Abstract
Objective
To further explore the anti-cancer effect of Tounong Powder (透脓散) extracts (TNSEs) on human colon cancer LoVo cells and examine the possible molecular mechanisms.
Methods
The contents of TNSEs were determined by liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer (LC-MS) analysis after extraction with water and methanol. Variations of cell morphological features were observed using fluorescence microscopy. Cytotoxicity was determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Cell cycle distribution and apoptosis were analyzed using flow cytometry at different TNSE doses (0, 62.5, 125, or 250 μg/mL). Protein expressions of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), phosphate protein kinase B (p-AKT), phosphate mammalian target of rapamycin (p-mTOR), p-p70s6k1, cleaved caspase-9 and -3 were detected using Western blot analysis.
Results
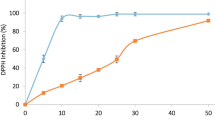
TNSEs induced cell growth inhibition in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Flow cytometric analysis showed apoptotic cells and cell cycle arrest at the G phase after TNSEs treatment compared with controls. Furthermore, TNSEs significantly down-regulated the proteins PI3K, p-AKT, p-mTOR, and p-p70s6k1, and up-regulated the proteins cleaved caspase-9 and -3 dosedependently, as determined by Western blot.
Conclusions
TNSEs reduced LoVo cell proliferation, and caused apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in LoVo cells. This effect might be associated with regulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E, Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010;60:277–300.
Lu JB, Sun XB, Dai DX, Zhu SK, Chang QL, Liu SZ, et al. Epidemiology of gastroenterologic cancer in Henan Province, China. World J Gastroenterol 2003;9:2400–2403.
Nakamura T, Seto M, Tajika M, Kawai H, Yokoi T, Yatabe Y, et al. Clinical features and prognosis of gastric MALT lymphoma with special reference to responsiveness to H. pylori eradication and API2-MALT1 status. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103:62–70.
Kenney S, Theodore E. Woodward award: development of novel, EBV-targeted therapies for EBV-positive tumors. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc 2006;117:55–73;discussion 73-74.
Fang LH, Wang RP, Hu SY, Zhang L, Liu SL. Tounongsan extract induces apoptosis in cultured Raji cells. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:522–528.
Shi ZY, Bao Z, Jiang Y, Tu PF. Quantitative analysis of calycosin glycoside and formononetin in Radix astragali from different sources. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2007;32:779–783.
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 2004;304:554.
Carpten JD, Faber AL, Horn C, Donoho GP, Briggs SL, Robbins CM, et al. A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature 2007;448:439–444.
Johnson SM, Gulhati P, Rampy BA, Han Y, Rychahou PG, Doan HQ, et al. Novel expression patterns of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway components in colorectal cancer. J Am Coll Surg 2010;210:767–776,776-778.
Auyeung KK, Law PC, Ko JK. Novel anti-angiogenic effects of formononetin in human colon cancer cells and tumor xenograft. Oncol Rep 2012;28:2188–2194.
Kan WL, Cho CH, Rudd JA, Lin G. Study of the antiproliferative effects and synergy of phthalides from Angelica sinensis on colon cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2008;120:36–43.
Qi H, Wei L, Han Y, Zhang Q, Lau AS, Rong J. Proteomic characterization of the cellular response to chemopreventive triterpenoid astragaloside in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. Int J Oncol 2010;36:725–735.
Chen QC, Lee J, Jin W, Youn U, Kim H, Lee IS, et al. Cytotoxic constituents from Angelicae sinensis radix. Arch Pharm Res 2007;30:565–569.
Rychahou PG, Jackson LN, Silva SR, Rajaraman S, Evers BM. Targeted molecular therapy of the PI3K pathway: therapeutic significance of PI3K subunit targeting in colorectal carcinoma. Ann Surg 2006;243:833–842; discussion 843-844.
Wang J, Kuropatwinski K, Hauser J, Rossi MR, Zhou Y, Conway A, et al. Colon carcinoma cells harboring PIK3CA mutations display resistance to growth factor deprivation induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 2007;6:1143–1150.
Liu Y, Chen L, Ko TC, Fields AP, Thompson EA. Evi1 is a survival factor which conveys resistance to both TGFbetaand taxol-mediated cell death via PI3K/AKT. Oncogene 2006;25:3565–3575.
Roulin D, Cerantola Y, Dormond-Meuwly A, Demartines N, Dormond O. Targeting mTORC2 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation in vitro and tumor formation in vitro. Mol Cancer 2010;9:57.
Mikami I, Zhang F, Hirata T, Okamoto J, Koizumi K, Shimizu K, et al. Inhibition of activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/ AKT pathway in malignant pleural mesothelioma leads to G1 cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep 2010;24:1677–1681.
Dituri F, Mazzocca A, Lupo L, Edling CE, Azzariti A, Antonaci S, et al. PI3K class IB controls the cell cycle checkpoint promoting cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2012;130:2505–2513.
Brown RE, Tan D, Taylor JS, Miller M, Prichard JW, Kott MM, Morphoproteomic confirmation of constitutively activated mTOR, ERK, and NF-kappaB pathways in high risk neuro-blastoma, with cell cycle and protein analyte correlates. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2007;37:141–147.
Gao N, Zhang Z, Jiang BH, Shi X. Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the cell cycle progression of human prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003;310:1124–1132.
Gao N, Flynn DC, Zhang Z, Zhong XS, Walker V, Liu KJ, et al. G1 cell cycle progression and the expression of G1 cyclins are regulated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR/ p70S6K1 signaling in human ovarian cancer cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004;287:C281–C291.
Feng W, Duan X, Liu J, Xiao J, Brown R E. Morphoproteomic evidence of constitutively activated and overexpressed mTOR pathway in cervical squamous carcinoma and high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2009;2:249–260.
Brown RE, Zhang PL, Lun M, Zhu S, Pellitteri PK, Riefkohl W, et al. Morphoproteomic and pharmacoproteomic rationale for mTOR effectors as therapeutic targets in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2006;36:273–282.
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, et al. Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 1998;282:1318–1321.
Martinou JC, Green DR. Breaking the mitochondrial barrier. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001;2:63–67.
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC. Cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 1994;371:346–347.
Lah JJ, Cui W, Hu KQ. Effects and mechanisms of silibinin on human hepatoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:5299–5305.
Fang LH, Wang RP, Hu SY, Teng YH, Xie WB. The effect of Tou Nong San on transplanted tumor growth in nude mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015;2015:518454.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20141034), the “Top Talented Personnel in Six Profession” grant in Jiangsu Province (No. 2011-WS-049), the Jiangsu Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. Y1008, 2010), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. 012062003010), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Lh., Liu, Sl., Wang, Rp. et al. Tounong Powder (透脓散) extracts induce G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in LoVo cells. Chin. J. Integr. Med. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2597-8
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2597-8