Abstract
Objective
To investigate the anti-inflflammatory effects of Sanguisorbae Radix on contact dermatitis (CD).
Methods
Mice were sensitized by painting 30 µL of 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) onto each ear for 3 days. Four days later, mice were challenged by painting with 50 µL of DNFB onto the shaved dorsum every 2 days. Sanguisorbae Radix methanol extract (MESR) was applied onto the shaved dorsum every 2 days. The effects of MESR on skin thickness, skin weights, histopathological changes, skin lesions and cytokine production in DNFB-induced CD mice were investigated, as well as its effects on body weights and spleen/body weight ratio.
Results
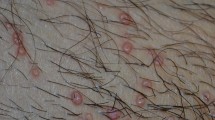
Topical application of MESR effectively inhibited enlargement of skin thickness and weight (P<0.05). MESR treatment also inhibited hyperplasia, spongiosis and immune cell infiltration induced by DNFB in inflamed tissues and improved lesions on dorsum skin in CD mice. Moreover, treatment with MESR suppressed the increase in the levels of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α,P<0.01) and interferon γ (IFN-γ,P<0.05), respectively. Finally, MESR had no effect on body weight gain or spleen/body weight ratio.
Conclusion
These data suggest that MESR acts as an anti-inflflammatory agent that decreases the production of TNF-α and IFN-γ, resulting in reductions of skin lesions and histopathological changes in inflamed skin tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diepgen TL. Occupational skin diseases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2012;10:297–313.
Wen M, Wei C, Hu Z, Srivastava K, Ko J, Xi S, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of anti-asthma herbal medicine intervention in adult patients with moderate-severe allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;116:517–524.
Trautmann A, Disch R, Bröcker EB, Akdis CA, Gillitzer R. How does eczema arise?. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2003;1:8–11.
Saint-Mezard P, Rosieres A, Krasteva M, Berard F, Dubois B, Kaiserlian D, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis. Eur J Dermatol 2004;14:284–295.
Zuo Y, Tang D, Xun J, eds. Science of Chinese materia medica. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Xinhua Printing Works; 2003:201–202.
Zhang S, Liu X, Zhang ZL, He L, Wang Z, Wang GS. Isolation and identification of the phenolic compounds from the roots of Sanguisorba officinalis L. and their antioxidant activities. Molecules 2012;17:13917–13922.
Choi ES, Kim JS, Kwon KH, Kim HS, Cho NP, Cho SD. Methanol extract of Sanguisorba officinalis L. with cytotoxic activity against PC3 human prostate cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 2012;6:670–674.
Yu T, Lee YJ, Yang HM, Han S, Kim JH, Lee Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of Sanguisorba officinalis ethanol extract on NOand PGE2 production is mediated by suppression of NF-κB and AP-1 activation signaling cascade. J Ethnopharmacol 2011;134:11–17.
Shin TY, Lee KB, Kim SH. Anti-allergic effects of Sanguisorba officinalis on animal models of allergic reactions. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2002;24:455–468.
Kim H, Lee MR, Lee GS, An WG, Cho SI. Effect of Sophora flavescens aiton extract on degranulation of mast cells and contact dermatitis induced by dinitrofluorobenzene in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2012;142:253–258.
Klaus MV, Wieselthier JS. Contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician 1993;48:629–632.
Sosroseno W. The immunology of nickel-induced allergic contact dermatitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 1995;13:173–181.
Traidl C, Merk HF, Cavani A, Hunzelmann N. New insights into the pathomechanisms of contact dermatitis by the use of transgenic mouse models. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol 2000;13:300–312.
Banno T, Gazel A, Blumenberg M. Effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) in epidermal keratinocytes revealed using global transcriptional profiling. J Biol Chem 2004;279:32633–32642.
Smith JGJr, Wehr RF, Chalker DK. Corticosteroid-induced cutaneous atrophy and telangiectasia. Experimental production associated with weight loss in rats. Arch Dermatol 1976;112:1115–1117.
Nagao K, Akabane H, Masuda T, Komai M, Tanaka H, Nagai H. Effect of MX-68 on airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in mice and guinea-pigs. J Pharm Pharmacol 2004;56:187–196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and study design: Kim H, Cho SI; funding obtaining: Kim H; data acquisition: Jo S, Ryu J, Kim H, Kim M; data analysis and interpretation: Jo S, Ryu J, Kim H, Cho SI; statistical expertise: Ryu MH, Kim H, Cho SI; administrative technical/logistic support, data collection and assembly: Jo S, Ryu J, Kim H; critical revision of the article for important intellectual content: Ryu MH, Kim H; article drafting and final approval: all authors.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2015R1A2A2A04005619)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, S., Ryu, J., Kim, H. et al. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Sanguisorbae Radix on Contact Dermatitis Induced by Dinitrofluorobenzene in Mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26, 688–693 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2148-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2148-8