Abstract
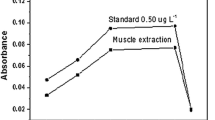
Biogenic amines forms in food by microbial enzymatic decarboxylation of amino acids and excessive consumption of these amines can be of health concern. Many techniques have been developed for the extraction of biogenic amines in food, including acidic or organic extraction as well as solid phase extraction. In this study, we described an alternative method based on a stirrer bead milling for extraction of biogenic amines from fish muscles. The rate and stirring time were optimized with an experimental design optimization procedure. The developed method was compared with the traditional homogenization extraction method. After a derivatization step with benzoyl chloride, samples were analyzed for amines quantitative determination with RP-HPLC system. The analysis method showed good linearity (correlation coefficients of 0.9989) and good recoveries (>94.23 %). The repeatability and reproducibility of the method, in terms of the relative standard deviation, ranged from 1.6 to 2.6 % and 3.3 to 4.9 % respectively. Moreover, the detection limits of biogenic amines were calculated between 0.05 and 0.09 mg kg−1 in fish samples. The proposed method has been applied to the analysis of different fish species of the Persian Gulf. Low biogenic amine levels were found in most fish samples. Total biogenic amine contents of selected samples were ≤68.3 mg kg−1.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Komprda, E. Rejchrtová, P. Sládková et al., Dairy Sci. Tech. 92(4), 367 (2012)
B. Bach, P. Vuchot, M. Grinbaum et al., Anal. Chim. Acta 732, 114 (2012)
B. Ten Brink, C. Damink, H. Joosten et al., Int. J. Food Mirobiol. 11(1), 73 (1990)
M. Latorre-Moratalla, J. Bosch-Fusté, T. Lavizzari et al., J. Chromatogr. A 1216(45), 7715 (2009)
A.R. Shalaby, Food Res. Int. 29(7), 675 (1996)
E. Chiacchierini, D. Restuccia, G. Vinci, Talanta 69(3), 548 (2006)
M. Křížek, F. Vácha, L. Vorlová et al., Food Chem. 88(2), 185 (2004)
C. Ruiz-Capillas, A. Moral, Food Chem. 89(3), 347 (2005)
G. Vinci, M. Antonelli, Food Control 13(8), 519 (2002)
V. Ladero, M. Calles-Enriquez, M. Fernández et al., Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 6(2), 145 (2010)
J. Lange, K. Thomas, C. Wittmann, J. Chromatogr. B 779(2), 229 (2002)
L. Prester, Food Addit. Contam. 28(11), 1547 (2011)
S. Rodtong, S. Nawong, J. Yongsawatdigul, Food Microbiol. 22(5), 475 (2005)
M. Křížek, K. Matějková, F. Vácha et al., Food Chem. 132(1), 367 (2012)
S. Bardócz, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 6(10), 341 (1995)
A. Halász, Á. Baráth, L. Simon-Sarkadi et al., Trends Food Sci. Technol. 5(2), 42 (1994)
M.N. Clifford, R. Walker, Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 27(6), 721 (1992)
J. McLauchlin, C. Little, K. Grant et al., J. Public Health 28(1), 61 (2006)
I.A. Bulushi, S. Poole, H.C. Deeth et al., Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 49(4), 369 (2009)
A.E. Ghaly, D. Dave, S. Budge et al., Am. J. Appl. Sci. 7(7), 859 (2010)
Y.M. Jaw, Y.Y. Chen, Y.C. Lee et al., Fish. Sci. 78(1), 155 (2012)
N. Innocente, M. Biasutti, M. Padovese et al., Food Chem. 101(3), 1285 (2007)
S. Moret, L.S. Conte, J. Chromatogr. A 729(1), 363 (1996)
S. Hernández-Cassou, J. Saurina, J. Chromatogr. B 879(17), 1270 (2011)
C. Almeida, J. Fernandes, S. Cunha, Food Control 25(1), 380 (2012)
A. Andrea, T. Lara, X. Xiong et al., Food Anal. Methods 7, 946 (2014)
R.M. Taskova, H. Zorn, U. Krings et al., Z. Naturforsch. 61(5/6), 347 (2006)
A. Veide, L. Strandberg, S.O. Enfors, Enzyme Microb. Technol. 9(12), 730 (1987)
G. Sagratini, M. Fernández-Franzón, F. De Berardinis et al., Food Chem. 132(1), 537 (2012)
F. Aflaki, N. Saemian, Anal. Methods 6, 1482 (2013)
J. Bakar, A. Yassoralipour, F.A. Bakar et al., Food Chem. 119(2), 467 (2010)
S. Koral, B. Tufan, A. Ščavničar et al., Food Control 32(2), 597 (2013)
M.A. Bezerra, R.E. Santelli, E.P. Oliveira et al., Talanta 76(5), 965 (2008)
S. Moret, R. Bortolomeazzi, G. Lercker, J. Chromatogr. A 591(1), 175 (1992)
C.W. Ho, W.S. Tan, W.B. Yap et al., Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 13(5), 577 (2008)
Y. Wang, E. Forssberg, Int. J. Miner. Process. 81(1), 1 (2006)
H. Zhai, X. Yang, L. Li et al., Food Control 25(1), 303 (2012)
F. Buňka, P. Budinský, B. Zimáková et al., Food Control 31(1), 49 (2013)
C.-C. Hwang, C.-M. Lin, C.-Y. Huang et al., Food Control 25(1), 415 (2012)
J.S. Park, C.H. Lee, E.Y. Kwon et al., Food Control 21(9), 1219 (2010)
L. Prester, Food Addit. Contam. 28(11), 1547 (2011)
L. Yongmei, L. Xin, C. Xiaohong et al., Food Chem. 100(4), 1424 (2007)
M. Nout, Food Res. Int. 27(3), 291 (1994)
M.H.S. Santos, Int. J. Food Mirobiol. 29(2–3), 213 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aflaki, F., Ghoulipour, V., Saemian, N. et al. Determination of biogenic amines in Persian Gulf fish: application of stirrer bead milling extraction method. Food Measure 9, 86–94 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-014-9213-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-014-9213-4