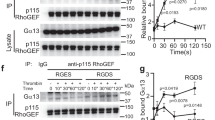
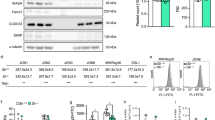
Summary
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is important for platelet activation. Recent studies showed that PI3K and oscillative calcium could cross talk to each other and positively regulate integrin α IIbβ3-mediated outside-in signaling. However, the mechanism of this feedback regulation remains to be further characterized. Here we found that treatments of both PI3K inhibitor wortmannin and P2Y1 inhibitor A3P5P could inhibit granular secretion in platelets. Additionally, when RGD-substrate adherent platelets were treated with the ADP scavenger apyrase to deplete the granular-released ADP, their attachments in engaging with substrates became looser and the frequency of calcium oscillation decreased. Since it is known that ADP stimulates the PI3K and calcium signal primarily through P2Y12 and P2Y1 receptors respectively, our data indicated that integrin αIIbβ3 downstream PI3K and calcium activation might be not completely coupled to integrin associated signaling complex, but in part through feedback stimulation by granular released ADP. Our data indicates the important roles of PI3K and granular released ADP in coordinating the feedback regulations in integrin αIIbβ3-mediated platelet activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun D.S., Lo S.J., Lin C.H., Yu M.S., Huang C.Y., Chen Y.F. and Chang H.H., Calcium oscillation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase positively-regulate integrin alphaIIbbeta3-mediated outside-in signaling. J. Biomed. Sci. 12: in press, 2005
Toker A, Cantley LC (1997) Signalling through the lipid products of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase. Nature 387: 673–676
Rittenhouse SE (1996) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation and platelet function. Blood 88: 4401–4414
Chang AY, Chan JY, Chan SH (2003) Differential distribution of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat. J Biomed Sci 10: 285–291
Chang HH, Chang CP, Chang JC, Dung SZ, Lo SJ (1997) Application of Recombinant Rhodostomin in Studying Cell Adhesion. J Biomed Sci 4: 235–243
Guinebault C, Payrastre B, Racaud-Sultan C, Mazarguil H, Breton M, Mauco G, Plantavid M, Chap H (1995) Integrin-dependent translocation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase to the cytoskeleton of thrombin-activated platelets involves specific interactions of p85 alpha with actin filaments and focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol 129: 831–842
Sultan C, Plantavid M, Bachelot C, Grondin P, Breton M, Mauco G, Levy-Toledano S, Caen JP, Chap H (1991) Involvement of platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa (alpha IIb-beta 3 integrin) in thrombin-induced synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 3′,4′-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem 266: 23554–23557
Kovacsovics TJ, Bachelot C, Toker A, Vlahos CJ, Duckworth B, Cantley LC, Hartwig JH (1995) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition spares actin assembly in activating platelets but reverses platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem 270: 11358–11366
Dorsam RT, Kunapuli SP (2004) Central role of the P2Y12 receptor in platelet activation. J Clin Invest 113: 340–345
Moake JL, Turner NA, Stathopoulos NA, Nolasco L, Hellums JD (1988) Shear-induced platelet aggregation can be mediated by vWF released from platelets, as well as by exogenous large or unusually large vWF multimers, requires adenosine diphosphate, and is resistant to aspirin. Blood 71: 1366–1374
Gachet C (2001) ADP receptors of platelets and their inhibition. Thromb Haemost 86: 222–232
Woulfe D, Yang J, Brass L (2001) ADP and platelets: the end of the beginning. J Clin Invest 107: 1503–1505
Hardy AR, Jones ML, Mundell SJ, Poole AW (2004) Reciprocal cross-talk between P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptors at the level of calcium signaling in human platelets. Blood 104: 1745–1752
Mazzucato M, Cozzi MR, Pradella P, Ruggeri ZM, De Marco L (2004) Distinct roles of ADP receptors in von Willebrand factor-mediated platelet signaling and activation under high flow. Blood 104: 3221–3227
Chang HH, Hu ST, Huang TF, Chen SH, Lee YH, Lo SJ (1993) Rhodostomin, an RGD-containing peptide expressed from a synthetic gene in Escherichia coli, facilitates the attachment of human hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 190: 242–249
Chang HH, Lin CH, Lo SJ (1999) Recombinant rhodostomin substrates induce transformation and active calcium oscillation in human platelets. Exp Cell Res 250: 387–400
Chang HH, Shyu HF, Wang YM, Sun DS, Shyu RH, Tang SS, Huang YS (2002) Facilitation of cell adhesion by immobilized dengue viral nonstructural protein 1 (NS1): arginine-glycine-aspartic acid structural mimicry within the dengue viral NS1 antigen. J Infect Dis 186: 743–751
Chang HH, Tsai WJ, Lo SJ (1997) Glutathione S-transferase-rhodostomin fusion protein inhibits platelet aggregation and induces platelet shape change. Toxicon 35: 195–204
Chang Y, Chen TL, Wu GJ, Hsiao G, Shen MY, Lin KH, Chou DS, Lin CH, Sheu JR (2004) Mechanisms involved in the antiplatelet activity of ketamine in human platelets. J Biomed Sci 11: 764–772
Wassmer SC, Lepolard C, Traore B, Pouvelle B, Gysin J, Grau GE (2004) Platelets reorient Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocyte cytoadhesion to activated endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 189: 180–189
Heilmann C, Niemann S, Sinha B, Herrmann M, Kehrel BE, Peters G (2004) Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin-binding protein (FnBP)-mediated adherence to platelets, and aggregation of platelets induced by FnBPA but not by FnBPB. J Infect Dis 190: 321–329
Hsiao G, Shen MY, Chou DS, Lin CH, Chen TF, Sheu JR (2004) Involvement of the antiplatelet activity of magnesium sulfate in suppression of protein kinase C and the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Biomed Sci 11: 19–26
Hsiao G, Shen MY, Fang CL, Chou DS, Lin CH, Chen TF, Sheu JR (2003) Morphine-potentiated platelet aggregation in in vitro and platelet plug formation in in vivo experiments. J Biomed Sci 10: 292–301
Kau J.H., Sun D.S., TW J., SH F., Huang H.H., Lin H.C. and Chang H.H., Anti-platelet activities of anthrax lethal toxin are associated with suppressed p42/44 and p38 MAPK pathways in the platelets. J. Infect. Dis. In press: 2005.
Chang HH, Lo SJ (1998) Full-spreading platelets induced by the recombinant rhodostomin are via binding to integrins and correlated with FAK phosphorylation. Toxicon 36: 1087–1099
Fan SS, Chen MS, Lin JF, Chao WT, Yang VC (2003) Use of gain-of-function study to delineate the roles of crumbs in Drosophila eye development. J Biomed Sci 10: 766–773
Mak NK, Kok TW, Wong RN, Lam SW, Lau YK, Leung WN, Cheung NH, Huang DP, Yeung LL, Chang CK (2003) Photodynamic activities of sulfonamide derivatives of porphycene on nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. J Biomed Sci 10: 418–429
Gorka M, Godlewski MM, Gajkowska B, Wojewodzka U, Motyl T (2004) Kinetics of Smac/DIABLO release from mitochondria during apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cell Biol Int 28: 741–754
Lee KG, Miller T, Anastassov I, Cohen WD (2004) Shape transformation and cytoskeletal reorganization in activated non-mammalian thrombocytes. Cell Biol Int 28: 299–310
Mascari LM, Ross JM (2003) Quantification of staphylococcal-collagen binding interactions in whole blood by use of a confocal microscopy shear-adhesion assay. J Infect Dis 188: 98–107
Oertel A, Holzinger A, Lutz-Meindl U (2003) Involvement of myosin in intracellular motility and cytomorphogenesis in Micrasterias. Cell Biol Int 27: 977–986
Yates-Siilata KE, Dahms TE, Webster RO, Heuertz RM (2004) C-reactive protein increases F-actin assembly and cortical distribution with resultant loss of lamellipod formation in human neutrophils. Cell Biol Int 28: 33–39
Chang HH, Kau JH, Lo SJ, Sun DS (2003) Cell-adhesion and morphological changes are not sufficient to support anchorage-dependent cell growth via non-integrin-mediated attachment. Cell Biol Int 27:123–133
Tseng YL, Peng HC, Huang TF (2004) Rhodostomin, a disintegrin, inhibits adhesion of neutrophils to fibrinogen and attenuates superoxide production. J Biomed Sci 11: 683–691
Kao YS, Fong JC (2004) Thapsigargin and EGTA inhibit endothelin-1-induced glucose transport. J Biomed Sci 11: 206–213
Wang JP, Tsai JJ, Chen YS, Hsu MF (2005) Stimulation of intracellular Ca2+ elevation in neutrophils by thiol-oxidizing phenylarsine oxide. Biochem Pharmacol 69: 1225–1234
Yang CM, Chien CS, Ma YH, Hsiao LD, Lin CH, Wu C (2003) Bradykinin B2 receptor-mediated proliferation via activation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/MAPK pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci 10: 208–218
Carroll RC, Butler RG, Morris PA, Gerrard JM, Separable assembly of platelet pseudopodal and contractile cytoskeletons. Cell 30: 385–393(1982)
Sun DS, Chang HH (2003) Differential regulation of JNK in caspase-3-mediated apoptosis of MPP(+)-treated primary cortical neurons. Cell Biol Int 27: 769–777
Ten Cate H (2003) Trombocytopenia: one of the markers of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 33: 413–416
Gibbins JM (2004) Platelet adhesion signalling and the regulation of thrombus formation. J Cell Sci 117: 3415–3425
Huang TF (1998) What have snakes taught us about integrins?. Cell Mol Life Sci 54: 527–540
Dorn GW 2nd, Force T (2005) Protein kinase cascades in the regulation of cardiac hypertrophy. J Clin Invest 115: 527–537
Saeed SA, Rasheed H, Fecto FA, Achakzai MI, Ali R, Connor JD, Gilani AU (2004) Signaling mechanisms mediated by G-protein coupled receptors in human platelets. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25: 887–892
Taylor CW (2002) Controlling calcium entry. Cell 111: 767–769
Bleasdale JE, Thakur NR, Gremban RS, Bundy GL, Fitzpatrick FA, Smith RJ, Bunting S (1990) Selective inhibition of receptor-coupled phospholipase C-dependent processes in human platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255: 756–768
Kageyama M, Mori T, Yanagisawa T, Taira N (1991) Is staurosporine a specific inhibitor of protein kinase C in intact porcine coronary arteries?. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259: 1019–1026
Hartwig JH, Kung S, Kovacsovics T, Janmey PA, Cantley LC, Stossel TP, Toker A (1996) D3 phosphoinositides and outside-in integrin signaling by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa mediate platelet actin assembly and filopodial extension induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem 271: 32986–32993
Curtis ASG (1964) The mechanism of adhesion of cells to glass. J Cell Biol 20: 199–215
Heemskerk JW, Vis P, Feijge MA, Hoyland J, Mason WT, Sage SO (1993) Roles of phospholipase C and Ca(2+)-ATPase in calcium responses of single, fibrinogen-bound platelets. J Biol Chem 268: 356–363
Jenks BG, Roubos EW, Scheenen WJ (2003) Ca2+ oscillations in melanotropes of Xenopus laevis: their generation, propagation, and function. Gen Comp Endocrinol 131: 209–219
Shvartsman SY (2002) Shooting from the hip: spatial control of signal release by intracellular waves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99: 9087–9089
Goncalves I, Hughan SC, Schoenwaelder SM, Yap CL, Yuan Y, Jackson SP (2003) Integrin alpha IIb beta 3-dependent calcium signals regulate platelet-fibrinogen interactions under flow. Involvement of phospholipase C gamma 2. J Biol Chem 278: 34812–34822
Haimovich B, Kaneshiki N, Ji P (1996) Protein kinase C regulates tyrosine phosphorylation of pp125FAK in platelets adherent to fibrinogen. Blood 87: 152–161
Haimovich B, Lipfert L, Brugge JS, Shattil SJ (1993) Tyrosine phosphorylation and cytoskeletal reorganization in platelets are triggered by interaction of integrin receptors with their immobilized ligands. J Biol Chem 268: 15868–15877
Heraud JM, Racaud-Sultan C, Gironcel D, Albiges-Rizo C, Giacomini T, Roques S, Martel V, Breton-Douillon M, Perret B, Chap H (1998) Lipid products of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and phosphatidylinositol 4′,5′-bisphosphate are both required for ADP-dependent platelet spreading. J Biol Chem 273: 17817–17823
Mazzucato M, Pradella P, Cozzi MR, De Marco L, Ruggeri ZM (2002) Sequential cytoplasmic calcium signals in a 2-stage platelet activation process induced by the glycoprotein Ibalpha mechanoreceptor. Blood 100: 2793–2800
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Chao-Zong Liu of the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, and Dr. Hui-Chun Li of the Biochemistry Department, Tzu-Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan, R.O.C., for their help with the manuscript. This work was supported by the Tzu-Chi University (TCMRC90104; 61030020; 61040020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, DS., Lo, S.J., Tsai, WJ. et al. PI3-kinase is essential for ADP-stimulated integrin αIIbβ3-mediated platelet calcium oscillation, implications for P2Y receptor pathways in integrin αIIbβ3-initiated signaling cross-talks. J Biomed Sci 12, 937–948 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-005-9016-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-005-9016-z