Abstract
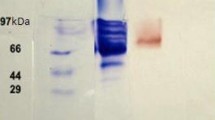
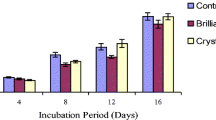
In our study, we produced intracellular blue laccase by growing the filamentous fungus Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146 in potato dextrose broth. The enzyme was then purified 22-fold to a specific activity of 4.81 U/mg using anion-exchange and size exclusion chromatography. The molecular weight of purified laccase was estimated as 68 kDa using sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The enzyme showed maximum substrate specificity toward 2,2′-Azinobis, 3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid than any other substrate. The optimum pH and temperature for laccase activity were 4.0 and 60°C, respectively. The purified enzyme was stable up to 50°C, and high laccase activity was maintained at pH 5.0 ∼ 7.0. Laccase activity was strongly inhibited by sodium azide, EDTA, dithiothreitol, and L-cysteine. Purified laccase decolorized various textile dyes within 4 h in the absence of redox mediators. HPLC and FTIR analysis confirmed degradation of methyl orange. The metabolite formed after decolorization of methyl orange was characterized as p-N,N′-dimethylamine phenyldiazine using GCMS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalyani, D. C., P. S. Patil, J. P. Jadhav, and S. P. Govindwar (2008) Biodegradation of reactive textile dye Red BLI by an isolated bacterium Pseudomonas sp. SUK1. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 4635–4641.
Cameron, M., S. Timofeevski, and S. Aust (2000) Mini-review: Enzymology of Phanerochaete chrysosporium with respect to the degradation of recalcitrant compounds and xenobiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54: 751–758.
Assadi, M. M. and M. R. Jahangiri (2001) Textile wastewater treatment by Aspergillus niger. Desalination 141: 1–6.
Sharma, P., L. Singh, and N. Dilbaghi (2009) Response surface methodological approach for the decolorization of simulated dye effluent using Aspergillus fumigatus fresenius. J. Hazard. Mater. 161: 1081–1086.
Corso, C. R. and A. C. M. Almeida (2009) Bioremediation of dyes in textile effluents by Aspergillus oryzae. Microb. Ecol. 57: 384–390.
Khelifi, E., L. Ayed, H. Bouallagui, Y. Touhami, and M. Hamdi (2009) Effect of nitrogen and carbon sources on Indigo and Congo red decolorization by Aspergillus alliaceus strain 121C. J. Hazard. Mater. 163: 1056–1062.
Saratale, G. D., S. D. Kalme, and S. P. Govindwar (2006) Decolorization of textile dyes by Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. Ind. J. Biotechnol. 5: 407–410.
Sharma, P., R. Goel, and N. Capalash (2007) Bacterial laccases. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 23: 823–832.
Claus, H. (2003) Laccases and their occurrence in prokaryotes. Arch. Microbiol. 179: 145–150.
Messerschmidt, A. and R. Huber (1990) The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships. Eur. J. Biochem. 187: 341–352.
Telke, A. A., D. C. Kalyani, U. U. Jadhav, G. K. Parshetti, and S. P. Govindwar (2009) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from a Pseudomonas sp. LBC1 and its application for the removal of bisphenol A. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzymatic 61: 252–260.
Kawai, S., T. Umezawa, and T. Higuchi (1988) Degradation mechanisms of phenolic β-1 lignin substructure model compounds by laccase of Coriolus versicolor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 262: 99–110.
Wesenberg, D., I. Kyriakides, and S. Agathos (2003) White-rot fungi and their enzymes for the treatment of industrial dye effluents. Biotechnol. Advan. 22: 161–187.
Claus, H. (2004) Laccases: Structure, reactions, distribution. Micron 35: 93–96.
Palonen, H. and L. Viikari (2004) Role of oxidative enzymatic treatments on enzymatic hydrolysis of softwood. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 86: 550–557.
Murugesan, K., A. Dhamija, I. Nam, Y. Kim, and Y. Chang (2007) Decolorization of Reactive black 5 by laccase: Optimization by response surface methodology. Dyes Pigments. 75: 176–184.
Baldrian, P. (2006) Fungal laccases-occurrence and properties. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30: 215–242.
Kurtz, M. and S. Champe (1982) Purification and characterization of the Conidial Laccase of Aspergillus nidulans. J. Bacteriol. 151: 1338–1345.
Scherer, M. and R. Fischer (1998) Purification and characterization of laccase II of Aspergillus nidulans. Arch. Microbiol. 170: 78–84.
Parshetti, G. K., S. D. Kalme, S. S. Gomare, and S. P. Govindwar (2007) Biodegradation of Reactive blue-25 by Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. Bioresour. Technol. 98: 3638–3642.
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. L. Randall (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275.
Eisenman, H., M. Mues, S. Weber, S. Frases, S. Chaskes, G. Gerfen, and A. Casadevall (2007) Cryptococcus neoformans laccase catalyses melanin synthesis from both D- and L-DOPA. Microbiol. 153: 3954–3962.
Nagai, M., T. Sato, H. Watanabe, K. Saito, M. Kawata, and H. Enei (2002) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes and decolorization of chemically different dyes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 60: 327–335.
Blaich, R. and K. Esser (1975) Function of enzymes in wood destroying fungi. Arch. Microbiol. 103: 271–277.
Ko, E. M., Y. E. Leem, and H. T. Choi (2001) Purification, and characterization of laccase isozymes from the white-rot basidiomycete Ganoderma lucidum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57: 98–102.
Sadhasivam, S., S. Savitha, K. Swaminathan, and F. Lin (2008) Production, purification and characterization of mid-redox potential laccase from a newly isolated Trichoderma harzianum WL1. Proc. Biochem. 43: 736–742.
Minussi, R. C., G. M. Pastorea, and N. Durán (2007) Laccase induction in fungi and laccase/N-OH mediator systems applied in paper mill effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 98: 158–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Telke, A.A., Kadam, A.A., Jagtap, S.S. et al. Biochemical characterization and potential for textile dye degradation of blue laccase from Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15, 696–703 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3126-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3126-9