Abstract
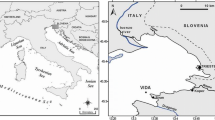
Mercury (Hg) mobility at the sediment–water interface was investigated during a laboratory incubation experiment conducted with highly contaminated sediments (13 μg g-1) of the Gulf of Trieste. Undisturbed sediment was collected in front of the Isonzo River mouth, which inflows Hg-rich suspended material originating from the Idrija (NW Slovenia) mining district. Since hypoxic and anoxic conditions at the bottom are frequently observed and can influence the Hg biogeochemical behavior, a redox oscillation was simulated in the laboratory, at in situ temperature, using a dark flux chamber. Temporal variations of several parameters were monitored simultaneously: dissolved Hg (DHg) and methylmercury (MeHg), O2, NH4 +, NO3 - + NO2 -, PO4 3-, H2S, dissolved Mn2+, dissolved inorganic and organic carbon (DIC and DOC). Under anoxic conditions, both Hg (665 ng m2 day-1) and MeHg (550 ng m2 day-1) fluxed from sediments into the water column, whereas re-oxygenation caused concentrations of MeHg and Hg to rapidly drop, probably due to re-adsorption onto Fe/Mn-oxyhydroxides and enhanced demethylation processes. Hence, during anoxic events, sediments of the Gulf of Trieste may be considered as an important source of DHg species for the water column. On the contrary, re-oxygenation of the bottom compartment mitigates Hg and MeHg release from the sediment, thus acting as a natural “defence” from possible interaction between the metal and the aquatic organisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belias C, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2007) Study of the N, P and Si fluxes between fish farm sediment and seawater. Results of simulation experiments employing a benthic chamber under various redox conditions. Mar Chem 103:266–275
Benoit JM, Gilmour CC, Mason RP, Heyes A (1999) Sulphide controls on mercury speciation and the bioavailability in sediment porewaters. Environ Sci Technol 33:951–957
Benoit JM, Mason RP, Gilmour CC, Aiken GR (2001) Constants for mercury binding by dissolved organic matter isolates from the Florida Everglades. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:4445–4451
Biester H, Gosar M, Covelli S (2000) Mercury speciation in sediments affected by dumped mining residues in the drainage area of the Idrija mercury mine. Environ Sci Technol 34:3330–3336
Bloom N, Fitzgerald WF (1989) Determination of volatile mercury species at the picogram level by low-temperature gas chromatography with cold-vapour atomic fluorescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 208:151–161
Bloom NS, Gill GA, Cappellino S, Dobbs C, McShea L, Driscoll C, Mason R, Rudd J (1999) Speciation and cycling of mercury in Lavaca Bay, Texas, sediments. Environ Sci Technol 33:7–13
Bloom NS, Preus E, Katon J, Hiltner M (2003) Selective extractions to assess the biogeochemically relevant fractionation of inorganic mercury in sediments and soils. Anal Chim Acta 479:233–248
Bouchet S, Bridou R, Tessier E, Rodriguez-Gonzalez P, Monperrus M, Abril G, Amouroux D (2011) An experimental approach to investigate mercury species transformations under redox oscillations in coastal sediments. Mar Environ Res 71:1–9
Canfield DE, Kristensen E, Thamdrup B (2005) Aquatic geomicrobiology. Adv Mar Biol 48:1–599
Cantoni C, Cozzi S, Pecchiar I, Cabrini M, Mozetič P, Catalano G, Fonda Umani S (2003) Short-term variability of primary production and inorganic nitrogen uptake related to the environmental conditions in a shallow coastal area (Gulf of Trieste, N Adriatic Sea). Oceanol Acta 26:565–575
Clarkson TW (1998) Human toxicology of mercury. J Trace Elem Exp Med 11:303–317
Comici C, Bussani A (2007) Analysis of the Isonzo River discharge (1998–2005). Boll Geof Teor Appl 48:435–454
Compeau G, Bartha R (1985) Sulphate-reducing bacteria: principal methylators of mercury in anoxic estuarine sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 50:498–502
Covelli S, Faganeli J, Horvat M, Brambati A (1999) Porewater distribution and benthic fluxes measurements of mercury and methylmercury in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 48:415–428
Covelli S, Faganeli J, Horvat M, Brambati A (2001) Mercury contamination of coastal sediments as the result of long-term cinnabar activity (Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic Sea). Appl Geochem 16:541–558
Covelli S, Piani R, Kotnik J, Horvat M, Faganeli J, Brambati A (2006) Behaviour of Hg species in a microtidal deltaic system: the Isonzo River mouth (northern Adriatic Sea). Sci Total Environ 368:210–223
Covelli S, Piani R, Acquavita A, Predonzani S, Faganeli J (2007) Transport and dispersion of particulate Hg associated to a river plume in coastal Northern Adriatic environments. Mar Pollut Bull 55:436–450
Covelli S, Faganeli J, De Vittor C, Predonzani S, Acquavita A, Horvat M (2008) Benthic fluxes of mercury species in a lagoon environment (Grado lagoon, Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Appl Geochem 23:529–546
Emili A, Koron N, Covelli S, Faganeli J, Acquavita A, Predonzani S, De Vittor C (2011) Does anoxia affect mercury cycling at the sediment–water interface in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea)? Incubation experiments using benthic flux chambers. Appl Geochem 26:194–204
EPA (1998) Method 1630. Methylmercury in water by distillation, aqueous ethylation, purge and trap, and CVAFS. Draft. March 1998
Faganeli J, Avčin A, Fanuko N, Malej A, Turk V, Tušnik P, Vrišer B, Vukovič A (1985) Bottom layer anoxia in the central part of the Gulf of Trieste in the late summer of 1983. Mar Pollut Bull 16(2):75–78
Faganeli J, Pezdic J, Ogorelec B, Herndl GJ, Dolenec T (1991) The role of sedimentary biogeochemistry in the formation of hypoxia in shallow coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic). In: Tyson RV and Pearson TH (eds) Modern and ancient continental shelf anoxia. Geological Society, London, Spec. Publ. 58, pp 107–117
Faganeli J, Horvat M, Covelli S, Fajon V, Logar M, Lipej L, Cermelj B (2003) Mercury and methylmercury in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Sci Total Environ 304:315–326
Fitzgerald WF, Lamborg CH, Hammerschmidt CR (2007) Marine biogeochemical cycling of mercury. Chem Rev 107:641–662
Froelich PN, Klinkhammer GP, Bender ML, Luedtke NA, Heath GR, Cullen D, Dauphin P, Hammond D, Hartman B, Maynard V (1979) Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43:1075–1090
Gagnon C, Pelletier M, Mucci A (1997) Behaviour of anthropogenic mercury in coastal marine sediments. Mar Chem 59:159–176
Gilmour CC, Henry EA (1991) Mercury methylation in aquatic systems affected by acid deposition. Environ Pollut 71:131–169
Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (1983) Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Weinheim, Verlag Chemie
Hines ME, Horvat M, Faganeli J, Bonzongo JCJ, Barkay T, Major EB, Scott KJ, Bailey EA, Warwick JJ, Lyons WB (2000) Mercury biogeochemistry in the Idrija River, Slovenia, from above the mine into the Gulf of Trieste. Environ Res 83:129–139
Hines ME, Faganeli J, Adatto I, Horvat M (2006) Microbial Mercury transformations in marine, estuarine and freshwater sediment downstream of the Idrija Mercury Mine, Slovenia. Appl Geochem 21:1924–1939
Hissler C, Probst JL, Mortatti J (2006) Annual inorganic mercury speciation in river water disturbed by chlor-alkali effluents: role and competition of ligands (Cl-, Br-, DOC). Geochim Bras 20:133–147
Horvat M, Miklavčič V, Pihlar B (1991) Determination of total mercury in coal fly ash by gold amalgamation cold vapour atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 243:71–79
Horvat M, Bloom NS, Liang L (1993) Comparison of distillation with other current isolation methods for the determination of methyl mercury compounds in low level environmental samples: Part II. Water. Anal Chim Acta 282:153–168
Horvat M, Covelli S, Faganeli J, Logar M, Mandic V, Rajar R, Sirca A, Zagar D (1999) Mercury in contaminated coastal environments; a case study: the Gulf of Trieste. Sci Total Environ 237(238):43–56
Huerta-Diaz MA, Morse JW (1992) Pyritization of trace metals in anoxic marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:2681–2702
Jonsson S, Skyllberg U, Nilsson MB, Westlund P, Shchukarev A, Lundberg E, Björn E (2012) Mercury Methylation Rates for Geochemically Relevant Hg(II) Species in Sediments. Environ Sci Technol 46:11653–11659
Kemp M, Faganeli J, Puskaric S, Smith EM, Boynton WR (1999) Pelagic–benthic coupling and nutrient cycling. In: Malone TC et al (eds) Ecosystems at the land–sea margin: drainage basin to coastal sea. AGU, Washington DC, USA, pp 295–339
Koron N, Faganeli J (2012) Benthic fluxes of mercury during redox changes in pristine coastal marine sediments from the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). J Soils Sediments 12:1604–1614
Malej A, Mozetic P, Malacic V, Terzic S, Ahel M (1995) Phytoplankton responses to freshwater inputs in a small semi-enclosed gulf (Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 120:111–121
Mason R, Kim E-H, Cornwell J, Heyes D (2006) An examination of the factors influencing the flux of mercury, methylmercury and other constituents from estuarine sediment. Mar Chem 102:96–110
Merritt KA, Amirbahman A (2009) Mercury methylation dynamics in estuarine and coastal marine environments—a critical review. Earth Sci Rev 96:54–66
Muresan B, Cossa D, Jezequel D, Prevot F, Kerbellec S (2007) The biogeochemistry of mercury at the sediment–water interface in the Thau Lagoon: 1. Partition and speciation. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 72:472–484
Ogrinc N, Faganeli J (2006) Phosphorus regeneration and burial in near-shore marine sediments (the Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 67:579–588
Shi J, Liang L, Jiang G, Jin X (2005) The speciation and bioavailability of mercury in sediments of Haihe River, China. Environ Int 31:357–365
Stravisi F (1983) The vertical structure annual cycle of the mass field parameters in the Gulf of Trieste. Boll Oceanol Teor Appl 1:239–250
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Michele Giani and Cinzia De Vittor of OGS Trieste for H2S and DIC analyses, Daniela Berto of ISPRA Chioggia for DOC analyses, and Brenda Lasorsa of Battelle Marine Sciences Laboratory Sequim, WA for DMeHg analyses. Luis Carrasco kindly acknowledges a predoctoral fellowship (programa I3P) from the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC, Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vera Slaveykova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emili, A., Carrasco, L., Acquavita, A. et al. A laboratory-incubated redox oscillation experiment to investigate Hg fluxes from highly contaminated coastal marine sediments (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 4124–4133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2225-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2225-5