Abstract
Purpose
An advanced estimation model CARS-PLS (competitive adaptive reweighted sampling-partial least squares) has been developed for feature extraction and soil contamination analysis. However, this method works well for a single mining area and has limited capacity in coping with the variations from multiple sites. In this paper, we present an improved estimation model, CARS-PLS-SVM, to cope with the nonlinear problem in multiple sites with SVM (support vector machines).
Materials and methods
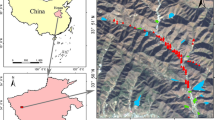
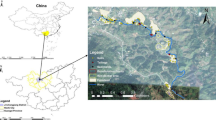
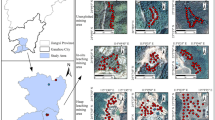
We selected two study areas located in metal mining and coal mining areas of north China. A total of 65 soil samples were collected. The heavy metal(loid) concentrations (Cr and As) were determined by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS), and the visible and near-infrared spectra of the soil samples were measured with an ASD (Analytical Spectral Devices) field spectrometer (350–2500 nm). Samples were divided into calibration set (n = 41) and validation set (m = 24) according to heavy metal(loid) concentration. After different pretreatment methods, the new features extracted from CARS-PLS are used as the input to model the data further with SVMs.
Results and discussion
The performance of CARS-PLS-SVM was investigated under seven different pretreatment methods. Results showed that using combination of Savitzky-Golay and standard normal transformation pretreatment method achieved the best accuracy for Cr estimation (coefficient of determination for prediction, Rp2 = 0.9705, root-mean-square error for prediction, RMSEP = 5.0253, residual prediction deviation, RPD = 5.9001, ratio of prediction performance to interquartile range, RPIQ = 11.4043) and for As prediction (Rp2 = 0.9483; RMSEP = 1.2024; RPD = 3.0689; RPIQ = 5.3643). Besides, CARS-PLS-SVM is better than partial least squares (PLS) regression under the same pretreatment methods. Compared with three current state-of-the-art models: wavelet transform PLS (WT-PLS), synergy interval PLS (siPLS), and the CARS-PLS model, CARS-PLS-SVM was found to be superior to the other methods for Cr prediction (Rp2 = 0.9705; RMSEP = 5.0253; RPD = 5.9001; RPIQ = 11.4043) and As prediction (Rp2 = 0.9483; RMSEP = 1.2024; RPD = 3.0689; RPIQ = 11.5.3643).
Conclusions
The results demonstrate that compared with other linear models, the nonlinear model CARS-PLS-SVM has the highest precision in soil heavy metal(loid) estimation modeling of multiple mining areas by the use of proper spectral feature extraction from the pretreated spectra.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aring R, Berg FVD, Oslash Engelsen RB (2009) Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 28:1201–1222
Balabin RM, Smirnov SV (2011) Variable selection in near-infrared spectroscopy: benchmarking of feature selection methods on biodiesel data. Anal Chim Acta 692(1-2):63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.03.006
Barnes R, Dhanoa M, Lister SJ (1989) Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Appl Spectrosc 43:772–777
Blackburn GA, Ferwerda JG (2008) Retrieval of chlorophyll concentration from leaf reflectance spectra using wavelet analysis. Remote Sens Environ 112(4):1614–1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.08.005
Cao H, Chen J, Zhang J, Zhang H, Qiao L, Men Y (2010) Heavy metals in rice and garden vegetables and their potential health risks to inhabitants in the vicinity of an industrial zone in Jiangsu, China. J Environ Sci 22(11):1792–1799. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60321-1
Chang CW, Laird DA, Mausbach MJ, Hurburgh CR (2001) Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy-principal components regression analyses of soil properties. Soil Soc Am J 65(2):480–490. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2001.652480x
Chauchard F, Cogdill R, Roussel S, Roger JM, Bellon-Maurel V, Cogdill R (2004) Application of LS-SVM to non-linear phenomena in NIR spectroscopy: development of a robust and portable sensor for acidity prediction in grapes. Chemometr Intell Lab 71(2):141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2004.01.003
Chia KS, Rahim HA, Rahim RA (2013) Evaluation of common pre-processing approaches for visible (VIS) and shortwave near infrared (SWNIR) spectroscopy in soluble solids content (SSC) assessment. Biosyst Eng 115(1):82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2013.02.008
Choe E, van der Meer F, van Ruitenbeek F, van der Werff H, de Smeth B, Kim K-W (2008) Mapping of heavy metal pollution in stream sediments using combined geochemistry, field spectroscopy, and hyperspectral remote sensing: a case study of the Rodalquilar mining area, SE Spain. Remote Sens Environ 112(7):3222–3233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2008.03.017
Chu X, Yuan H, Lu W (2004) Progress and application of spectral data pretreatment and wavelength selection methods in NIR analytical technique. Prog Chem 16:528–542
Cozzolino D, Morón A (2006) Potential of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy and chemometrics to predict soil organic carbon fractions. Soil Till Res 85(1-2):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.12.006
Delwiche SR, Graybosch RA (2003) Examination of spectral pretreatments for partial least-squares calibrations for chemical and physical properties of wheat. Appl Spectrosc 57(12):1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.1366/000370203322640161
Ettler V, Kíbek B, Majer V, Knésl I, Mihaljevi M (2012) Differences in the bioaccessibility of metals/metalloids in soils from mining and smelting areas (Copperbelt, Zambia). J Geochem Explor 113:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.08.001
Fadock M, Brown RB, Reynolds AG (2016) Visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for nondestructive analysis of red winegrapes. Am J Enol Viticult 67d:38-46
Fan W, Shan Y, Li G, Lv H, Li H, Liang Y (2012) Application of competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method to determine effective wavelengths for prediction of total acid of vinegar. Food Anal Method 5(3):585–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9285-2
Hong-wei D, Rong-guang Z, Wei-dong X, Yuan-yuan Q, Xue-dong Y, Cheng-jian X (2017) Hyperspectral imaging detection of total viable count from vacuum packing cooling mutton based on GA and CARS algorithms. Spectroscop Spectral Anal 37:847–852
Hui J, Liu G, Mei C, Shuang Y, Xiao X, Ding Y (2012) Measurement of process variables in solid-state fermentation of wheat straw using FT-NIR spectroscopy and synergy interval PLS algorithm. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 97:277–283
Kemper T, Sommer S (2002) Estimate of heavy metal contamination in soils after a mining accident using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 36(12):2742–2747. https://doi.org/10.1021/es015747j
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng Y, Huang Y, Zhu Y (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 152:686–692
Khosravi V, Ardejani FD, Yousefi S (2017) Spectroscopic-based assessment of the content and geochemical behaviour of arsenic in a highly heterogeneous sulphide-rich mine waste dump. Environ Earth Sci 76(13):459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6793-4
Li H, Liang Y, Xu Q, Cao D (2009) Key wavelengths screening using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method for multivariate calibration. Anal Chim Acta 648(1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.06.046
Malley D, Williams P (1997) Use of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy in prediction of heavy metals in freshwater sediment by their association with organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 31(12):3461–3467. https://doi.org/10.1021/es970214p
Nawar S, Buddenbaum H, Hill J, Kozak J, Mouazen AM (2016) Estimating the soil clay content and organic matter by means of different calibration methods of vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Soil Till Res 155:510–522
Nawar S, Mouazen AM (2017) Predictive performance of mobile vis-near infrared spectroscopy for key soil properties at different geographical scales by using spiking and data mining techniques. Catena 151:118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.12.014
Pang G, Wang T, Sun J, Li S (2014) Quantitative analysis of soil salinity content with hyperspectra data in Minqin,Gansu,China. J Desert Res 34:1073–1079
Parisotto G, Ferro MF, Müller ALH, Müller EI, Santos MFP, Guimares RCL, Dias JCM, Flores rMM (2010) Total acid number determination in residues of crude oil distillation using ATR-FTIR and variable selection by chemometric methods. Energy Fuel 24(10):5474–5478. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef1002974
Pascucci S, Belviso C, Cavalli RM, Palombo A, Pignatti S, Santini F (2012) Using zimaging spectroscopy to map red mud dust waste: the Podgorica aluminum complex case study. Remote Sens Environ 123:139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.03.017
Pazheri FR, Othman MF, Malik NH (2014) A review on global renewable electricity scenario. Renew Sust Energ Rev 31:835–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.12.020
Pittner S, Kamarthi SV (1999) Feature extraction from wavelet coefficients for pattern recognition tasks. IEEE T Pattern Anal 21(1):83–88. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.745739
Rinnan Å, van den Berg F, Engelsen SB (2009) Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 28:1201–1222
Rossel RAV, Behrens T, Guerrero C, Viscarra Rossel RA, Mouazen AM (2010) Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 158(1-2):46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.12.025
Shi T, Chen Y, Liu Y, Wu G (2014) Visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy—an alternative for monitoring soil contamination by heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 265:166–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.059
Smola AJ, Schölkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14(3):199–222. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88
Sun W, Zhang X (2017) Estimating soil zinc concentrations using reflectance spectroscopy. Int J Appl Earth Obs 58:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2017.01.013
Tan K, Ye Y, Du P (2014a) Estimation of arsenic contamination in reclaimed agricultural soils using reflectance spectroscopy and ANFIS model. IEEE J Sel Top Appl 7:2540–2546
Tan K, Ye Y, Du P (2014b) Estimation of heavy-metals concentration in reclaimed mining soils using reflectance spectroscopy. Spectroscop Spect Anal 34:3317–3322
Tang G, Huang Y, Tian K, Song X, Yan H, Hu J, Xiong Y, Min S (2014) A new spectral variable selection pattern using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling combined with successive projections algorithm. Analyst 139(19):4894–4902. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN00837E
Thomas K, Stefan S (2002) Estimate of heavy metal contamination in soils after a mining accident using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 36:2742–2747
Tian X, Su Z, Chen E, Li Z, van der Tol C, Guo J, He Q (2012) Estimation of forest above-ground biomass using multi-parameter remote sensing data over a cold and arid area. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf 14(1):160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2011.09.010
Vohland M, Besold J, Hill J, Fründ HC (2011) Comparing different multivariate calibration methods for the determination of soil organic carbon pools with visible to near infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 166(1):198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.08.001
Vohland M, Emmerling C (2011) Determination of total soil organic C and hot water-extractable C from VIS-NIR soil reflectance with partial least squares regression and spectral feature selection techniques. Eur J Soil Sci 62(4):598–606. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2011.01369.x
Vohland M, Ludwig M, Thiele-Bruhn S, Ludwig B (2014) Determination of soil properties with visible to near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy: effects of spectral variable selection. Geoderma 223-225:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.01.013
Wali MK, Murugappan M, Ahmad RB, Zheng BS (2012) Development of discrete wavelet transform (DWT) toolbox for signal processing applications. Int Conf Biomed Eng:211–216
Wang J, Cui L, Gao W, Shi T, Chen Y, Gao Y (2014) Prediction of low heavy metal concentrations in agricultural soils using visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 216:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.10.024
Wang Z, Skidmore A, Darvishzadeh R, Heiden U, Heurich M, Wang T (2015) Leaf nitrogen content indirectly estimated by leaf traits derived from the PROSPECT model. IEEE J Sel Top Appl 8(6):3172–3182
Xiaobo Z, Jiewen Z, Xingyi H, Yanxiao L (2007) Use of FT-NIR spectrometry in non-invasive measurements of soluble solid contents (SSC) of 'Fuji' apple based on different PLS models. Chemometr Intell Lab 87(1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2006.09.003
Zhang X, Yang L, Li Y, Li H, Wang W, Ye B (2012) Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ Monit Assess 184(4):2261–2273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2115-6
Zhuang P, Lu H, Li Z, Zou B, McBride MB (2014) Multiple exposure and effects assessment of heavy metals in the population near mining area in South China. PLoS One 9(4):e94484. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094484
Funding
This research was supported in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2014ZDPY14) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingfang Wu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, K., Wang, H., Zhang, Q. et al. An improved estimation model for soil heavy metal(loid) concentration retrieval in mining areas using reflectance spectroscopy. J Soils Sediments 18, 2008–2022 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1930-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1930-6