with an adsorbent resin. Food Science and Technology International, 14(5), 57–62.
Ibarz, R., Garvín, A., Falguera, V., Pagán, J., Garza, S., & Ibarz, A. (2014). Modelling of patulin photo-degradation by a UV multi-wavelength emitting lamp. Food Research International, 66, 158–166.
Ibarz, R., Garvín, A., Azuara, E., & Ibarz, A. (2015). Modelling of ochratoxin A photo-degradation by a UV multi-wavelength emitting lamp. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 61, 385–392.
Imai, T., & Hirata, F. (2005). Hydrophobic effects on partial molar volume. Journal of Chemical Physics, 122(9), 094509.
Koutchma, T. (2009). Advances in ultraviolet light technology for non-thermal processing of liquid foods. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2(2), 138–155.
Krug, R. R., Hunter, W. G., & Grieger, R. A. (1976). Enthalpy-entropy compensation.2—Separation of the chemical from the statistical effect. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 80(21), 2341–2351.
Labuza, T. P. (1980). Enthalpy/entropy compensation in food reactions. Food Technology, 34(2), 67–77.
Lee, T. P., Sakai, R., Manaf, N. A., Rodhi, A. M., & Saad, B. (2014). High performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of patulin and 5-hydroxymethilfurfural in fruit juices marketed in Malaysia. Food Control, 38, 142–149.
Leeson, S., Díaz, G. J., & Summers, J. D. (1995). Poultry metabolic disorders and mycotoxins. Guelp: University Books.
Leffler, J. E. (1955). The enthalpy-entropy relationship and its implications for organic chemistry. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 20(9), 1202–1231.
Lum, K., Chandler, D., & Weeks, J. D. (1999). Hydrophobicity at small and large length scales. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 103(22), 4570–4577.
Mikheev, Y. A., Guseva, L. N., Davydov, E. Y., & Ershov, Y. A. (2007). The hydration of hydrophobic substances. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 81(12), 1897–1913.
Missen, R. W., Mims, C. A., & Saville, B. A. (1999). Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics. New York: Wiley.
Morales, F. J. (2009). Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and related compounds. In T. H. Stadler & E. R. Lineback (Eds.), Process-induced food toxicants (pp. 135–174). New York: Wiley.
Murkovic, M., & Pichler, N. (2006). Analysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in coffee, dried fruits and urine. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research, 50(9), 842–846.
Ordóñez-Santos, L. E., Vázquez-Odériz, L., Arbones-Maciñeira, E., & Romero-Rodríguez, M. Á. (2009). The influence of storage time on micronutrients in bottled tomato pulp. Food Chemistry, 112(1), 146–149.
Pascual-Pineda, L. A., Flores-Andrade, E., Alamilla-Beltrán, L., Chanona-Pérez, J. J., Beristain, C. I., Gutiérrez-López, G. F., & Azuara, E. (2014). Micropores and their relationship with carotenoids stability: a new tool to study preservation of solid foods. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(4), 1160–1170.
Pysiak, J., & Sabalski, B. (1979). Compensation effect and isokinetic temperature in thermal dissociation reactions of the type: Asolid ↔ Bsolid + Cgas. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 17, 287–290.
Rada-Mendoza, M., Olano, A., & Villamiel, M. (2002). Determination of hydroxymethylfurfural in commercial jams and in fruit-based infant foods. Food Chemistry, 79(4), 513–516.
Rufián-Henares, J. A., Delgado-Andrade, C., & Morales, F. J. (2006). Analysis of heat-damage indices in breakfast cereals: influence of composition. Journal of Cereal Science, 43(1), 63–69.
Ryde, U. (2014). A fundamental view of enthalpy-entropy compensation. Medicinal Chemistry Communications, 5, 1324–1336.
Starikov, E. B., & Nordén, B. (2012). Entropy–enthalpy compensation as a fundamental concept and analysis tool for systematical experimental data. Chemical Physics Letters, 538, 118–120.
Sun, D., & Wicker, L. (1999). Kinetic compensation and the role of cations in pectinesterase catalysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 47(4), 1471–1475.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Exploratory data on furan in food: 2004. Available at http://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodSafety/Food Contaminants Adulteration/Chemical Contaminants/Furan/ucm078439.htm. Accessed 20 June 2015.
Vorlová, L., Borkovcová, I., Kalábová, K., & Večerek, V. (2006). Hydroxymethylfurfural contents in foodstuffs determined by HPLC method. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, 45(1), 34–38.
Wilfong, E. M., Kogiso, Y., Muthukrishnan, S., Kowatz, T., Du, Y., Bowie, A., Naismith, J. H., Hadad, C. M., Toone, E. J., & Gustafson, T. L. (2011). A multidisciplinary approach to probing enthalpy-entropy compensation and the interfacial mobility model. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 133, 11515–11523.
Williams, D. H., O’Brien, D. P., & Bardsley, B. (2001). Enthalpy/entropy compensation as a competition between dynamics and bonding: the relevance to melting of crystals and biological aggregates. Journal of American Chemical Society, 123(4), 737–738.
Zimmer, K. D., Shoemaker, R., & Ruminski, R. R. (2006). Synthesis and characterization of a fluxional Re(I) carbonyl complex fac-[Re(CO)3(dpop’)Cl] with the nominally tri-dentate ligand dipyrido (2,3-a:3’,2’-j) phenazine (dpop’). Inorganica Chimica Acta, 359(5), 1478–1484.
Zsako, J. (1976). The kinetic compensation effect. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 9, 101–108.
Acknowledgments
The authors kindly thank the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación of the Spanish Government for the funding received in the project CTQ2011-26569. Ebner Azuara thanks CONACYT-México for his sabbatical grant (project 203997). Karla Aguilar thanks CONACYT-México for the doctoral fellowship received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguilar, K., Garvín, A., Azuara, E. et al. Rate-Controlling Mechanisms in the Photo-degradation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 1399–1407 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1729-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1729-7