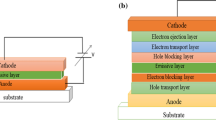
Abstract
Plasmonic metal nanostructures have recently attracted extensive research and developed into a promise approach for enhancing the performance of various optoelectronic devices. This brief article reviews recent research advances on the plasmonic enhanced optoelectronic devices and highlights a variety of strategies of incorporating plasmonic nanostructures into different optoelectronics such as solar cells, light-emitting diode, and multicolor photodetector, etc. In addition, the benefits of using various plasmonic metal nanostructures are discussed and the resulting enhancement mechanisms are displayed and summarized.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozbay E (2006) Plasmonics: merging photonics and electronics at nanoscale dimensions. Science 311:189–193
Halas NJ (2010) Plasmonics: an emerging field fostered by nano letters. Nano Lett 10:3816–3822
Jiang L, Guan J, Zhao LL et al (2009) pH-dependent aggregation of citrate-capped Au nanoparticles induced by Cu2+ ions: the competition effect of hydroxyl groups with the carboxyl groups. Colloids Surf A 346:216–220
Jiang L, Sun YH, Huo FW et al (2012) Free-standing one-dimensional plasmonic nanostructures. Nanoscale 4:66–75
Weibel DB, DiLuzio WR, Whitesides GM (2007) Microfabrication meets microbiology. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:209–218
Brongersma ML, Shalaev VM (2010) The case for plasmonics. Science 328:440–441
Jiang L, Sun YH, Nowak C et al (2011) Patterning of plasmonic nanoparticles into multiplexed one-dimensional arrays based on spatially modulated electrostatic potential. ACS Nano 5:8288–8294
Jiang L, Tang YX, Liow CH et al (2013) Synthesis of fivefold stellate polyhedral gold nanoparticles with {110}-facets via a seed-mediated growth method. Small 9:705–710
Jiang L, Wang WC, Fuchs H et al (2009) One-dimensional arrangement of gold nanoparticles with tunable interparticle distance. Small 5:2819–2822
Hu M, Chen JY, Li ZY et al (2006) Gold nanostructures: engineering their plasmonic properties for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 35:1084–1094
Lee J-S, Han MS, Mirkin CA (2007) Colorimetric detection of mercuric Ion (Hg2+) in aqueous media using DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:4093–4096
Haes AJ, Chang L, Klein WL et al (2005) Detection of a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease from synthetic and clinical samples using a nanoscale optical biosensor. J Am Chem Soc 127:2264–2271
Jin YD (2012) Engineering plasmonic gold nanostructures and metamaterials for biosensing and nanomedicine. Adv Mater 24:5153–5165
Du JJ, Jiang L, Shao Q et al (2013) Colorimetric detection of mercury ions based on plasmonic nanoparticles. Small 9:1467–1481
Du JJ, Sun YH, Jiang L et al (2011) Flexible colorimetric detection of mercuric Ion by simply mixing nanoparticles and oligopeptides. Small 7:1407–1411
Du JJ, Yin SY, Jiang L et al (2013) A colorimetric logic gate based on free gold nanoparticles and the coordination strategy between melamine and mercury ions. Chem Commun 49:4196–4198
Paul A, Solis D, Bao K et al (2012) Identification of higher order long-propagation-length surface plasmon polariton modes in chemically prepared gold nanowires. ACS Nano 6:8105–8113
Zhang SP, Xu HX (2012) Optimizing substrate-mediated plasmon coupling toward high-performance plasmonic nanowire waveguides. ACS Nano 6:8128–8135
Chen K, Adato R, Altug H (2012) Dual-band perfect absorber for multispectral plasmon-enhanced infrared spectroscopy. ACS Nano 6:7998–8006
Fu YQ, Zhou XL (2010) Plasmonic lenses: a review. Plasmonics 5:287–310
Dionne JA, Lezec HJ, Atwater HA (2006) Highly confined photon transport in subwavelength metallic slot waveguides. Nano Lett 6:1928–1932
Kern J, Großmann S, Tarakina NV et al (2012) Atomic-scale confinement of resonant optical fields. Nano Lett 12:5504–5509
Yoon I, Kim K, Baker SE et al (2012) Stimulus-responsive light coupling and modulation with nanofiber waveguide junctions. Nano Lett 12:1905–1911
Stewart ME, Anderton CR, Thompson LB et al (2008) Nanostructured plasmonic sensors. Chem Rev 108:494–521
Ren MX, Plum E, Xu JJ et al (2012) Giant nonlinear optical activity in a plasmonic metamaterial. Nat Commun 3:833
Hess O, Pendry JB, Maier SA et al (2012) Active nanoplasmonic metamaterials. Nat Mater 11:573–584
Tsung CK, Kuhn JN, Huang WY et al (2009) Sub-10 nm platinum nanocrystals with size and shape control: catalytic study for ethylene and pyrrole hydrogenation. J Am Chem Soc 131:5816–5822
Nagaoka Y, Wang T, Lynch J et al (2012) Binary assembly of colloidal semiconductor nanorods with spherical metal nanoparticles. Small 8:843–846
Choi H, Lee J-P, Ko S-J et al (2013) Multipositional silica-coated silver nanoparticles for high-performance polymer solar cells. Nano Lett 13:2204–2208
Lu L, Luo Z, Xu T et al (2012) Cooperative plasmonic effect of Ag and Au nanoparticles on enhancing performance of polymer solar cells. Nano Lett 13:59–64
Gan Q, Bartoli FJ, Kafafi ZH (2012) Research highlights on organic photovoltaics and plasmonics. IEEE Photon J 4:620–624
Kwon M-K, Kim J-Y, Kim B-H et al (2008) Surface-plasmon-enhanced light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 20:1253–1257
Gan QQ, Bartoli FJ, Kafafi ZH (2013) Plasmonic-enhanced organic photovoltaics: breaking the 10% efficiency barrier. Adv Mater 25:2385–2396
Janković V, Yang Y, You J et al (2013) Active layer-incorporated, spectrally tuned Au/SiO2 core/shell nanorod-based light trapping for organic photovoltaics. ACS Nano 7:3815–3822
Banerjee P, Conklin D, Nanayakkara S et al (2010) Plasmon-induced electrical conduction in molecular devices. ACS Nano 4:1019–1025
Liu Y, Cheng R, Liao L et al (2011) Plasmon resonance enhanced multicolour photodetection by graphene. Nat Commun 2:579
Zheng YB, Yang Y-W, Jensen L et al (2009) Active molecular plasmonics: controlling plasmon resonances with molecular switches. Nano Lett 9:819–825
Mathieu LJ, Maurizio R, Romain Q (2011) Plasmon nano-optical tweezers. Nat Photonics 5:349–356
Van Duyne RP (2004) Molecular plasmonics. Science 306:985–986
Haes AJ, Haynes CL, McFarland AD et al (2005) Plasmonic materials for surface-enhanced sensing and spectroscopy. MRS Bull 30:368–375
Brockman JM, Nelson BP, Corn RM (2000) Surface plasmon resonance imaging measurements of ultrathin organic films. Annu Rev Phys Chem 51:41–63
Knoll W (1998) Interfaces and thin films as seen by bound electromagnetic waves. Annu Rev Phys Chem 49:569–638
Gu XF, Qiu T, Zhang WJ et al (2011) Light-emitting diodes enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonance. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:1–12
Jiang L, Zou CJ, Zhang DH et al (2013) Synergistic modulation of surface interaction to assemble metal nanoparticles into two-dimensional arrays with tunable plasmonic properties. Small. doi:10.1002/smll.201302126
Murray WA, Barnes WL (2007) Plasmonic materials. Adv Mater 19:3771–3782
Vigderman L, Khanal BP, Zubarev ER (2012) Functional gold nanorods: synthesis, self-assembly, and sensing applications. Adv Mater 24:4811–4841
Jiang L, Zhang HX, Zhuang JQ et al (2005) Sterically mediated two-dimensional architectures in aggregates of Au nanoparticles directed by phosphorothioate oligonucleotide-DNA. Adv Mater 17:2066–2070
Schuller JA, Barnard ES, Cai WS et al (2010) Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. Nat Mater 9:193–204
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9:205–213
Kelzenberg MD, Boettcher SW, Petykiewicz JA et al (2010) Enhanced absorption and carrier collection in Si wire arrays for photovoltaic applications. Nat Mater 9:239–244
Wang W, Wu SM, Reinhardt K et al (2010) Broadband light absorption enhancement in thin-film silicon solar cells. Nano Lett 10:2012–2018
Stuart HR, Hall DG (1998) Island size effects in nanoparticle-enhanced photodetectors. Appl Phys Lett 73:3815–3817
Heo M, Cho H, Jung JW et al (2011) High-performance organic optoelectronic devices enhanced by surface plasmon resonance. Adv Mater 23:5689–5693
Shi X, Ueno K, Takabayashi N et al (2013) Plasmon-enhanced photocurrent generation and water oxidation with a gold nanoisland-loaded titanium dioxide photoelectrode. J Phys Chem C 117:2494–2499
Conklin D, Nanayakkara S, Park TH et al (2013) Exploiting plasmon-induced hot electrons in molecular electronic devices. ACS Nano 7:4479–4486
Kao CS, Chen FC, Liao CW et al (2012) Plasmonic-enhanced performance for polymer solar cells prepared with inverted structures. Appl Phys Lett 101:193902
Chen MC, Yang YL, Chen SW et al (2013) Self-assembled monolayer immobilized gold nanoparticles for plasmonic effects in small molecule organic photovoltaic. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:511–517
Zhu JF, Xue M, Hoekstra R et al (2012) Light concentration and redistribution in polymer solar cells by plasmonic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 4:1978–1981
Knight MW, Sobhani H, Nordlander P et al (2011) Photodetection with active optical antennas. Science 332:702–704
Sundararaian SP, Grady NK, Mirin N et al (2008) Nanoparticle-induced enhancement and suppression of photocurrent in a silicon photodiode. Nano Lett 8:624–630
Hu MS, Chen HL, Shen CH et al (2006) Photosensitive gold-nanoparticle-embedded dielectric nanowires. Nat Mater 5:102–106
Hyun JK, Lauhon LJ (2011) Spatially resolved plasmonically enhanced photocurrent from Au nanoparticles on a Si nanowire. Nano Lett 11:2731–2734
Oh K, Jeon W, Lee SS (2012) One-dimensional TiO2@Ag nanoarchitectures with interface-mediated implementation of resistance-switching behavior in polymer nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:5727–5731
Xiao Y, Yang JP, Cheng PP et al (2012) Surface plasmon-enhanced electroluminescence in organic light-emitting diodes incorporating Au nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 100:013308
Ferry VE, Munday JN, Atwater HA (2010) Design considerations for plasmonic photovoltaics. Adv Mater 22:4794–4808
Stratakis E, Kymakis E (2013) Nanoparticle-based plasmonic organic photovoltaic devices. Mater Today 16:133–146
Chen B, Zhang W, Zhou X et al (2013) Surface plasmon enhancement of polymer solar cells by penetrating Au/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles into all organic layers. Nano Energy 2:906–915
Woo S, Jeong J, Lyu H et al (2012) In situ-prepared composite materials of PEDOT: PSS buffer layer-metal nanoparticles and their application to organic solar cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:1–6
Hagglund C, Zach M, Kasemo B (2008) Enhanced charge carrier generation in dye sensitized solar cells by nanoparticle plasmons. Appl Phys Lett 92:013113–013113
Choi H, Chen WT, Kamat PV (2012) Know thy nano neighbor. Plasmonic versus electron charging effects of metal nanoparticles in dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano 6:4418–4427
Brown MD, Suteewong T, Kumar RSS et al (2010) Plasmonic dye-sensitized solar cells using core−shell metal−insulator nanoparticles. Nano Lett 11:438–445
Takanezawa K, Hirota K, Wei Q-S et al (2007) Efficient charge collection with ZnO nanorod array in hybrid photovoltaic devices. J Phys Chem C 111:7218–7223
Lenes M, Koster LJA, Mihailetchi VD et al (2006) Thickness dependence of the efficiency of polymer:fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 88:243502
Zhang D, Choy WCH, Xie F et al (2013) Plasmonic electrically functionalized TiO2 for high-performance organic solar cells. Adv Funct Mater 23:4255–4261
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9:865–865
Kang M-G, Xu T, Park HJ et al (2010) Efficiency enhancement of organic solar cells using transparent plasmonic Ag nanowire electrodes. Adv Mater 22:4378–4383
Wang DH, Kim DY, Choi KW et al (2011) Enhancement of donor–acceptor polymer bulk heterojunction solar cell power conversion efficiencies by addition of Au nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5519–5523
Sha WEI, Choy WCH, Chew WC (2010) A comprehensive study for the plasmonic thin-film solar cell with periodic structure. Opt Express 18:5993–6007
Standridge SD, Schatz GC, Hupp JT (2009) Toward plasmonic solar cells: protection of silver nanoparticles via atomic layer deposition of TiO2. Langmuir 25:2596–2600
Ostrowski JC, Mikhailovsky A, Bussian DA et al (2006) Enhancement of phosphorescence by surface-plasmon resonances in colloidal metal nanoparticles: the role of aggregates. Adv Funct Mater 16:1221–1227
Yoon W-J, Jung K-Y, Liu J et al (2010) Plasmon-enhanced optical absorption and photocurrent in organic bulk heterojunction photovoltaic devices using self-assembled layer of silver nanoparticles. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 94:128–132
Wang DH, Park KH, Seo JH et al (2011) Enhanced power conversion efficiency in PCDTBT/PC70BM bulk heterojunction photovoltaic devices with embedded silver nanoparticle clusters. Adv Energy Mater 1:766–770
Kim S-S, Na S-I, Jo J et al (2008) Plasmon enhanced performance of organic solar cells using electrodeposited Ag nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 93:073307
Du P, Cao Y, Li D et al (2013) Synthesis of thermally stable Ag@TiO2 core-shell nanoprisms and plasmon-enhanced optical properties for a P3HT thin film. RSC Adv 3:6016–6021
Xu X, Kyaw AKK, Peng B et al (2013) A plasmonically enhanced polymer solar cell with gold–silica core–shell nanorods. Org Electron 14:2360–2368
Kozanoglu D, Apaydin DH, Cirpan A et al (2013) Power conversion efficiency enhancement of organic solar cells by addition of gold nanostars, nanorods, and nanospheres. Org Electron 14:1720–1727
Leonard K, Takahashi Y, You J et al (2013) Organic bulk heterojunction photovoltaic devices incorporating 2D arrays of cuboidal silver nanoparticles: enhanced performance. Chem Phys Lett 584:130–134
Wang DH, Kim JK, Lim G-H et al (2012) Enhanced light harvesting in bulk heterojunction photovoltaic devices with shape-controlled Ag nanomaterials: Ag nanoparticles versus Ag nanoplates. RSC Adv 2:7268–7272
Fang ZY, Wang YM, Liu Z et al (2012) Plasmon-induced doping of graphene. ACS Nano 6:10222–10228
Chen HY, He CL, Wang CY et al (2011) Far-field optical imaging of a linear array of coupled gold nanocubes: direct visualization of dark plasmon propagating modes. ACS Nano 5:8223–8229
Wang F, Li CH, Chen HJ et al (2013) Plasmonic harvesting of light energy for Suzuki coupling reactions. J Am Chem Soc 135:5588–5601
Schubert EF, Kim JK (2005) Solid-state light sources getting smart. Science 308:1274–1278
Okamoto K, Niki I, Shvartser A et al (2004) Surface-plasmon-enhanced light emitters based on InGaN quantum wells. Nat Mater 3:601–605
Sharma P, Liu CY, Hsu CF et al (2006) Ordered arrays of Ag nanoparticles grown by constrained self-organization. Appl Phys Lett 89:163110
Koo WH, Jeong SM, Araoka F et al (2010) Light extraction from organic light-emitting diodes enhanced by spontaneously formed buckles. Nat Photon 4:222–226
Cho KH, Ahn SI, Lee SM et al (2010) Surface plasmonic controllable enhanced emission from the intrachain and interchain excitons of a conjugated polymer. Appl Phys Lett 97:193306
Koo WH, Jeong SM, Nishimura S et al (2011) Polarization conversion in surface-plasmon-coupled emission from organic light-emitting diodes using spontaneously formed buckles. Adv Mater 23:1003–1007
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Code, 21373144), and the National Research Foundation of Singapore (CREATE Programme of Nanomaterials for Energy and Water Management and NRF-RF2009-04). This is also a project supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Project Code, SBK201341597).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Z., Sun, J., Jiang, Y. et al. Plasmonic Enhanced Optoelectronic Devices. Plasmonics 9, 859–866 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9682-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9682-7