Abstract
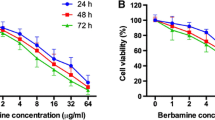
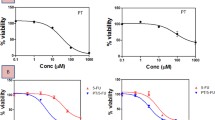
Berberine is an alkaloid isolated from the Chinese herbal medicine Huanglian, and has long been used as an antibiotic. Its antineoplastic properties were subsequently discovered in vitro. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of berberine on the growth of human colorectal carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that berberine inhibited human colorectal adenocarcinoma (LoVo) cell growth in a time- and dose-dependent manner. A WST-1 assay showed that the IC50 value after 72 h was 40.79 ± 4.11 μM. Cell cycle analysis of 40 μM berberine-treated LoVo cells by flow cytometry showed accumulation of cells in the G2/M phase. The inhibition of LoVo cell growth by berberine was associated with the suppression of cyclin B1, cdc2, and cdc25c proteins. Berberine at a dose of 50 mg kg−1 day−1 showed inhibitory rates of 45.3 % in a human colorectal adenocarcinoma xenograft in nude mice. The combination of berberine and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) had a higher inhibitory rate (59.8 %) than the berberine group (36.4 %, P = 0.01), but no significant difference was observed between the 5-FU group (43.0 %, P = 0.06) and the combination group. These results support the possibility that berberine may be useful as an alternative therapy for colorectal carcinoma.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee DU, Kang YJ, Park MK, Lee YS, Seo HG, Kim TS, Kim CH, Chang KC (2003) Effects of 13-alkyl-substituted berberine alkaloids on the expression of COX-II, TNF-alpha, iNOS, and IL-12 production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Life Sci 73:1401–1402
Lau CW, Yao XQ, Chen ZY, Ko WH, Huang Y (2001) Cardiovascular actions of berberine. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 19:234–244
Kuo CL, Chi CW, Liu TY (2004) The anti-inflammatory potential of berberine in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett 203:127–137
Lee CH, Chen JC, Hsiang CY, Wu SL, Wu HC, Ho TY (2007) Berberine suppresses inflammatory agents-induced interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha productions via the inhibition of IkappaB degradation in human lung cells. Pharmacol Res 56:193–201
Yan D, Jin C, Xiao XH, Dong XP (2008) Antimicrobial properties of berberines alkaloids in Coptis chinensis Franch by microcalorimetry. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:845–849
Hayashi K, Minoda K, Nagaoka Y, Hayashi T, Uesato S (2007) Antiviral activity of berberine and related compounds against human cytomegalovirus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:1562–1564
Ho YT, Lu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, Li TC, Ip SW, Hsia TC, Liao CL, Lin JG, Wood WG, Chung JG (2009) Berberine induced apoptosis via promoting the expression of caspase-8, -9 and -3, apoptosis inducing factor and endonuclease G in SCC-4 human tongue squamous carcinoma cancer cells. Anticancer Res 29:4063–4070
Iizuka N, Miyamoto K, Okita K, Tangoku A, Hayashi H, Yosino S, Abe T, Morioka T, Hazama S, Oka M (2000) Inhibitory effect of Coptidis Rhizoma and berberine on the proliferation of human esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett 148:19–25
Tang F, Wang D, Duan C, Huang D, Wu Y, Chen Y, Wang W, Xie C, Meng J, Wang L, Wu B, Liu S, Tian D, Zhu F, He Z, Deng F, Cao Y (2009) Berberine inhibits metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 5–8F cells by targeting Rho kinase mediated Ezrin phosphorylation at threonine 567. J Biol Chem 284:27456–27466
Kim JB, Yu JH, Ko E, Lee KW, Song AK, Park SY, Shin I, Han W, Noh DY (2010) The alkaloid berberine inhibits the growth of Anoikis-resistant MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines by inducing cell cycle arrest. Phytomedicine 17:436–440
Hur JM, Hyun MS, Lim SY, Lee WY, Kim D (2009) The combination of berberine and irradiation enhances anti-cancer effects via activation of p38 MAPK pathway and ROS generation in human hepatoma cells. J Cell Biochem 107:955–964
Mitani N, Murakami K, Yamaura T, Ikeda T, Saiki I (2001) Inhibitory effect of berberine on the mediastinal lymph node metastasis produced by orthotopic implantation of Lewis lung carcinoma. Cancer Lett 165:35–42
Katiyar SK, Meeran SM, Katiyar N, Akhtar S (2009) p53 cooperates berberine induced growth inhibition and apoptosis of non-small cell human lung cancer cells in vitro and tumor xenograft growth in vivo. Mol Carcinog 48:24–37
Lin JP, Yang JS, Lee JH, Hsieh WT, Chung JG (2006) Berberine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma SNU-5 cell line. World J Gastroenterol 12:21–28
Kheir MM, Wang Y, Hua L, Hu J, Li L, Lei F, Du L (2010) Acute toxicity of berberine and its correlation with the blood concentration in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1105–1110
Singh T, Vaid M, Katiyar N, Sharma S, Katiyar SK (2011) Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid, inhibits melanoma cancer cell migration by reducing the expressions of cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E and prostaglandin E receptors. Carcinogenesis 32:86–92
Li-Weber M (2013) Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer by Chinese medicine. Cancer Lett 332:304–312
Tsang CM, Lau EP, Di K, Cheung PY, Hau PM, Ching YP, Wong YC, Cheung AL, Wan TS, Tong Y, Tsao SW, Feng Y (2009) Berberine inhibits Rho GTPases and cell migration at low doses but induces G2 arrest and apoptosis at high doses in human cancer cells. Int J Mol Med 24:131–138
Zhang X, Gu L, Li J, Shah N, He J, Yang L, Hu Q, Zhou M (2010) Degradation of MDM2 by the interaction between berberine and DAXX leads to potent apoptosis in MDM2-overexpressing cancer cells. Cancer Res 70:9895–9904
Meeran SM, Katiyar S, Katiyar SK (2008) Berberine-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells is initiated by reactive oxygen species generation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 229:33–43
Chen TC, Lai KC, Yang JS, Liao CL, Hsia TC, Chen GW, Lin JJ, Lin HJ, Chiu TH, Tang YJ, Chung JG (2009) Involvement of reactive oxygen species and caspase-dependent pathway in berberine-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in C6 rat glioma cells. Int J Oncol 34:1681–1690
Lu B, Hu M, Liu K, Peng J (2010) Cytotoxicity of berberine on human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells through mitochondria, death receptor and MAPK pathways, and in silico drug-target prediction. Toxicol In Vitro 24:1482–1490
Qin Y, Pang JY, Chen WH, Zhao ZZ, Liu L, Jiang ZH (2007) Inhibition of DNA topoisomerase I by natural and synthetic mono- and dimeric protoberberine alkaloids. Chem Biodivers 4:481–487
Mazzini S, Bellucci MC, Mondelli R (2003) Mode of binding of the cytotoxic alkaloid berberine with the double helix oligonucleotide d(AAGAATTCTT)(2). Bioorg Med Chem 11:505–514
Qin Y, Pang JY, Chen WH, Cai Z, Jiang ZH (2006) Synthesis, DNA-binding affinities, and binding mode of berberine dimers. Bioorg Med Chem 14:25–32
Pandey MK, Sung B, Kunnumakkara AB, Sethi G, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB (2008) Berberine modifies cysteine 179 of IkappaBalpha kinase, suppresses nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic gene products, and potentiates apoptosis. Cancer Res 68:5370–5379
Wu K, Yang Q, Mu Y, Zhou L, Liu Y, Zhou Q, He B (2012) Berberine inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer cells by inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol 41:292–298
Chidambara Murthy KN, Jayaprakasha GK, Patil BS (2012) The natural alkaloid berberine targets multiple pathways to induce cell death in cultured human colon cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol 688:14–21
Hsu WH, Hsieh YS, Kuo HC, Teng CY, Huang HI, Wang CJ, Yang SF, Liou YS, Kuo WH (2007) Berberine induces apoptosis in SW620 human colonic carcinoma cells through generation of reactive oxygen species and activation of JNK/p38 MAPK and FasL. Arch Toxicol 81:719–728
Lin JG, Chung JG, Wu LT, Chen GW, Chang HL, Wang TF (1999) Effects of berberine on arylamine N-acetyltransferase activity in human colon tumor cells. Am J Chin Med 27:265–275
Fukuda K, Hibiya Y, Mutoh M, Koshiji M, Akao S, Fujiwara H (1999) Inhibition by berberine of cyclooxygenase-2 transcriptional activity in human colon cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2:227–233
Creasey WA (1979) Biochemical effects of berberine. Biochem Pharmacol 28:1081–1084
Cushman M, Dekow FW, Jacobsen LB (1979) Conformations, DNA binding parameters, and antileukemic activity of certain cytotoxic protoberberine alkaloids. J Med Chem 22:331–333
Chi CW, Chang YF, Chao TW, Chiang SH, P’eng FK, Liu WY, Liu TY (1994) Flowcytometric analysis of the effect of berberine on the expression of glucocorticoid reception in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Life Sci 54:2099–2107
Yamagishi H (1962) Interaction between nuclei acid and berberine sulfate. J Cell Biol 15:589–592
Krey AK, Hahn FE (1969) Berberine: complex with DNA. Science 166:755–757
Li XK, Motwani M, Bornmann W, Schartz GK (2000) Huanglian, a Chinese herbal extract, inhibits cell growth by suppressing the expression of cyclin B1 and inhibiting cdc2 kinase activity in human cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 58:1287–1293
Xiong CY, Shi XB, Dai ZS (1989) Pharmacokinetic study of 3H-berberine in rabbits and mouse. Chin Pharmacol Bull 5:293–296
Pang ZG, Wang BQ, Jiang HT (1997) Study on the pharmacokinetics of berberine. Fenxi Kexue Xuebao 13:51–53
Zhao XZ (1989) The clinical observation of anti-arrhythmia effects of berberine and the electrophysiology of cardiac muscle. Zhonghua Xinxueguanbing Zazhi 17:159–161
Zhang RX (1990) Laboratory studies of berberine used alone and in combination with 1,3-bis (2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea to treat malignant brain tumors. Chin Med J 103:658–665
Iizuka N, Miyamoto K, Kayano K, Hayashi H, Tangoku A, Oka M (1998) The enhancement of cisplatin-induced antitumor activity by Kampo medicines in human esophageal cancer. J Trad Med 15:340–341
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National-Eleventh Five technology major project (Grant number: 2008ZX09312-002) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Young Scientist Project #81201716).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Xia, Q., Luo, R. et al. Berberine inhibits the growth of human colorectal adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. J Nat Med 68, 53–62 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-013-0766-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-013-0766-z