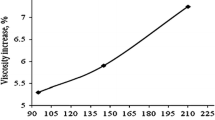
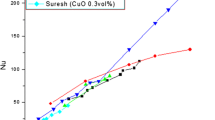
Abstract
By measuring the effective thermal conductivity, taking photos of the distribution of the nano-particles in the fluids and photos that reflect the interfacial phenomena between nano-particles and fluids, we try to explain the possible mechanism for heat conductive enhancement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maxwell, J E. Electricity and Magnetism, Part II. 3rd ed.. U.S.A.: Clarendon, Oxford, 1904. 440
Jeffrey, D J. Conduction Through a Random Suspension of Spheres. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A, 1973, 335(1602): 355–367
Davis, R H. The Effective Thermal Conductivity of a Composite Material with Spherical Inclusions. International J. Thermophysics, 1986, 7(3): 609–620
Lu, S, Lin, H. Effective Conductivity of Composites Containing Aligned Spherical Inclusions of Finite Conductivity. Journal of Applied Physics, 1996, 79(9): 6761–6769
Bonnecaze, R T, Brady, J F. The Effective Conductivity of Random Suspensions of Spherical Particles. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A, 1991, 432(1886): 445–465
Stephen, U S Choi. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles. Energy Technology Division Argonne National Laboratory, 1995
Eastmen, J A, Stephen, U S, Choi, Li, S, et al. Enhanced Thermal Conductivity Through the Development of Nanofluids. In: Material Research for Symposium Proceedings, Pittsburg, USA, 1996, 457: 3–11
Bu-Xuan Wang. Engineering Heat and Mass Transfer (Vol. I, II). Beijing: Science Press, 1998
Tiren Gu. Physical Chemistry on the Surface. Beijing: Science press, 1984
Chongming Cai. Brownian Motion. Beijing: World Publication Press Inc., 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B.X., Li, H. & Peng, X.F. Research on the heat-conduction enhancement for liquid with nano-particle suspensions. J. of Therm. Sci. 11, 214–219 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-002-0057-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-002-0057-6