Abstract
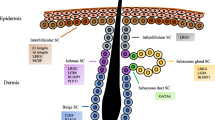
Epidermal stem cells could contribute to skin repair through the migration of cells from the neighboring uninjured epidermis, infundibulum, hair follicle, or sebaceous gland. However, little is known about the factors responsible for the complex biological processes in wound healing. Herein, we will show that the attracting chemokine, SDF-1/CXCR4, is a major regulator involved in the migration of epidermal stem cells during wound repair. We found that the SDF-1 levels were markedly increased at the wound margins following injury and CXCR4 expressed in epidermal stem cells and proliferating epithelial cells. Blocking the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis resulted in a significant reduction in epidermal stem cell migration toward SDF-1 in vitro and delayed wound healing in vivo, while an SDF-1 treatment enhanced epidermal stem cell migration and proliferation and accelerated wound healing. These results provide direct evidence that SDF-1 promotes epidermal stem cell migration, accelerates skin regeneration, and makes the development of new regenerative therapeutic strategies for wound healing possible.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiuti A, Webb IJ, Bleul C, Springer T, Gutierrez-Ramos JC (1997) The chemokine SDF-1 is a chemoattractant for human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and provides a new mechanism to explain the mobilization of CD34+ progenitors to peripheral blood. J Exp Med 185(1):111–120
Ara T, Tokoyoda K, Okamoto R, Koni PA, Nagasawa T (2005) The role of CXCL12 in the organ-specific process of artery formation. Blood 105(8):3155–3161
Ara T, Tokoyoda K, Sugiyama T, Egawa T, Kawabata K, Nagasawa T (2003) Long-term hematopoietic stem cells require stromal cell-derived factor-1 for colonizing bone marrow during ontogeny. Immunity 19(2):257–267
Askari AT, Unzek S, Popovic ZB, Goldman CK, Forudi F, Kiedrowski M, Rovner A, Ellis SG, Thomas JD, DiCorleto PE, Topol EJ, Penn MS (2003) Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor 1 on stem-cell homing and tissue regeneration in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet 362(9385):697–703
Avniel S, Arik Z, Maly A, Sagie A, Basst HB, Yahana MD, Weiss ID, Pal B, Wald O, Ad-El D, Fujii N, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Jung S, Galun E, Gur E, Peled A (2006) Involvement of the CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway in the recovery of skin following burns. J Investig Dermatol 126(2):468–476
Blanpain C, Lowry WE, Geoghegan A, Polak L, Fuchs E (2004) Self-renewal, multipotency, and the existence of two cell populations within an epithelial stem cell niche. Cell 118(5):635–648
Brem H, Tomic-Canic M (2007) Cellular and molecular basis of wound healing in diabetes. J Clin Invest 117(5):1219–1222
Butler JM, Guthrie SM, Koc M, Afzal A, Caballero S, Brooks HL, Mames RN, Segal MS, Grant MB, Scott EW (2005) SDF-1 is both necessary and sufficient to promote proliferative retinopathy. J Clin Invest 115(1):86–93
Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME, Capla JM, Galiano RD, Levine JP, Gurtner GC (2004) Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med 10(8):858–864
Falanga V (2005) Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet 366(9498):1736–1743
Fu X, Li H (2009) Mesenchymal stem cells and skin wound repair and regeneration: possibilities and questions. Cell Tissue Res 335(2):317–321
Fu X, Sun X, Li X, Sheng Z (2001) Dedifferentiation of epidermal cells to stem cells in vivo. Lancet 358(9287):1067–1068
Galiano RD, Tepper OM, Pelo CR, Bhatt KA, Callaghan M, Bastidas N, Bunting S, Steinmetz HG, Gurtner GC (2004) Topical vascular endothelial growth factor accelerates diabetic wound healing through increased angiogenesis and by mobilizing and recruiting bone marrow-derived cells. Am J Pathol 164(6):1935–1947
Gallagher KA, Liu ZJ, Xiao M, Chen H, Goldstein LJ, Buerk DG, Nedeau A, Thom SR, Velazquez OC (2007) Diabetic impairments in NO-mediated endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and homing are reversed by hyperoxia and SDF-1 alpha. J Clin Invest 117(5):1249–1259
Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, Longaker MT (2008) Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 453(7193):314–321
Inokuma D, Abe R, Fujita Y, Sasaki M, Shibaki A, Nakamura H, McMillan JR, Shimizu T, Shimizu H (2006) CTACK/CCL27 accelerates skin regeneration via accumulation of bone marrow-derived keratinocytes. Stem Cells 24(12):2810–2816
Kollet O, Shivtiel S, Chen YQ, Suriawinata J, Thung SN, Dabeva MD, Kahn J, Spiegel A, Dar A, Samira S, Goichberg P, Kalinkovich A, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Nagler A, Hardan I, Revel M, Shafritz DA, Lapidot T (2003) HGF, SDF-1, and MMP-9 are involved in stress-induced human CD34+ stem cell recruitment to the liver. J Clin Invest 112(2):160–169
Lavker RM, Sun TT (1982) Heterogeneity in epidermal basal keratinocytes: morphological and functional correlations. Science 215(4537):1239–1241
Lavker RM, Sun TT (2000) Epidermal stem cells: properties, markers, and location. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(25):13473–13475
Levy V, Lindon C, Zheng Y, Harfe BD, Morgan BA (2007) Epidermal stem cells arise from the hair follicle after wounding. FASEB J 21(7):1358–1366
Liu ZJ, Velazquez OC (2008) Hyperoxia, endothelial progenitor cell mobilization, and diabetic wound healing. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(11):1869–1882
Ma Q, Jones D, Borghesani PR, Segal RA, Nagasawa T, Kishimoto T, Bronson RT, Springer TA (1998) Impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, and derailed cerebellar neuron migration in CXCR4- and SDF-1-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(16):9448–9453
McGrath KE, Koniski AD, Maltby KM, McGann JK, Palis J (1999) Embryonic expression and function of the chemokine SDF-1 and its receptor, CXCR4. Dev Biol 213(2):442–456
Nagasawa T, Hirota S, Tachibana K, Takakura N, Nishikawa S, Kitamura Y, Yoshida N, Kikutani H, Kishimoto T (1996) Defects of B-cell lymphopoiesis and bone-marrow myelopoiesis in mice lacking the CXC chemokine PBSF/SDF-1. Nature 382(6592):635–638
Pablos JL, Amara A, Bouloc A, Santiago B, Caruz A, Galindo M, Delaunay T, Virelizier JL, Arenzana-Seisdedos F (1999) Stromal-cell derived factor is expressed by dendritic cells and endothelium in human skin. Am J Pathol 155(5):1577–1586
Ponomaryov T, Peled A, Petit I, Taichman RS, Habler L, Sandbank J, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Magerus A, Caruz A, Fujii N, Nagler A, Lahav M, Szyper-Kravitz M, Zipori D, Lapidot T (2000) Induction of the chemokine stromal-derived factor-1 following DNA damage improves human stem cell function. J Clin Invest 106(11):1331–1339
Ratajczak MZ, Zuba-Surma E, Kucia M, Reca R, Wojakowski W, Ratajczak J (2006) The pleiotropic effects of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis in organogenesis, regeneration and tumorigenesis. Leukemia 20(11):1915–1924
Tiede S, Kloepper JE, Bodo E, Tiwari S, Kruse C, Paus R (2007) Hair follicle stem cells: walking the maze. Eur J Cell Biol 86(7):355–376
Toksoy A, Muller V, Gillitzer R, Goebeler M (2007) Biphasic expression of stromal cell-derived factor-1 during human wound healing. Br J Dermatol 157(6):1148–1154
Zou YR, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, Taniuchi I, Littman DR (1998) Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 393(6685):595–599
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81272121) for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Editor: T. Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, R., Chai, L., Chen, L. et al. Stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) accelerated skin wound healing by promoting the migration and proliferation of epidermal stem cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 51, 578–585 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-014-9862-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-014-9862-y