Abstract
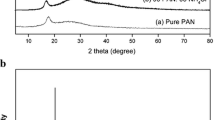
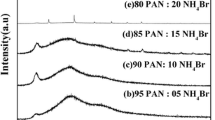
Solid polymer electrolytes based on polyacrylonitrile (PAN) doped with ammonium thiocyanate (NH4SCN) in different molar ratios of polymer and salt have been prepared by solution-casting method using DMF as solvent. The increase in amorphous nature of the polymer electrolytes has been confirmed by XRD analysis. A shift in glass transition temperature (T g) of the PAN : NH4SCN electrolytes has been observed from the DSC thermograms which indicates the interaction between the polymer and the salt. From the AC impedance spectroscopic analysis, the ionic conductivity has been found to increase with increasing salt concentration up to 30 mol% of NH4SCN beyond which the conductivity decreases and the highest ambient temperature conductivity has been found to be 5.79 × 10−3 S cm−1. The temperature-dependent conductivity of the polymer electrolyte follows an Arrhenius relationship which shows hopping of ions in the polymer matrix. The dielectric loss curves for the sample 70 mol% PAN : 30 mol% NH4SCN reveal the low-frequency β-relaxation peak pronounced at high temperature, and it may be caused by side group dipoles. The ionic transference number of polymer electrolyte has been estimated by Wagner’s polarization method, and the results reveal that the conductivity species are predominantly ions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Bhuvaneswari MS (2004) J Power Sources 134:235–240
Avellaneda CO, Vieira DF, Al-kahlout A, Leite ER, Pawlicka A, Aegerter MA (2007) Electrochem Acta 53:1648–1654
Anantha RS, Hariharan K (2005) Solid State Ionics 176:155–162
Abrahan KM, Alangir M (1990) J Electrochem Soc 137:1657–1658
Abrahan KM, Alangir M (1993) J Electrochem Soc 140:L96–L97
Panero S, Scrosati B (2000) J Power Sources 90:13–19
Herington TM, Staveley LAK (1964) J Phys Chem Solids 25:921
Hodge RM, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Polymer 37:1371–1376
Gowariker VR, Viswanathan NV, Sreedhar J (2000) Polymer science. New Age International (P), New Delhi
Jacob MME, Arof AK (2000) Electrochem. Acta 45:1701
Hema M, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Sakunthala A, Nithya H (2009) J Phys Chem Solids 70:1098–1103
Boukamp BA (1986) Solid State Ionics 20:301
Boukamp BA (1986) Solid State Ionics 18:136
Zhu W, Wang X, Yang B, Tang X (2001) Polym Sci B Polym Phys 39:1246
Takakazu Yamamoto, Minoru Inami, Takaki Kanabara, (1994) Chem. Mater 44
Takshashi Y (1973) J Polym Sci 11:213
Funke K (1998) Solid State Ionics 28:100
Nithya H, Selvasekarapandian S, Christopher Selvin P, Arun kumar D, Kawamura J (2012) Electrochim Acta 66:110–120
Ramya CS, Selvasekarapandian S, Savitha T, Hirankumar G (2007) Physica B 11:393
Dutta P, Biswas S (2002) Mater Res Bull 37:193–200
Pillai PKC, Khurana P, Tripattan A (1986) J Mater Sci 5:629–632
Vijayalakshmi Rao R, Sridhar MH (2002) Mater Lett 55:34–40
Dutta P, Biswas S, Subodhkumar D (2002) Mater Res Bull 37:193–200
Moon GH, Seung SI (2001) J Appl Poly Sci 83:2760–2769
Karabanova LV, Boiteux G, Gain O, Seytre G, Bondaranko PA (2003) J Appl Poly Sci 90:1191–1201
Armstrong RD, Dickinson T, Wills PM (1974) J Electronal chem 3:53
Armstrong RD, Race WP (1976) J Electronal Chem 74:125
Singh KP, Gupta PN (1998) Eur Polym J 34(7):1023
Wagner JB, Wagner C (1957) J Chem Phys 26:1597
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nithya, S., Selvasekarapandian, S., Karthikeyan, S. et al. AC impedance studies on proton-conducting PAN : NH4SCN polymer electrolytes. Ionics 20, 1391–1398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1091-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1091-6