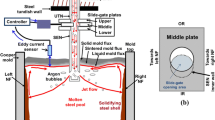
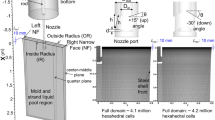
Abstract
Transient turbulent flow in the mold region during continuous casting of steel is related to many quality problems, such as surface defects and slag entrainment. This work applies an efficient multi-GPU based code, CUFlow, to perform large eddy simulations (LES) of the turbulent flow in a domain that includes the slide gate, SEN, and mold region. The computations were first validated by comparing the predicted surface velocity with plant measurements. Then, seven LES simulations were conducted to study the effects of casting speed, electromagnetic braking (EMBr) field strength, and submerged entry nozzle (SEN) depth on the transient flow. The results show that EMBr has an important influence on flow inside the SEN, in addition to flow in the mold. With EMBr, an “M-shaped” flow profile is seen inside the SEN. The swirling flow behavior in the SEN and ports is more symmetrical at high casting speed and with higher EMBr strength. The position of the SEN ports relative to the peak magnetic field affects the EMBr performance. The results confirm and quantify how applying EMBr greatly lowers both the magnitude and turbulent variations of the surface velocity and level profile.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Steel Association: World Steel in figures 2014, World Steel Association, 2014.
Kouji Takatani, Ken Nakai, Norifumi Kasai, Tadao Watanabe, and Hidemasa Nakajima: ISIJ Int., 1989, vol. 29, pp. 1063–68.
Deok-Soo Kim, Woo-Seung Kim, and Kee-Hyeon Cho: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 670–676.
Kevin Cukierski and Brian G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39, pp. 94–107.
Haiqi Yu, Baofeng Wang, Huiqin Li, and Jianchao Li: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, vol. 202, pp. 179–87.
Yufeng Wang and Lifeng Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 1319–51.
H. Harada, T. Toh, T. Ishii, K. Kaneko, and E. Takeuchi: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1236–44.
Xincheng Miao, Klaus Timmel, Dirk Lucas, Zhongmin Ren, Sven Eckert, and Gunter Gerbeth: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43, pp. 954–972.
Zhong-Dong Qian and Yu-Lin Wu: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 100–107.
Yun-Seong Hwang, Pil-Ryung Cha, Ho-Seok Nam, Ki-Hyeon Moon, and Jong-Kyu Yoon: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 659–67.
Ramnik Singh, Brian G. Thomas, and Surya P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 1201–21.
R. Chaudhary, B. G. Thomas, and S. P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43, pp. 532–53.
Akira Idogawa, M. Sugizawa, Shuji Takeuchi, K. Sorimachi, and T. Fujii: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1993, vol. 173, pp. 293–97.
Baokuan Li, Toshimitsu Okane, and Takateru Umeda: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31, pp. 1491–1503.
Yuji Miki and Shuji Takeuchi: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1548–55.
Ramnik Singh, Brian G. Thomas, and Surya P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 1098–1115.
Seong-Mook Cho, Seon-Hyo Kim, and Brian G. Thomas: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 855–64.
B. Thomas and Rajneesh Chaudhary: in 6th Int. Conf. Electromagn. Process. Mater. EPM, Electromagnetic Processing of Materials, Dresden, Germany, 2009, pp. 9–14.
J.-E. Eriksson: US Patent US6938674 B2, Sep. 2005.
Klaus Timmel, Sven Eckert, Gunter Gerbeth, Frank Stefani, and Thomas Wondrak: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 1134–41.
Klaus Timmel, Sven Eckert, and Gunter Gerbeth: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 68–80.
Rajneesh Chaudhary, C. Ji, Brian G. Thomas, and S. P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 987–1007.
Pierre H. Dauby: Rev. Métallurgie, 2012, vol. 109, pp. 113–136.
Fei Li, Engang Wang, Mingjie Feng, and Zhuang Li: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 814–820.
Kai Jin, Brian G. Thomas, and Xiaoming Ruan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 548–65.
Q. Yuan: PhD Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2004.
R. Liu: PhD Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2015.
Hiromichi Kobayashi: Phys. Fluids, 2005, vol. 17, p. 45104.
Hiromichi Kobayashi: Phys. Fluids, 2008, vol. 20, p. 15102.
S.P. Vanka, A.F. Shinn, and K.C. Sahu: in ASME 2011 Int. Mech. Eng. Congr. Expo., American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2011, pp. 429–37.
A.F. Shinn: PhD Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, 2011.
R. Chaudhary: PhD Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, 2011.
P. Kumar, K. Jin, and S.P. Vanka: in Proc. 1st Therm. Fluids Eng. Summer Conf., American Society of Thermal and Fluids Engineers, New York City, August 9, pp. 1–17.
S.P. Vanka: J. Fluids Eng., 2013, vol. 135, p. 61401.
Kai Jin, S. Pratap Vanka, and Brian G. Thomas: J. Fluids Eng., 2015, vol. 137, p. 71104.
K. Jin, S.P. Vanka, and R.K. Agarwal: in 52nd AIAA Aerosp. Sci. Meet., American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Inc., 2014, pp. 1–16.
P. Kumar and S. P. Vanka: Int. J. Multiph. Flow, 2015, vol. 77, pp. 32–47.
P. Kumar, K. Jin, and S.P. Vanka: in Proc. 1st Therm. Fluids Eng. Summer Conf., American Society of Thermal and Fluids Engineers, New York City, August 9, pp. 1–15.
K. Jin, S.P. Vanka, B.G. Thomas, and X.M. Ruan: in Proc. CFD Model. Simul. Mater. Process., The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, Nashville, Tennessee, 2016, pp. 159–66.
Shinichiro Yokoya, Shigeo Takagi, Shingo Ootani, Manabu Iguchi, Katsukiyo Marukawa, and Shigeta Hara: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1208–14.
Saul Garcia-Hernandez, Rodolfo D. Morales, José de Jesús Barreto, and Ken Morales-Higa: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 1794–1802.
Shinichiro Yokoya, Shigeo Takagi, Manabu Iguchi, Katsukiyo Marukawa, and Shigeta Hara: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. S47–51.
R. Liu, J. Sengupta, D. Crosbie, S. Chung, M. Trinh, and B.G. Thomas: in Sens. Sampl. Simul. Process Control, Wiley, San Diego, 2011, pp. 51–58.
Rui Liu, Brian G. Thomas, Joydeep Sengupta, Stephen D. Chung, and ManhKha Trinh: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 2314–23.
Jun Kubota, Noriko Kubo, Toshio Ishii, Makoto Suzuki, Norichika Aramaki, and Ryuzo Nishimachi: NKK Tech. Rev., 2001, vol. 85, pp. 1–9.
Lifeng Zhang, Subo Yang, Kaike Cai, Jiying Li, Xiaoguang Wan, and Brian G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2007, vol. 38, pp. 63–83.
K. Jin, B. G. Thomas, R. Liu, S. P. Vanka, and X. M. Ruan: IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2015, vol. 84, p. 12095.
Brian G. Thomas, Quan Yuan, Sana Mahmood, Rui Liu, and Rajneesh Chaudhary: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 22–35.
J. Kubota, K. Okimoto, A. Shirayama, and H. Mukarami: in 1991 Steelmak. Conf., 1991.
J. Knoepke, M. Hubbard, J. Kelly, R. Kittridge, and J. Lucas: in Steelmak. Conf. Proc., Iron and Steel Society, Chicago, IL, 1994, pp. 381–88.
Manabu Iguchi, Jin Yoshida, Tomoyuki Shimizu, and Yoshiteru Mizuno: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 685–91.
R.J. Moreau: Magnetohydrodynamics, Springer Science & Business Media, Netherlands, 1990.
R. Chaudhary, A. F. Shinn, S. P. Vanka, and Brian G. Thomas: Comput. Fluids, 2011, vol. 51, pp. 100–114.
Lance C. Hibbeler and Brian G. Thomas: Iron Steel Technol., 2013, vol. 10, pp. 121–36.
R. Chaudhary, B.T. Rietow, and B.G. Thomas: in Incl. Clean Steels Mater. Sci. Technol. Conf. AISTTMS, AIST and TMS, Pittsburgh, PA, 2009, pp. 1090–1101.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial supports from the National Science Foundation (Grant No. CMMI 11-30882) and the Continuous Casting Consortium, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. We also thank Baosteel, Shanghai, P. R. China for providing the measurements and corresponding casting conditions. This research is also part of the Blue Waters sustained-petascale computing project, which is supported by the National Science Foundation (awards OCI-0725070 and ACI-1238993) and the State of Illinois. Blue Waters is a joint effort of the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign and its National Center for Supercomputing Applications. The authors also thank NVIDIA Hardware Grant Program for providing the GPUs for an in-house workstation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 1, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, K., Vanka, S.P. & Thomas, B.G. Large Eddy Simulations of the Effects of EMBr and SEN Submergence Depth on Turbulent Flow in the Mold Region of a Steel Caster. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 162–178 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0801-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0801-z