Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate safety and clinical efficacy of percutaneous transcatheter embolization (PTE) in the treatment of spontaneous bleedings (SBs) in patients submitted to chronic anticoagulation therapy.
Materials and methods
From January 2007 to December 2012, 20 patients (mean age 75.8 years, range 68–91 years) with 23 SBs were retrospectively evaluated. Active bleeding was documented by contrast enhanced-multidetector row computed tomography (CE-MDCT). PTE was performed using different embolic agents. Technical success (TS), clinical success (CS), late success (LS) and mortality rate (M) related to the angiographic procedure and complications were evaluated.
Results
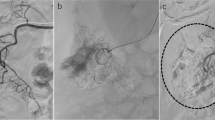
CE-MDCT and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) identified active bleeding sites in 18 cases (18/20). In two cases (2/20) DSA did not confirm the arterial bleeding diagnosed on CE-MDCT. Twenty-three sessions of PTE were performed. TS, CS, LS and M were, respectively, 100, 85, 15 and 0 %. No major complications were observed.
Conclusions
PTE could be considered a safe and effective “first line” approach to treat SB associated with anticoagulation therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida Gde Q, Noblat Lde A, Passos LC, do Nascimento HF (2011) Quality of life analysis of patients in chronic use of oral anticoagulant: an observational study. Health Qual Life Outcomes 25(9):91
Katznelson R, Djaiani GN, Karski J (2009) Guideline on antiplatelet and anticoagulation management in cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 35(3):555; author reply 555. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.11.023
Berkovits A, Aizman A, Zúñiga P, Pereira J, Mezzano D (2011) New oral anticoagulant drugs. Rev Med Chile 139(10):1347–1355
Palareti G, Leali N, Coccheri S, Poggi M, Manotti C, D’Angelo A et al (1996) Bleeding complications of oral anticoagulant treatment: an inception-cohort, prospective collaborative study (ISCOAT). Italian Study on Complications of Oral Anticoagulant Therapy. Lancet 348(9025):423–428
Van der Meer FJ, Rosendaal FR, Vandenbroucke JP, Briët E (1993) Bleeding complications in oral anticoagulant therapy. An analysis of risk factors. Arch Intern Med 153(13):1557–1562
Angle JF, Siddiqi NH, Wallace MJ, Kundu S, Stokes L, Wojak JC et al (2010) Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transcatheter embolization: Society of Interventional Radiology Standards of Practice Committee. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21(10):1479–1486
Sá SP, Rodrigues RP, Santos-Antunes J, Rocha Gonçalves F, Nunes JP (2011) Antithrombotic therapy in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: a narrative review. Rev Port Cardiol 30(12):905–924
Fitzmaurice DA, Kesteven P, Gee KM, Murray ET, McManus R (2003) A systematic review of outcome measures reported for the therapeutic effectiveness of oral anticoagulation. J Clin Pathol 56(1):48–51
Isokangas JM, Perälä JM (2004) Endovascular embolization of spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhage secondary to anticoagulant treatment. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 27(6):607–611
Pathi R, Voyvodic F, Thompson WR (2004) Spontaneous extraperitoneal haemorrhage: computed tomography diagnosis and treatment by selective arterial embolization. Australas Radiol 48(2):123–128
Won DY, Kim SD, Park SC, Moon IS, Kim JI (2011) Abdominal compartment syndrome due to spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhage in a patient undergoing anticoagulation. Yonsei Med J 52(2):358–361
Fortina M, Carta S, Del Vecchio EO, Crainz E, Urgelli S, Ferrata P (2007) Retroperitoneal hematoma due to spontaneous lumbar artery rupture during fondaparinux treatment. Case report and review of the literature. Acta Biomed 78(1):46–50
Torres GM, Cernigliaro JG, Abbitt PL, Mergo PJ, Hellein VF, Fernandez S et al (1995) Iliopsoas compartment: normal anatomy and pathologic process. Radiographics 15:1285–1297
Machuca Santa Cruz J, Julve Villalta E, Galacho Bech A, Pérez Rodríguez D, Quiñonero Díaz A, Alonso Dorrego JM et al (1999) Spontaneous retroperitoneal hematoma: our experience. Actas Urol Esp 23(1):43–50
Dabney A, Bastani B (2001) Enoxaparin-associated severe retroperitoneal bleeding and abdominal compartment syndrome: a report of two cases. Intensive Care Med 27(12):1954–1957
Vaya’ A, Mira Y, Aznar J, Todolì J, Arguedas J, Sola’ E (2003) Enoxaparin-related fatal spontaneous retroperitoneal haematoma in the elderly. Thromb Res 110:69–71
Halak M, Klingman M, Loberman Z, Eyal E, Karmeli R (2001) Spontaneous ruptured artery in a chronic renal failure patient. Eur J Endovasc Surg 21:569–571
Kalinwski EA, Trerotola SO (1998) Postcatheterization retroperitoneal haematoma due to spontaneous lumbar arterial hemorrage. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 21(4):337–339
Shuster F, Stosslein F, Steinbach F (2003) Spontaneous rupture of a lumbar artery. A rare etiology of retroperitoneal haematoma. Urologe A 42(6):840–844
Park SH, Lee SW, Jeon U, Jeon MH, Lee SJ, Shin WY et al (2011) Transcatheter arterial embolization as treatment for a life-threatening retroperitoneal hemorrage complicating heparin therapy. Korean J Intern Med 26(3):352–355
Sessa B, Trinci M, Ianniello S, Menichini C, Galluzzo M, Miele V (2014) Blunt abdominal trauma: role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the detection and staging of abdominal traumatic lesions compared to US and CE-MDCT. Radiol Med. doi:10.1007/s11547-014-0425-9
Pinto F, Valentino M, Romanini L, Basilico R, Miele R (2014) The role of CEUS in the assessment of haemodynamically stable patients with blunt abdominal trauma. Radiol Med. doi:10.1007/s11547-014-0455-3
Fitzgerald JE, Fitzgerald LA, Anderson FE, Acheson AG (2009) The changing nature of rectus sheath haematoma: case series and literature review. Int J Surg 7(2):150–154
Sharafuddin MJ, Andresen KJ, Sun S, Lang E, Stecker MS, Wibbenmeyer LA (2001) Spontaneous extraperitoneal hemorrhage with hemodynamic collapse in patients undergoing anticoagulation: management with selective arterial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12(10):1231–1234
Romano S, Scaglione M, Tortora G, Martino A, Di Pietto F, Romano L et al (2006) MDCT in blunt intestinal trauma. Eur J Radiol 59(3):359–366
Scaglione M, Pinto F, Lassandro F, Romano L, Pinto A, Grassi R (2002) Value of contrast-enhanced CT for managing mesenteric injuries after blunt trauma: review of five-year experience. Emerg Radiol 9(1):26–31
Zissin R, Gayer G, Kots E, Ellis M, Bartal G, Griton I (2007) Transcatheter arterial embolisation in anticoagulant-related haematoma—a current therapeutic option: a report of four patients and review of the literature. Int J Clin Pract 61(8):1321–1327
Guzzardi G, Fossaceca R, Cerini P, De Bonis M, Malatesta E, Divenuto I et al (2014) Endovascular treatment of spontaneous extraperitoneal haemorrhage: immediate and long-term clinical efficiency. Radiol Med 119(2):121–127
Furlan A, Fakhran S, Federle MP (2009) Spontaneous abdominal Hemorrhage: causes, CT findings and clinical implication. AJR 193:1077–1087
Zissin R, Ellis M, Gayer C (2006) The CT findings of abdominal anticoagulant-related hematomas. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI 27:117–125
Lu C, Min P, Wu B (2012) CT evaluation of spontaneously ruptured renal angiomyolipomas with massive hemorrhage spreading into multi-retroperitoneal fascia and fascial spaces. Acta Radiol Short Rep 1:18
Farrelly C, Fidelman N, Durack JC, Hagiwara E, Kerlan RK Jr (2011) Transcatheter arterial embolization of spontaneous life-threatening extraperitoneal hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22(10):1396–1402
Xiao L, Shen J, Tong J-J (2013) Emergency stent-graft implantation for iatrogenic peripheral arterial rupture. Radiol Med 118:152–157
Laganà D, Carrafiello G, Lumia D et al (2013) Removable vena cava filter: single-centre experience with a single device. Radiol Med 118:816–825
Ierardi AM, Floridi C, Fontana F et al (2014) Transcatheter embolisation of iatrogenic renal vascular injuries. Radiol Med 119:261–268
Niola R, Cavaliere C, Lorenza M et al (2014) Role of interventional radiology in treating obstetric haemorrhages. Radiol Med 119:607–615
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ierardi, A.M., Floridi, C., Pellegrino, C. et al. Role of percutaneous transcatheter embolization (PTE) in the treatment of spontaneous bleeding associated with anticoagulant therapy. Radiol med 120, 149–157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0470-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0470-4