Abstract
Purpose
The aim of our study was to review our experience and long-term follow-up in the treatment of iatrogenic renal vascular injuries using transcatheter embolisation.
Materials and methods
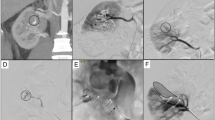
Our retrospective analysis of cases collected in two interventional centres consists of a total of 21 patients who underwent renal arterial embolisation (RAE) for iatrogenic arterial kidney bleeding. Biopsy (n = 4), percutaneous nephrolithotomy (n = 4), nephron-sparing surgery (n = 4), guidewire-induced arterial perforation during coronary angiography or renal stenting (n = 3), percutaneous nephrostomy (n = 3), renal endopyelotomy/pyeloplasty (n = 2) and surgical nephrectomy were the iatrogenic causes. Seven patients presented with haemodynamic instability requiring blood transfusion (33.3 %), the remaining were haemodynamically stable (66.7 %). Diagnostic renal angiography revealed 9 actively bleeding vessels, 6 pseudoaneurysms, 4 arteriovenous fistulas and 1 arterio-calyceal fistula. In one patient selective renal arteriography was negative probably because the bleeding observed at CT angiography was self-limited. Twenty-one embolisation procedures were performed in 20 patients; one patient required a second embolisation 3 h after the first one. Embolisation was performed with microcoils, polyvinyl alcohol particles, embospheres, spongostan emulsion and vascular plug.
Results
The technical success rate was 100 %. The overall clinical success rate was 95 %. Apart from a patient who died due to disseminated intravascular coagulation, no major complications requiring intensive care treatment were encountered during or after the procedures. No patient required emergency surgery or subsequent surgical treatment. No statistically significant differences in eGFR or renal function stage appeared after RAE.
Conclusions
Percutaneous treatment can be proposed as a first-line treatment in iatrogenic renal arterial injuries, resulting in a safe and effective procedure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Somani BK, Nabi G, Thorpe P, McClinton S (2006) Endovascular control of haemorrhagic urological emergencies: an observational study. BMC Urol 6:27
Morris CS, Bonnevie GJ, Najarian KE (2001) Nonsurgical treatment of acute iatrogenic renal artery injuries occurring after renal artery angioplasty and stenting. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:1353–1357
Cohenpour M, Strauss S, Gottlieb P et al (2007) Pseudoaneurysm of the renal artery following partial nephrectomy: imaging findings and coil embolization. Clin Radiol 62:1104–1109
Poulakis V, Ferakis N, Betch E et al (2006) Treatment of renal vascular injury by transcatheter embolization: immediate and longterm effects on renal function. J Endourol 20:405–409
Mavili E, Do¨nmez H, Özcan N et al (2009) Transarterial embolization for renal arterial bleeding. Diagn Interv Radiol 15:143–147
Cantasdemir M, Adaletli I, Cebi D et al (2003) Emergency endovascular embolization of traumatic intrarenal arterial pseudoaneurysms with N-butyl cyanoacrylate. Clin Radiol 58:560–565
Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E et al (2003) National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. National Kidney Foundation. Ann Intern Med 139:137–147
Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF et al (2003) Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14(suppl):S199–S202
Permpongkosol S, Link RE, Su LM et al (2007) Complications of 2775 urological laparoscopic procedures: 1993 to 2005. J Urol 177:580e5
Heye S, Maleux G, Van Poppel H et al (2005) Hemorrhagic complications after nephron-sparing surgery: angiographic diagnosis and management by transcatheter embolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:1661e4
Huppert PE, Duda SH, Erley CM et al (1993) Embolization of renal vascular lesions: clinical experience with microcoils and tracker catheters. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 16:361–367
Golzarian J, Sapoval MR, Kundu S et al (2010) Guidelines for peripheral and visceral vascular embolization training: joint writing groups of the Standards of Practice Committees for the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR), Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE), and Canadian Interventional Radiology Association (CIRA). J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:436–441
Cimsit NC, Baltacioglu F, Cengic I et al (2008) Transarterial glue embolization in iatrogenic renovascular injuries. Int Urol Nephrol 40:875–879
Sam K, Gahide G, Soulez G et al (2011) Percutaneous embolization of iatrogenic arterial kidney injuries: safety, efficacy, and impact on blood pressure and renal function. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22:1563–1568
Morris CS, Bonnevie GJ, Najarian KE (2001) Nonsurgical treatment of acute iatrogenic renal artery injuries occurring after renal artery angioplasty and stenting. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:1353–1357
Mavili E, Dönmez H, Ozcan N et al (2009) Transarterial embolization for renal arterial bleeding. Diagn Interv Radiol 15:143–147
Maleux G, Messiaen T, Stockx L et al (2003) Transcatheter embolization of biopsy-related vascular injuries in renal allografts long-term technical, clinical and biochemical results. Acta Radiol 44:13–17
Singh D, Gill IS (2005) Renal artery pseudoaneurysm following laparoscopic partial Negoro. J Urol 174:2256e9
Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Tanaka N et al (2000) Transcatheter arterial embolization of ruptured pseudoaneurysms with coils and nbutyl cyanoacrylate. J Vasc Interv Radiol 11:66–72
Parildar M, Oran I, Memis A (2003) Embolization of visceral pseudoaneurysms with platinum coils and N-butyl cyanoacrylate. Abdom Imaging 28:36–40
Sofocleous CT, Hinrichs C, Hubbi B et al (2005) Angiographic findings and embolotherapy in renal arterial trauma. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 28:39–47
El-Nahas A, Shokeir A, Mohsen T et al (2008) Functional and morphological effects of postpercutaneous nephrolithotomy superselective renal angiographic embolization. Urology 71:408–412
Loffroy R, Guiu B, Lambert A et al (2008) Management of post-biopsy renal allograft arteriovenous fistulas with selective arterial embolization: immediate and long-term outcomes. Clin Radiol 63:657–665
Baldieri A, Antonietti A, Ferro L et al (2012) Endovascular treatment of visceral artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms: our experience. Radiol Med 117:815–830
Pozzi-Mucelli F, Medeot A, Cernic S et al (2011) Multimodal approach to the endovascular treatment of embolisation or exclusion of the renal arteries and their distal and/or polar branches: personal experience. Radiol Med 116:945–959
Conflict of interest
Gianpaolo Carrafiello, Anna Maria Ierardi, Monica Mangini, Federico Fontana, Chiara Floridi, Jessica Lanza, Antonio Pinto, Elias Kehagias, Dimitrios Tsetis declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ierardi, A.M., Floridi, C., Fontana, F. et al. Transcatheter embolisation of iatrogenic renal vascular injuries. Radiol med 119, 261–268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0343-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0343-2