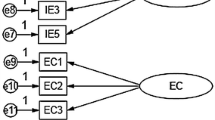
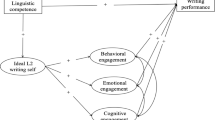
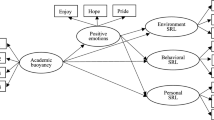
Abstract
Motivational regulation has long been recognized as an essential but insufficiently investigated aspect of self-regulated learning (SRL), especially in relation to learning English-as-a-foreign-language (EFL) writing. This study intends to fill the gap by investigating the predictive effect of motivational regulation strategies on EFL students’ writing performance mediated by SRL strategies. Data were collected from undergraduate students in mainland China (N = 512) through self-report questionnaires and an English writing test. Results of structural equation modeling (SEM) confirmed a partial mediation model in which motivational regulation strategies, as a whole, not only had direct and indirect effects on students’ writing performance but were also significantly correlated with their reported use of SRL strategies relating to cognition, metacognition, and social behavior. In addition, only cognitive and metacognitive strategies were found to be significant mediators in the model while social behavior strategies were not. The findings suggest that cumulative knowledge of motivational regulation is an antecedent of the reported use of other SRL strategies in affecting EFL writing performance. The inclusion of SRL strategies in the mediation model also contributes to a clear understanding of L2 writing processes within the SRL mechanism for improving writing outcomes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade, M. S., & Evans, N. W. (2013). Principles and practices for response in second language writing: Developing self-regulated learners. New York: Routledge.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2013). IBM SPSS Amos 22 user’s guide. Crawfordville: Amos Development Corporation.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Boekaerts, M. (1996). Self-regulated learning at the junction of cognition and motivation. European Psychologist, 1, 100–112.
Boscolo, P., & Hidi, S. (2007). The multiple meanings of motivation to write. In S. Hidi & P. Boscolo (Eds.), Writing and motivation (pp. 1–14). Oxford: Elsevier.
Byrne, B. M. (1991). The Maslach burnout inventory: Validating factorial structure and invariance across intermediate, secondary, and university educators. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 26(4), 583–605.
Chinese Ministry of Education. (2004). English teaching syllabus for English majors. Shanghai: Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press.
Cohen, A. D., & Macaro, E. (Eds.). (2007). Language learner strategies: Thirty years of research and practice. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cooper, C. A., & Corpus, J. H. (2009). Learners’ developing knowledge of strategies for regulating motivation. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 30, 525–536.
Cumming, A. (2012). Goal theory and second-language writing development, two ways. In R. Manchón (Ed.), L2 writing development: Multiple perspectives (pp. 135–164). Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton.
Dörnyei, Z. (2001). Motivation strategies in the language classroom. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Dörnyei, Z. (2005). The psychology of the language learner: Individual differences in second language acquisition. Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Greene, J. A., Costa, L. J., & Dellinger, K. (2011a). Analysis of self-regulated learning processing using statistical models for count data. Metacognition and Learning, 6(3), 275–301.
Greene, J. A., Robertson, J., & Costa, L.-J. C. (2011b). Assessing self-regulated learning using think-aloud protocol methods. In B. J. Zimmerman & D. Schunk (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 313–328). New York: Routledge Publishers.
Greene, J. A., Bolick, C. M., Jackson, W. P., Caprino, A. M., Oswald, C., & McVea, M. (2015). Domain-specificity of self-regulated learning processing in science and history. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 42, 111–128.
Harris, K. R., Graham, S., MacArthur, C., Reid, R., & Mason, L. H. (2011). Self-regulated learning processes and children’s writing. In B. J. Zimmerman & D. H. Schunk (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 187–202). New York: Routledge.
Hayes, J. R. (2012). Modeling and remodeling writing. Written Communication, 29, 369–388.
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. New York: Guilford.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55.
Jacobs, H. L., Zingraf, S. A., Wormuth, D. R., & Hartfiel, V. F. (1981). Testing ESL composition: A practical approach. Rowley: Newbury House.
Manchón, R. M. (2009). Introduction: Broadening the perspective of L2 writing scholarship: The contribution of research on foreign language writing. In R. Manchón (Ed.), Writing in foreign language contexts: Learning, teaching, and research (pp. 1–19). Buffalo: Multilingual Matters.
Manchón, R. M., Roca de Larios, J., & Murphy, L. (2007). A review of writing strategies: Focus on conceptualization and impact of first language. In A. D. Cohen & E. M. Macaro (Eds.), Language learner strategies: Thirty years of research and practice (pp. 229–250). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
McCann, E. J., & Garcia, T. (1999). Maintaining motivation and regulating emotion: Measuring individual differences in academic volitional strategies. Learning and Individual Differences, 11(3), 259–279.
McCardle, L., & Hadwin, A. F. (2015). Using multiple, contextualized data sources to measure learners’ perceptions of their self-regulated learning. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 43–75.
Mueller, R. O., & Hancock, G. R. (2008). Best practices in structural equation modeling. In J. W. Osborne (Ed.), Best practices in quantitative methods (pp. 488–508). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
O’Malley, J. M., & Chamot, A. U. (1990). Learning strategies in second language acquisition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ong, J., & Zhang, L. J. (2013). Effects of the manipulation of cognitive processes on EFL writers’ text quality. TESOL Quarterly, 47, 375–398.
Oxford, R. L. (2013). Teaching and researching language learning strategies. Harlow: Pearson.
Oxford, R. L., Rubin, J., Chamot, A. U., Schramm, K., Lavine, R., Gunning, P., & Nel, C. (2014). The learning strategy prism: Perspectives of learning strategy experts. System, 43, 30–49.
Pintrich, P. R. (2004). A conceptual framework for assessing motivation and self-regulated learning in college students. Educational Psychology Review, 16, 385–407.
Pintrich, P. R., & De Groot, E. V. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82, 33–40.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D. A., García, T., & McKeachie, W. J. (1993). Reliability and predictive validity of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ). Educational and Psychological Measurement, 53(3), 801–813.
Pintrich, P. R., Wolters, C. A., & Baxter, G. P. (2000). Assessing metacognition and self-regulated learning issues in the measurement of metacognition (pp. 43–97). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40(3), 879–891.
Sansone, C., & Thoman, D. B. (2005). Interest as the missing motivator in self-regulation. European Psychologist, 10, 175–186.
Schunk, D. H., & Zimmerman, B. J. (2008). Motivation and self-regulated learning: Theory, research, and applications. New York: Erlbaum.
Schwinger, M., & Stiensmeier-Pelster, J. (2012). Effects of motivational regulation on effort and achievement: a mediation model. International Journal of Educational Research, 56, 35–47.
Schwinger, M., Steinmayr, R., & Spinath, B. (2009). How do motivational regulation strategies affect achievement: mediated by effort management and moderated by intelligence. Learning and Individual Differences, 19, 621–627.
Teng, L. S. (2016). Changes in teachers’ beliefs after a professional development project for teaching writing: two Chinese cases. Journal of Education for Teaching, 42(1), 106–109.
Teng, L. S., & Zhang, L. J. (2016a). A questionnaire-based validation of multidimensional models of self-regulated learning strategies. Modern Language Journal, 100(3), 674–701.
Teng, L. S., & Zhang, L. J. (2016b). Fostering strategic learning: The development and validation of the writing strategies for motivational regulation questionnaire (WSMRQ). Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 25, 123–134.
Troia, G. A., Harbaugh, A. G., Shankland, R. K., Wolbers, K. A., & Lawrence, A. M. (2013). Relationships between writing motivation, writing activity, and writing performance: Effects of grade, sex, and ability. Reading and Writing, 26, 17–44.
Varghese, S. A., & Abraham, S. A. (1998). Undergraduates arguing a case. Journal of Second Language Writing, 7(3), 287–306.
Wilde, J. (2004). Definitions for the no child left behind act of 2001: Assessment. National Clearinghouse for English Language Acquisition and Language Instruction NCELA. Washington, DC: The George Washington University.
Winne, P. H., & Perry, N. E. (2000). Measuring self-regulated learning in M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, M. (Ed), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 531-566). San Diego: Academic Press.
Wolters, C. A. (1998). Self- regulated learning and college students’ regulation of motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90, 224–235.
Wolters, C. A. (1999). The relation between high school students’ motivational regulation and their use of learning strategies, effort, and classroom performance. Learning and Individual Differences, 11, 281–299.
Wolters, C. A. (2003). Regulation of motivation: Evaluating an underemphasized aspect of self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 38, 189–205.
Wolters, C. A., & Benzon, M. B. (2013). Assessing and predicting college students’ use of strategies for the self-regulation of motivation. Journal of Experimental Education, 81, 199–221.
Wolters, C. A., & Mueller, S. A. (2010). Motivation regulation. In P. P. B. McGaw (Ed.), International encyclopedia of education (3rd ed., pp. 631–635). Oxford: Elsevier.
Wolters, C. A., Benzon, M. B., & Arroyo-Giner, C. (2011). Assessing strategies for the self-regulation of motivation. In B. Zimmerman & D. H. Schunk (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 298–312). New York: Routledge.
Wu, H. Y., & Liu, R. Q. (2004). Investigating the effects of metacognition in EFL writing: A structural equation modeling approach. Modern Foreign Languages, 27(4), 370–377.
Zhang, L. J. (2008). Constructivist pedagogy in strategic reading instruction: Exploring pathways to learner development in the English as a second language (ESL) classroom. Instructional Science, 36(2), 89–116.
Zhang, L. J. (2013). Second language writing as and for second language learning. Journal of Second Language Writing, 22(4), 446–447.
Zhang, L. J. (2016). Reflections on pedagogical imports of western practices for professionalizing second-language writing and writing-teacher education. Australian Review of Applied Linguistics, 39(3), 203–232.
Zhang, L. J., & Zhang, D. (2013). Thinking metacognitively about metacognition in second and foreign language learning, teaching, and research: Toward a dynamic metacognitive systems perspective. Contemporary Foreign Language Studies, 369, 111–121.
Zhang, L. J., Aryadoust, V., & Zhang, D. (2016). Taking stock of the effects of strategies-based instruction on writing in Chinese and English in Singapore primary schools. In R. E. Silver & W. Bokhorst-Heng (Eds.), Quadrilingual education in Singapore: Pedagogical innovation in language education (pp. 103–126). New York: Springer.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2008). Investigating self-regulation and motivation: Historical background, methodological developments, and future prospects. American Educational Research Journal, 45, 166–183.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2011). Motivational sources and outcomes of self-regulated learning and performance. In B. J. Zimmerman & D. H. Schunk (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 49–64). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Bandura, A. (1994). Impact of self-regulatory influences on writing course attainment. American Educational Research Journal, 31(4), 845–862.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Risemberg, R. (1997). Becoming a self-regulated writer: A social cognitive perspective. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 22, 73–101.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. H. (2008). Motivation: An essential dimension of self-regulated learning. In D. H. Schunk & B. J. Zimmerman (Eds.), Motivation and self-regulated learning: Theory, research, and applications (pp. 1–30). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that this paper was based on the first author, Lin Sophie Teng’s doctoral thesis, which was completed with the assistance of a scholarship from The University of Auckland, New Zealand. We both declare that there are no conflicts of interest whatsoever in connection with this publication. The doctoral scholarship does not have any strings attached to it for the recipient of the scholarship. It was awarded to worthy candidates purely for academic study that should lead to the award of the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Degree. It is not commercially motivated whatsoever.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Writing Topic
Prompts: It was recently reported in a newspaper that six students who shared a dorm at a local university hired a cleaner to do laundry and cleaning once a week. And each of them paid her 60 yuan a month. This has led to a heated debate as to whether college students should hire cleaners.
Please write a composition of more than 200 words on the following topic: Should College Students Hire Cleaners?
Appendix 2
Appendix 3
Appendix 4
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, L.S., Zhang, L.J. Effects of motivational regulation strategies on writing performance: a mediation model of self-regulated learning of writing in English as a second/foreign language. Metacognition Learning 13, 213–240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-017-9171-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-017-9171-4