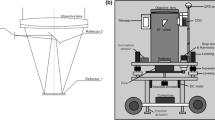
Abstract
Like other optical astrometric techniques, the Photographic Zenith Tube (PZT) has played a key role in the past observations of the Earth rotation, and it also has a potential to be applied to several other observations by taking advantage of automatic observations with self compensation of tilt of the tube. We here propose In-situ Lunar Orientation Measurement (ILOM) to study lunar rotational dynamics by direct observations of the lunar rotation from the lunar surface by using a small telescope like PZT with an accuracy of 1 milli-seconds of arc (1 mas) in the post-SELENE mission. Our second application is to obtain local gravity field on the Earth by combining deflection of the vertical measured by PZT and the position measured by Global Positioning System (GPS) or Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). The accuracy required for this purpose is not as strict as ILOM. We have already developed a Bread Board Model (BBM) of the telescope for ILOM and made some experiments in order to know the performance of the driving mechanism under a similar condition to the lunar environment showing high vacuum, large temperature change and dusty condition. We have also shown that it is possible to correct the effects of uniform temperature change upon the optical system by using a simple model with an accuracy of better than 1 mas. This model has the potential to attain the accuracy of 1 mas, based on the results of the experiments and the simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoder C F. The free librations of a dissipative Moon. Phil Trans R Soc London Ser A, 1981, 303: 327–338
Dickey J O, Bender P L, Faller J E, et al. Lunar laser ranging: A continuing legacy of the Apollo program. Science, 1994, 265: 482–490
Williams J G, Boggs D H, Yoder C F, et al. Lunar rotational dissipation in solid body and molten core. J Geophys Res, 2001, 106: 27933–27968
Kato M, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, et al. The Japanese lunar mission SELENE: Science goals and present status. Adv Space Res, 2008, 42: 294–300
Murphy T M, Strasburg J D, Stubbs C W, et al. The Apache Point Observatory Lunar Laser-Ranging Operation (APOLLO). In: Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Laser Ranging. Washington: NASA, 2002. 1–10
Currie D G, Dell’Agnello D G, Delle G. A lunar laser reflector for the 21st century. In: Abstract of 41st Lunar and Pianetary Science Conference. Houston: LPI, 2010. 2269
Resolution of the Commission 19 of the IAV. Application of optical astrometry time and latitude programs. In: Proceedings of the Twenty- First General Assembly, International Astronomical Union. Buenos Aires: Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1991. 209
Hanada H, Heki H, Araki H, et al. Application of PZT telescope to In-situ Lunar Orientation Measurement (ILOM). In: Sanso F, ed. A Window on the Future of Geodesy. Sapporo: Springer, 2004. 128: 163–168
Noda H, Heki K, Hanada H. In Situ Lunar Orientation Measurement (ILOM): Simulation of observation. Adv Space Res, 2008, 42(2): 358–362
Petrova N, Gusev A, Hanada H, et al. Application of the analytical theory of lunar physical libration for the simulation of observations of stars for the future Japanese Lunar project ILOM. AstroKazan 2009 Rep, 2009, 197–201
Takagi S, Aihara M, Kitago H, et al. Preliminary results of the astronomicdql observation made by the new PZT at the Mizusawa Latitude Observatory. Publ Int Latit Obs Mizusawa, 1974, 9: 283–289
Hirt C, Bürki B. The digital zenith camera-a new high-precision and economic astrogeodetic observation system for real-time measurement of deflections of the vertical. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Meeting of the International Gravity and Geoid Commission of the International Association of Geodesy. Thessaloniki: ZITI Editions, 2002. 161–166
Heiskanene W A, Moritz H. Physical Geodesy. San Francisco: Freeman, 1967. 364
Hanada H, Ping J S, Funazaki K, et al. Development of a photographic zenith tube for observation of the lunar rotation and the deflection of the vertical. In: Proceedings of International Symposium, Terrestrial Gravimetry: Static and Mobile Measurements 2010, St. Petersburg: Elektropribor, in press
Yoshizawa M, Andreasen G K, Høg E. Astrometric and photometric estimates for TYCHO photon counts. Astron Astrophys, 1985, 147: 227–236
Lindegren L. Photoelectric astrometry. A comparison of methods for precise image location. In: Prochazka F V, Tucker R H, eds. Modern Astrometry, IAU Col. No. 48. Vienna: University Observatory, 1978. 197–217
Yano T, Gouda N, Kobayashi Y, et al. CCD centroiding experiment for the Japan Astrometry Satellite Mission (JASMINE) and In situ Lunar Orientation Measurement (ILOM). Publ Astron Soc Pacific, 2004, 116: 667–673
Yano T, Araki H, Gouda N, et al. CCD centroiding experiment for correcting a distorted image on the focal plane. Publ Astron Soc Pacific, 2006, 118: 1448–1454
Funazaki K, Sato J, Taniguchi H, et al. Studies on controllability and optical characteristics of BBM for ILOM telescope (in Japanese). In: Proceedings of the 52nd Space Sciences and Technology Conference. Awaji: JSASS, 2008. 3A12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanada, H., Araki, H., Tazawa, S. et al. Development of a digital zenith telescope for advanced astrometry. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55, 723–732 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4673-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4673-1