Abstract
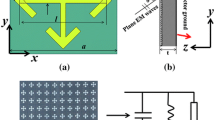
An ultra-thin low-frequency broadband microwave absorber (MWA) based on a magnetic rubber plate (MRP) and cross-shaped structure (CSS) metamaterial (MM) was presented numerically and experimentally. The designed composite MWA is consisted of the MRP, CSS resonator, dielectric substrate and metallic background plane. The low-frequency absorption can be easily adjusted by tuning the geometric parameter of the CSS MM and the thickness of MPR. A bandwidth (i.e. the reflectance is below −10 dB) from 2.5 GHz to 5 GHz can be achieved with the total thickness of about 2 mm in experiments. The broadband absorption is attributed to the overlap of two resonant absorption peaks originated from MRP and CSS MM, respectively. More importantly, the thickness of the composite WMA is much thinner (λ/40; λ is the operation center frequency), which could operate well at wide incidence angles for both transverse electric and transverse magnetic waves. Thus, it can be expected that our design will be applicable in the area of eliminating microwave energy and electromagnetic stealth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.R. Smith and J.B. Pendry, JOSA B 23, 391 (2006).
R.A. Shelby, D.R. Smith, and S. Schultz, Science 292, 77 (2001).
J.B. Pendry, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3966 (2000).
N. Fang, H. Lee, C. Sun, and X. Zhang, Science 308, 534 (2005).
D. Schurig, J. Mock, B. Justice, S.A. Cummer, J. Pendry, A. Starr, and D. Smith, Science 314, 977 (2006).
N.I. Landy, S. Sajuyigbe, J.J. Mock, D.R. Smith, and W.J. Padilla, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 207402 (2008).
N.I. Landy, C. Bingham, T. Tyler, N. Jokerst, D.R. Smith, and W.J. Padilla, Phys. Rev. B 79, 125104 (2009).
Y. Cui, K.H. Fung, J. Xu, H. Ma, Y. Jin, S. He, and N.X. Fang, Nano Lett. 12, 1443 (2012).
Y. Liu, S. Gu, C. Luo, and X. Zhao, Appl. Phys. A 108, 19 (2012).
Y. Ma, Q. Chen, J. Grant, S.C. Saha, A. Khalid, and D.R. Cumming, Opt. Lett. 36, 945 (2011).
L. Huang, D.R. Chowdhury, S. Ramani, M.T. Reiten, S.N. Luo, A.J. Taylor, and H.T. Chen, Opt. Lett. 37, 154 (2012).
Y.Z. Cheng, X.S. Mao, C.J. Wu, L. Wu, and R.Z. Gong, Opt. Mater. 53, 195 (2016).
C.M. Watts, X. Liu, and W.J. Padilla, Adv. Mater. 24, 98 (2012).
H. Li, L.H. Yuan, B. Zhou, X.P. Shen, Q. Cheng, and T.J. Cui, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 014909 (2011).
X. Shen, T.J. Cui, J. Zhao, H.F. Ma, W.X. Jiang, and H. Li, Opt. Express 19, 9401 (2011).
Y.N. Fan, Y.Z. Cheng, Y. Nie, X. Wang, and R.Z. Gong, Chin. Phys. B 22, 067801 (2013).
M.H. Li, L.Y. Guo, J.F. Dong, and H.L. Yang, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 47, 185102 (2014).
Y.Z. Cheng, Y. Nie, and R.Z. Gong, Appl. Phys. B 111, 483 (2013).
Y.Q. Ye, Y. Jin, and S. He, JOSA B 27, 498 (2010).
B.X. Wang, L.L. Wang, G.Z. Wang, W.Q. Huang, X.F. Li, and X. Zhai, IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 26, 111 (2014).
Y. Nie, Y.Z. Cheng, and R.Z. Gong, Chin. Phys. B 22, 044102 (2013).
L. Zhang, P. Zhou, H. Chen, H. Lu, J. Xie, and L. Deng, Appl. Phys. A 121, 233 (2015).
H.B. Zhang, L.W. Deng, P.H. Zhou, L. Zhang, D.M. Cheng, H.Y. Chen, D.F. Liang, and L.J. Deng, J. Appl. Phys. 113, 013903 (2013).
Y.Z. Cheng, Y. Nie, X. Wang, and R.Z. Gong, J. Appl. Phys. 115, 064902 (2014).
W.B. Weir, Proc. IEEE 62, 33 (1974).
E. Michielssen, J.M. Sajer, S. Ranjithan, and R. Mittra, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 41, 1024 (1993).
A. Aharoni, J. Appl. Phys. 81, 830 (1997).
Y.Z. Cheng, R.Z. Gong, and Z.Z. Cheng, Opt. Commun. 361, 41 (2016).
J.C. Zhao and Y.Z. Cheng, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 4269 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., He, B., Zhao, J. et al. Ultra-thin Low-Frequency Broadband Microwave Absorber Based on Magnetic Medium and Metamaterial. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 1293–1299 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5115-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5115-z