Abstract
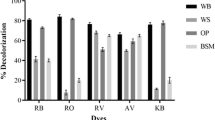
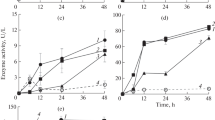
Bioremediation of textile dyestuffs under solid-state fermentation (SSF) using industrial wastes as substrate pose an economically feasible, promising, and eco-friendly alternative. The purpose of this study was to adsorb Red M5B dye, a sample of dyes mixture and a real textile effluent on distillery industry waste-yeast biomass (DIW-YB) and its further bioremediation using Bacillus cereus EBT1 under SSF. Textile dyestuffs were allowed to adsorb on DIW-YB. DIW-YB adsorbed dyestuffs were decolorized under SSF by using B. cereus. Enzyme analysis was carried out to ensure decolorization of Red M5B. Metabolites after dye degradation were analyzed using UV–Vis spectroscopy, FTIR, HPLC, and GC-MS. DIW-YB showed adsorption of Red M5B, dyes mixture and a textile wastewater sample up to 87, 70, and 81 %, respectively. DIW-YB adsorbed Red M5B was decolorized up to 98 % by B. cereus in 36 h. Whereas B. cereus could effectively reduce American Dye Manufacture Institute value from DIW-YB adsorbed mixture of textile dyes and textile wastewater up to 70 and 100 %, respectively. Induction of extracellular enzymes such as laccase and azoreductase suggests their involvement in dye degradation. Repeated utilization of DIW-YB showed consistent adsorption and ADMI removal from textile wastewater up to seven cycles. HPLC and FTIR analysis confirms the biodegradation of Red M5B. GC-MS analysis revealed the formation of new metabolites. B. cereus has potential to bioremediate adsorbed textile dyestuffs on DIW-YB. B. cereus along with DIW-YB showed enhanced decolorization performance in tray bioreactor which suggests its potential for large-scale treatment procedures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu Z (2003) Reactive dye bioaccumulation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in submerged fermentation conditions. Process Biochem 38:1437–1444
Ali I, Gupta VK (2007) Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat Protoc 1:2661–2667
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Bhatnagar A, Sillanpaa M (2010) Utilization of agro-industrial and municipal waste materials as potential adsorbents for water treatment—a review. Chem Eng J 157:277–296
Chen H, Hopper S, Cerniglia C (2005) Biochemical and molecular characterization of an azoreductase from Staphylococcus aureus, a tetrameric NADPH-dependent flavoprotein. Soc Gen Microbiol 151:1433–1441
Dawkar VV, Jadhav UU, Jadhav SU, Govindwar SP (2008) Biodegradation of disperse textile dye Brown 3REL by newly isolated Bacillus sp. VUS. J Appl Microbiol 105:14–24
Duckworth HW, Coleman JE (1970) Physicochemical and kinetic properties of mushroom tyrosinase. J Biol Chem 245:1613–1625
Göksungur Y, Üren S, Güvenç U (2005) Biosorption of cadmium and lead ions by ethanol treated waste baker’s yeast biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:103–109
Gupta VK, Ali I (2008) Removal of endosulfan and methoxychlor from water on carbon slurry. Environ Sci Technol 42:766–770
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008a) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium (II) biosorption by nonliving algal biomass Oedogonium sp. from aqueous phase. J Hazard Mater 153:759–766
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008b) Sorption and desorption studies of chromium (VI) from nonviable cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum biomass. J Hazard Mater 154:347–354
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by raw and acid-treated green alga Oedogonium hatei from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 163:396–402
Gupta VK, Sharma S (2003) Removal of zinc from aqueous solutions using bagasse fly ash—a low cost adsorbent. Ind Eng Chem Res 42:6619–6624
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Dwivedi MK, Mohan D (1997) Process development for the removal of zinc and cadmium from wastewater using slag—a blast furnace waste material. Sep Sci Technol 32:2883–2912
Gupta VK, Mohan D, Sharma S (1998) Removal of lead from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste material. Sep Sci Technol 33:1331–1343
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Gajbe V, Mittal J (2006a) Removal and recovery of the hazardous azo dye acid orange 7 through adsorption over waste materials: bottom ash and de-oiled soya. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:1446–1453
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Jain R, Mathur M, Sikarwar S (2006b) Adsorption of safranin-T from wastewater using waste materials- activated carbon and activated rice husks. J Colloid Interface Sci 303:80–86
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Kurup L, Mittal J (2006c) Adsorption of a hazardous dye, erythrosine, over hen feathers. J Colloid Interface Sci 304:52–57
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Krishnan L, Mittal J (2006d) Adsorption treatment and recovery of the hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, over bottom ash and de-oiled soya. J Colloid Interface Sci 293:16–26
Gupta VK, Jain R, Mittal A, Mathur M, Sikarwar S (2007a) Photochemical degradation of the hazardous dye Safranin-T using TiO2 catalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 154:347–354
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007b) Electrochemical removal of the hazardous dye Reactofix Red 3 BFN from industrial effluents. J Colloid Interface Sci 312:292–296
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007c) Adsorption studies on the removal of Vertigo Blue 49 and Orange DNA13 from aqueous solutions using carbon slurry developed from a waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 315:87–93
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007d) Removal of Reactofix golden yellow 3 RFN from aqueous solution using wheat husk-An agricultural waste. J Hazard Mater 142:443–448
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007e) Defluoridation of wastewaters using waste carbon slurry. Water Res 41:3307–3316
Gupta VK, Goyal RN, Sharma RA (2009a) Novel PVC membrane based alizarin sensor and its application; determination of vanadium, zirconium and molybdenum. Int J Electrochem Sci 4:156–172
Gupta VK, Carrott PJM, Ribeiro Carrott MML (2009b) Low-cost adsorbents: growing approach to wastewater treatment—a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 9:783–842
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Malviya A, Mittal J (2009c) Adsorption of carmoisine A from wastewater using waste materials—bottom ash and deoiled soya. J Colloid Interface Sci 335:24–33
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Nayak A (2010) Adsorption studies on the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using a low cost fertilizer industry waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 342:135–141
Hu T (1994) Decolorization of reactive azo dyes by transformation with Pseudomonas luteola. Bioresour Technol 49:47–51
Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP (2006) Biotransformation of Malachite green by Saccharomyces cerevisiae MTCC 463. Yeast 23:315–323
Jain AK, Gupta VK, Sahoo BB, Singh LP (1995) Copper(II)-selective electrodes based on macrocyclic compounds. Anal Proc 32:99–101
Jain AK, Gupta VK, Khurana U, Singh LP (1997) A new membrane sensor for UO2+ 2 ions based on 2-hydroxyacetophenoneoxime-thiourea-trioxane resin. Electroanalysis 9:857–860
Kadam A, Telke AA, Jagtap SS, Govindwar SP (2011) Decolorization of adsorbed textile dyes by developed consortium of Pseudomonas sp. SUK1 and Aspergillus ochraceus under solid state fermentation. J Hazard Mater 189:486–494
Kumar A (2006) Industrial pollution: problems and solutions. Daya, New Delhi
Kumar A, Bohra CP, Singh LK (2003) Environment, pollution and management. A.P.H., New Delhi
Kurade MB, Waghmode TR, Govindwar SP (2011) Preferential biodegradation of structurally dissimilar dyes from a mixture by Brevibacillus laterosporus. J Hazard Mater 192:1746–1755
Laasri L, Elamrani MK, Cherkaoui O (2007) Removal of two cationic dyes from a textile effluent by filtration adsorption on wood sawdust. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14:237–240
Landolo D, Amore A, Birola L, Leo G, Olivieri G, Faraco V (2011) Fungal solid state fermentation on agro-industrial waste for acid wastewater decolorization in a continuous flow packed-bed bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 102:7603–7607
Mittal A (2006) Removal of the dye, Amaranth from waste water using hen feathers as potential adsorbent. Electron J Environ Agr Food Chem 5:1296–1305
Mittal A, Gupta VK (2010) Adsorptive removal and recovery of the azo dye Eriochrome Black T. Toxicol Environ 92:1813–1823
Mittal A, Kurup L (2006) Column operations for the removal and recovery of a hazardous dye ’Acid Red - 27′ from aqueous solutions, using waste materials—bottom ash and de-oiled soya. Ecol Environ Conserv 12:181–186
Mittal A, Mittal J, Kurup-Krishnan L (2007) Utilization of hen feathers for the adsorption of indigo carmine from simulated effluents. J Environ Prot Sci 1:92–100
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2009a) Adsorptive removal of hazardous anionic dye “Congo red” from wastewater using waste materials and recovery by desorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 340:16–26
Mittal A, Kaur D, Mittal J (2009b) Batch and bulk removal of a triarylmethane dye, Fast Green FCF, from wastewater by adsorption over waste materials. J Hazard Mater 163:568–577
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2010a) Removal and recovery of Chrysoidine Y from aqueous solutions by waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:497–507
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Kaur D, Gupta VK (2010b) Decoloration treatment of a hazardous triarylmethane dye, Light Green SF (Yellowish) by waste material adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 342:518–527
Mittal A, Jain R, Mittal J, Varshney S, Sikarwar S (2010c) Removal of Yellow ME 7 GL from industrial effluent using electrochemical and adsorption techniques. Int J Environ Pollut 43:308–323
Mittal A, Jain R, Mittal J (2010d) Adsorptive removal of hazardous dye Quinoline Yellow from wastewater using coconut-husk as potential adsorbent. Fresenius Environ Bull 19:1–9
Mittal A, Thakur V, Gajbe V (2012a) Evaluation of adsorption characteristics of an anionic azo dye Brilliant Yellow onto hen feathers in aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0756-9
Mittal A, Thakur V, Gajb V (2012b) Adsorptive removal of toxic azo dye Amido Black 10B by hen feather. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0843-y
Murugesan K, Nam I, Kim Y, Chang Y (2007) Decolorization of reactive dyes by a thermostable laccase produced by Ganoderma lucidum in solid state culture. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1662–1672
Nigam P, MeMullun GM, Banat IM, Merchant R (1996) Decolorization of effluent from textile industry by a microbial consortium. Biotechnol Lett 18:117–120
Nilsson R, Nordlinder R, Wass U (1993) Asthma, rhinitis, and dermatitis in workers exposed to reactive dyes. Brit J Ind Med 50:65–70
Pandey A (2003) Solid state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 13:81–84
Papinutti L, Mouso N, Forchiassin F (2006) Removal and degradation of the fungicide dye malachite green from aqueous solution using the system wheat bran–Fomes sclerodermeus. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:848–853
Phugare SS, Patil PS, Govindwar SP, Jadhav JP (2010) Exploitation of yeast biomass generated as a waste product of distillery industry for remediation of textile industry effluent. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 64:716–726
Phugare SS, Kagalkar AN, Govindwar SP, Jadhav JP (2011) A study on significant microbial interaction leading to decolorization and degradation of textile dye Rubine 3GP. J Basic Microbiol 51:499–514
Polman JK, Breckenridge CR (1996) Biomass-mediated binding and recovery of textile dyes from waste effluents. Text Chem Color 28:31–35
Riordan C, Bustard M, Putt R, McHale AP (1997) Removal of uranium from solution using residual brewery yeast: combined biosorption and precipitation. Biotechnol Lett 19:4385–4388
Robinson T, Nigam P (2008) Remediation of textile dye waste water using a white-rot fungus Bjerkandera adusta through solid-state fermentation (SSF). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 151:618–628
Robinson T, McMullan GR, Marchant NP (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol 77:247–255
Salokhe MD, Govindwar SP (1999) Effect of carbon source on the biotransformation enzymes in Serratia marcescens. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 15:229–232
Santhy K, Selvapathy P (2006) Removal of reactive dyes 6from wastewater by adsorption on coir pith activated carbon. Bioresour Technol 97:1329–1336
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Chang JS, Govindwar SP (2009) Decolorization and biodegradation of textile dye Navy blue HER by Trichosporon beigelii NCIM-3326. J Hazard Mater 166:1421–1428
Senan RC, Abraham TE (2004) Bioremediation of textile azo dyes by aerobic bacterial, consortium. Biodegradation 15:275–280
Srivastava SK, Gupta VK, Dwivedi MK, Jain S (1995) Caesium PVC-crown (dibenzo-24-crown-8) based membrane sensor. Anal Proc 32:21–23
Telke AA, Joshi SM, Jadhav SU, Tamboli DP, Govindwar SP (2009) Decolorization and detoxification of Congo red and textile industry effluent by an isolated bacterium Pseudomonas sp. SU-EBT. Biodegradation 2:283–296
Telke AA, Kadam AA, Jagtap SS, Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP (2010) Biochemical characterization and potential for textile dye degradation of blue laccase from Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 15:696–703
Zhang F, Yediler A, Liang X, Kettrup A (2004) Effects of dye additives on the ozonation process and oxidation by-products: a comparative study using hydrolyzed CI Reactive red 120. Dyes Pigments 60:1–7
Acknowledgments
The author Avinash A. Kadam is thankful to Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi for providing the DST-PURSE fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vinod Kumar Gupta
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadam, A.A., Kamatkar, J.D., Khandare, R.V. et al. Solid-state fermentation: tool for bioremediation of adsorbed textile dyestuff on distillery industry waste-yeast biomass using isolated Bacillus cereus strain EBT1. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 1009–1020 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0929-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0929-6