Abstract
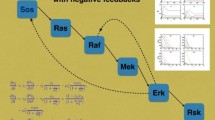
We consider a kinetic law of mass action model for Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) signaling, focusing on the induction of the RAS-MAP kinase pathway via GRB2 binding. Our biologically simple model suffers a combinatorial explosion in the number of differential equations required to simulate the system. In addition to numerically solving the full model, we show that it can be accurately simplified. This requires combining matched asymptotics, the quasi-steady state hypothesis, and the fact subsets of the equations decouple asymptotically. Both the full and simplified models reproduce the qualitative dynamics observed experimentally and in previous stochastic models. The simplified model also elucidates both the qualitative features of GRB2 binding and the complex relationship between SHP2 levels, the rate SHP2 induces dephosphorylation and levels of bound GRB2. In addition to providing insight into the important and redundant features of FGF signaling, such work further highlights the usefulness of numerous simplification techniques in the study of mass action models of signal transduction, as also illustrated recently by Borisov and co-workers (Borisov et al. in Biophys. J. 89, 951–66, 2005, Biosystems 83, 152–66, 2006; Kiyatkin et al. in J. Biol. Chem. 281, 19925–9938, 2006). These developments will facilitate the construction of tractable models of FGF signaling, incorporating further biological realism, such as spatial effects or realistic binding stoichiometries, despite a more severe combinatorial explosion associated with the latter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, T., Cui, C., Kanda, A., Kayaba, H., Ohta, K., Chihara, J., 2004. Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor via CCR3 in bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 320, 292–96.
Agazie, Y.M., Hayman, M.J., 2003. Molecular mechanism for a role of SHP2 in epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 7875–886.
Aldridge, B.B., Burke, J.M., Lauffenburger, D.A., Sorger, P.K., 2006. Physicochemical modelling of cell signalling pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1195–203.
Augoff, K., Tabola, R., Kula, J., Gosk, J., Rutowski, R., 2005. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) in dupuytren’s disease. J. Hand Surg.: J. Br. Soc. Surg. Hand 30, 570–73.
Basilico, C., 2005. Editorial: Introduction to the special FGF issue. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 105–06.
Bender, C.M., Orszag, S.A., 1991. Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers: Asymptotic Methods and Perturbation Theory. Springer, New York.
Billingham, J., King, A.C., 2000. Wave Motion. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Borisov, N.M., Markevich, N.I., Hoek, J.B., Kholodenko, B.N., 2005. Signaling through receptors and scaffolds: Independent interactions reduce combinatorial complexity. Biophys. J. 89, 951–66.
Borisov, N.M., Markevich, N.I., Hoek, J.B., Kholodenko, B.N., 2006. Trading the micro-world of combinatorial complexity for the macro-world of protein interaction domains. Biosystems 83, 152–66.
Bublil, E.M., Yarden, Y., 2007. The EGF receptor family: Spearheading a merger of signalling and therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19, 124–34.
Chen, P., Xie, H., Wells, A., 1996. Mitogenic signaling from the EGF receptor is attenuated by a phospholipase C-gamma/protein kinase C feedback mechanism. Mol. Biol. Cell 7, 871–81.
Citri, A., Yarden, Y., 2006. EGF-ErbB signalling: Towards the systems level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 505–16.
Crampin, E.J., Schnell, S., McSharry, P.E., 2004. Mathematical and computational techniques to reduce complex biochemical reaction mechanisms. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 86, 77–12.
Dailey, L., Ambrosetti, D., Mansukhani, A., Basilico, C., 2005. Mechanisms underlying differential responses to FGF signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 233–47.
Eswarakumar, V.P., Lax, I., Schlessinger, J. 2005. Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 139–49.
Gavutis, M., Jaks, E., Lamken, P., Piehler, J., 2006. Determination of the two-dimensional interaction rate constants of a cytokine receptor complex. Biophys. J. 90, 3345–355.
Greenman, C., Stephens, P., Smith, R., Dalgliesh, G.L., Hunter, C., Bignell, G., Davies, H., Teague, J., Butler, A., Stevens, C., et al., 2007. Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer genomes. Nature 446, 153–58.
Grose, R., Dickson, C., 2005. Fibroblast growth factor signaling in tumorigenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 179–86.
Hanafusa, H., Torii, S., Yasunaga, T., Matsumoto, K., Nishida, E., 2004. Shp2, an SH2-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase, positively regulates receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by dephosphorylating and inactivating the inhibitor sprouty. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 22992–2995.
Heath, J.K., Kwiatkowska, M.Z., Norman, G., Parker, D., Tymchyshyn, O., 2006. Probabilistic model checking of complex biological pathways. In: Proc. Computational Methods in Systems Biology CMSB–6.
Heath, J., Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., Parker, D., Tymchyshyn, O., 2007. Probabilistic model checking of complex biological pathways. Theor. Comput. Sci. (Special Issue on Converging Sciences: Informatics and Biology).
Hucka, M., Finney, A., Sauro, H.M., Bolouri, H., Doyle, J.C., Kitano, H., Arkin, A.P., Bornstein, B.J., Bray, D., et al., 2003. (SBML Forum). The systems biology markup language (SBML): a medium for representation and exchange of biochemical network models. Bioinformatics 19, 524–31.
Jarvis, L.A., Toering, S.J., Simon, M.A., Krasnow, M.A., Smith-Bolton, R.K., 2006. Sprouty proteins are in vivo targets of Corkscrew/SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatases. Development 133, 1133–142.
Julien, S.G., Dube, N., Read, M., Penney, J., Paquet, M., Han, Y., Kennedy, B.P., Muller, W.J., Tremblay, M.L., 2007. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis. Nat. Genet. 39, 338–46.
Kiyatkin, A., Aksamitiene, E., Markevich, N.I., Borisov, N.M., Hoek, J.B., Kholodenko, B.N., 2006. Scaffolding protein Grb2-associated binder 1 sustains epidermal growth factor-induced mitogenic and survival signaling by multiple positive feedback loops. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 19925–9938.
Kramer, S., Okabe, M., Hacohen, N., Krasnow, M.A., Hiromi, Y., 1999. Sprouty: A common antagonist of FGF and EGF signaling pathways in Drosophila. Development 126, 2515–525.
Krueger, G., Ellis, C.N., 2005. Psoriasis-recent advances in understanding its pathogenesis and treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 53(Supplement 1), S94–S100.
Kudryavtsev, A.B., Jameson, R.F., Linert, W., 2001. The Law of Mass Action, Springer Statistical Thermodynamics. Springer, New York.
Kwiatkowska, M.Z., Norman, G., Parker, D., Tymchyshyn, O., Heath, J.K., Gaffney, E., 2006. Simulation and verification for computational modelling of signalling pathways. In: Perrone, L.F., Wieland, F.P., Liu, J., Lawson, B.G., Nicol, D.M., Fujimoto, R.M. (Eds.), Proc. Winter Simulation Conference 2006 (WSC–6), ISBN: 1-4244-0501-7.
Li, X., Brunton, V.G., Burgar, H.R., Wheldon, L.M., Heath, J.K., 2004. FRS2-dependent SRC activation is required for fibroblast growth factor receptor-induced phosphorylation of Sprouty and suppression of ERK activity. J. Cell Sci. 117, 6007–017.
Millat, T., Bullinger, E., Rohwer, J., Wolkenhauer, O., 2007. Approximations and their consequences for dynamic modelling of signal transduction pathways. Math. Biosci. 207, 4057.
Mohammadi, M., Olsen, S.K., Ibrahimi, O.A., 2005. Structural basis for fibroblast growth factor receptor activation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 107–37.
Murray, J.D., 1989. Mathematical Biology. Springer, New York.
Schlessinger, J., 2000. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103, 211–25.
Schoeberl, B., Eichler-Jonsson, C., Gilles, E.D., Muller, G., 2002. Computational modeling of the dynamics of the MAP kinase casca de activated by surface and internalized EGF receptors. Nat. Biotechnol. 20, 370–75.
Sevecka, M., MacBeath, G., 2006. State-based discovery: A multidimensional screen for small-molecule modulators of EGF signalling. Nat. Methods 3, 825–31.
Suckley, R., Biktashev, V.N., 2003. Comparison of asymptotics of heart and nerve excitability. Phys. Rev. E 68, 011902.
Thisse, B., Thisse, C., 2005. Functions and regulations of fibroblast growth factor signaling during embryonic development. Dev. Biol. 287, 390–02.
Tikhonov, A.N., 1952. Systems of differential equations containing a small parameter in the derivatives. Mat. Sb. 31, 575–86.
Tyson, J.J., Chen, K., Novak, B., 2001. Network dynamics and cell physiology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 908–16.
Vallabhajosyula, R.R., Sauro, H.M., 2006. Complexity reduction of biochemical networks. In: Perrone, L.F., Wieland, F.P., Liu, J., Lawson, B.G., Nicol, D.M., Fujimoto, R.M. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2006 Winter Simulation Conference, ISBN: 1-4244-0501-7.
Wilkie, A.O.M., 2005. Bad bones, absent smell, selfish testes: The pleiotropic consequences of human FGF receptor mutations. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 187–03.
Wolkenhauer, O., Ullah, M., Kolch, W., Cho, K., 2004. Modelling and simulation of IntraCellular dynamics: Choosing an appropriate framework. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 3, 200–07.
Wong, E.S., Lim, J., Low, B.C., Chen, Q., Guy, G.R., 2001. Evidence for direct interaction between sprouty and Cbl. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 5866–875.
Yamada, S., Taketomi, T., Yoshimura, A., 2004. Model analysis of difference between EGF pathway and FGF pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 314, 1113–120.
Yarden, Y., Sliwkowski, M.X., 2001. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 127–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaffney, E.A., Heath, J.K. & Kwiatkowska, M.Z. A Mass Action Model of a Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling Pathway and Its Simplification. Bull. Math. Biol. 70, 2229–2263 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-008-9342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-008-9342-1