Abstract
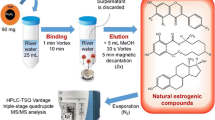
The easiness-to-handle of the magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction (Mag-dSPE) procedure was developed for preconcentration of 24 steroid hormones in river water. Ethylenediamine-functionalized magnetic carbon nanotubes (EDA@Mag-CNTs) were synthesised by a simple one-pot reaction and were used as sorbent in Mag-dSPE procedure. The properties of the EDA@Mag-CNTs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). An ultra-fast liquid chromatography–tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (UFLC-MS/MS) method for determination of 24 steroid hormones in river water at nanograms per liter had been developed with pretreatment of the samples by Mag-dSPE. The obtained results demonstrated the higher extraction capacity of EDA@Mag-CNT Mag-dSPE with recoveries between 82.1 and 113 %. The limits of quantification (LOQs) for the steroid hormone were between 0.020 and 1.00 ng/L. The developed method had been successfully applied to 60 river water samples, and it was confirmed that EDA@Mag-CNT Mag-dSPE was a highly effective extraction method for the steroid hormone analyses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann CHL, Winther-Nielsen M, Helweg C (2002) Feminization of fish-the effect of estrogenic compounds and their fate in sewage treatment plant and nature. Danish Environmental Protection Agency, Danish Ministry of the Environment, København, Denmark, Environmental Project no. 729. Available at http://www2.mst.dk/udgiv/publications/2002/87-7972-305-5/pdf/87-7972-306-3.pdf
Barbara SR, Javier HB, Pedro S (2015) Core-shell polydopamine magnetic nanoparticles as sorbent in micro-dispersive solid-phase extraction for the determination of estrogenic compounds in water samples prior to high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. J Chromatogr A 1397:1–10
Briciu RD, Wasik AK, Namiesnik J (2009) Analytical Challenges and Recent Advances in the Determination of Estrogens in Water Environments. J Chromatogr Sci 47:127–139
Chiu T-C, Chang L-C, Chiang C-K, Chang H-T (2008) Determining estrogens using surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry with silver nanoparticles as the matrix. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19:1343–1346
Commission Decision (2002) /657/EC implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results, Off. J. Eur. Communities L221 (17.8.2002) 8–36
Fang G, Min G, He J, Zhang C, Qian K, Wang S (2009) Multiwalled carbon nanotubes as matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction absorbents to determine 31 pesticides in agriculture samples by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 57:3040–3045
Görög S (2011) Advances in the analysis of steroid hormone drugs in pharmaceuticals and environmental samples (2004–2010). J Pharm Biomed Anal 55:728–743
Gromov AV, Gray N, Szilagyi PA, Campbell EEB (2012) Direct grafting of carbon nanotubes with ethylenediamine. J Mater Chem 22:21242–21248
Guan Y, Jiang C, Hu C, Jia L (2010) Preparation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized magnetic particles by sol–gel technology and its application in extraction of estrogens. Talanta 83:337–343
Guo F, Liu Q, G-b Q, S-j S, J-t S, J-b S, G-b J (2013) Simultaneous determination of five estrogens and four androgens in water samples by online solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1281:9–18
Guo S, Li D, Zhang L, Li J, Wang E (2009) Monodisperse mesoporous super- paramagnetic single-crystal magnetite nanoparticles for drug delivery. Biomaterials 30:1881–1889
Hamid H, Eskicioglu C (2012) Fate of estrogenic hormones in wastewater and sludge treatment: A review of properties and analytical detection techniques in sludge matrix. Water Res 46:5813–5833
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Palumbo M, Piccioli V, Parrella A (2007) Influence of alkylphenols and trace elements in toxic, genotoxic, and endocrine disruption activity of wastewater treatment plants. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:1686–1694
Jiao Q, Hao L, Shao Q, Zhao Y (2013) In situ synthesis of iron-filled nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes and their magnetic properties. Carbon 61:640–649
Kozłowska-Tylingo K, Konieczka P, Gustaw E, Wasik A, Namieśnik J (2014) Comparison of high performance liquid chromatography methods with different detectors for determination of steroid hormones in aqueous matrices. Anal Lett 47:1449–1464
Li Q, Lam MHW, Wu RSS, Jiang B (2010) Rapid magnetic-mediated solid-phase extraction and pre-concentration of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals in natural waters by poly(divinylbenzene-co-methacrylic acid) coated Fe3O4 core-shell magnetite microspheres for their liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry determination. J Chromatogr A 1217:1219–1226
Li W, Gao C, Qian H, Ren J, Yan D (2006) Multiamino-functionalized carbon nanotubes and their applications in loading quantum dots and magnetic nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 16:1852–1859
Liu Y, Jia L (2008) Analysis of estrogens in water by magnetic octadecylsilane particles extraction and sweeping micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Microchem J 89:72–76
Liu Z, Ogejo JA, Pruden A, Knowlton KF (2011) Occurrence, fate and removal of synthetic oral contraceptives (SOCs) in the natural environment: A review. Sci Total Environ 409:5149–5161
Pérez RA, Albero B, Tadeo JL (2014) Analysis of steroid hormones in water using palmitate-coated magnetite nanoparticles solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Chromatographia 77:837–843
Pérez RL, Escandar GM (2014) Liquid chromatography with diode array detection and multivariate curve resolution for the selective and sensitive quantification of estrogens in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 835:19–28
Ripollés C, Ibáñez M, Sancho JV, López FJ, Hernández F (2014) Determination of 17b-estradiol and 17a-ethinylestradiol in water at sub-ppt levels by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 6:5028–5037
Ronan JM, McHugh B (2013) A sensitive liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of natural and synthetic steroid estrogens in seawater and marine biota, with a focus on proposed Water Framework Directive Environmental Quality Standards. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 27:738–746
Su R, Wang X, Xu X, Wang Z, Li D, Zhao X, Li X, Zhang H, Yu A (2011) Application of multiwall carbon nanotubes-based matrix solid phase dispersion extraction for determination of hormones in butter by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1218:5047–5054
Terzic S, Senta I, Ahel M, Gros M, Petrovic M, Barcelo D, Müller J, Knepper T, Martí I, Ventura F, Jovancic P, Jabucar D (2008) Occurrence and fate of emerging wastewater contaminants in Western Balkan Region. Sci Total Environ 399:66–77
Tölgyesi Á, Verebey Z, Sharma VK, Kovacsics L, Fekete J (2010) Simultaneous determination of corticosteroids, androgens, and progesterone in river water by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 78:972–979
Tylingo KK, Namiesnik J, Górecki T (2010) Determination of estrogenic endocrine disruptors in environmental samples-A Review of chromatographic methods. Crit Rev Anal Chem 40:194–201
Zha JM, Sun LW, Zhou YQ, Spear PA, Ma M, Wang ZJ (2008) Assessment of 17α-ethinylestradiol effects and underlying mechanisms in a continuous, multigeneration exposure of the Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 226:298–308
Zhang H-C, Yu X-j, Yang W-c, Peng J-f XT, Yin D-Q, Hu X-l (2011) MCX based solid phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of 31 endocrine-disrupting compounds in surface water of Shanghai. J Chromatogr B 879:2998–3004
Zhou L, Pan S, Chen X, Zhao Y, Zou B, Jin M (2014) Kinetics and hermodynamics studies of pentachlorophenol adsorption on covalently functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2-MWCNTs core–shell magnetic microspheres. Chem Eng J 257:10–19
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21377114), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (No. LY12H26003, LY13B050003, LY14B040006), the Medical Health Foundation for Key Talents in Zhejiang Province, China (No.2013KYA187), Ningbo Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2013A610242 and No. 2014A610283), Ningbo Medical Technology Foundation (No. 2013A24), the Science and Technology Foundation for Benefit people of Ningbo (No. 2015C50041), the Zhejiang Provincial Analytical Foundation of China (No. 2014C37037), and Zhejiang Provincial Program for the Cultivation of High-Level Innovative Health Talents for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, YG., Zhang, Y., Zhan, PP. et al. Fast determination of 24 steroid hormones in river water using magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 1529–1539 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5399-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5399-1