Abstract
Purpose
[18F]-FEPPA is a translocator protein (18 kDa, TSPO) positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer. Radiation dosimetry was estimated from the whole body biodistribution, taking into consideration TSPO rs6971 (Ala147Thr) polymorphism.
Procedures
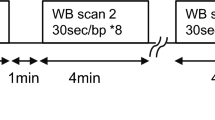
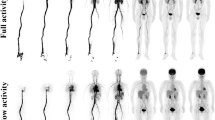
[18F]-FEPPA whole body PET scans were acquired for six healthy subjects. Time–activity curves were generated from regions of interest of nine organs, from which normalized accumulated activities were calculated and thus internal dose, using OLINDA/EXM 1.1. Genotyping of rs6971, associated with high- and low-affinity [18F]-FEPPA binding (high-affinity binder (HAB) and low-affinity binder (LAB)), was performed.
Results
Five subjects exhibited the C/C (HAB) allele, and the other carried the minor allele T/T (LAB). The LAB whole body biodistribution showed highest radioactivity accumulation in bladder, whereas in HABs, the spleen received the highest dose. The effective dose of the single LAB (16.3 μSv/MBq) was 23 % less than the mean of the HABs (21.0 ± 2.9 μSv/MBq). When including all subjects, the effective dose was 20.2 ± 3.0 μSv/MBq.
Conclusions
[18F]-FEPPA radiation dose is consistent with other 18F-labeled radioligands and the Ala147Thr genotype agreed with [18F]-FEPPA distribution.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braestrup C, Albrechtsen R, Squires RF (1977) High densities of benzodiazepine receptors in human cortical areas. Nature 269:702–704
Venneti S, Wiley C, Kofler J (2009) Imaging microglial activation during neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmune Pharm 4:227–243
Anholt RR, Pedersen PL, De Souza EB, Snyder SH (1986) The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. Localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem 261:576–583
Chen MK, Guilarte TR (2008) Translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO): molecular sensor of brain injury and repair. Pharmacol Ther 118:1–17
Debruyne JC, Versijpt J, Van Laere KJ et al (2003) PET visualization of microglia in multiple sclerosis patients using [11C]-PK11195. Eur J Neurol 10:257–264
Hammoud DA, Endres CJ, Chander AR et al (2005) Imaging glial cell activation with [11C]-R-PK11195 in patients with AIDS. J Neurovirol 11:346–355
Yasuno F, Ota M, Kosaka J et al (2008) Increased binding of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease measured by positron emission tomography with [11C]DAA1106. Biol Psychiatry 64:835–841
Cagnin A, Myers R, Gunn RN et al (2001) In vivo visualization of activated glia by [11C] (R)-PK11195-PET following herpes encephalitis reveals projected neuronal damage beyond the primary focal lesion. Brain 124:2014–2027
Gerhard A, Pavese N, Hotton G et al (2006) In vivo imaging of microglial activation with [11C](R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 21:404–412
Turner MR, Cagnin A, Turkheimer FE et al (2004) Evidence of widespread cerebral microglial activation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Neurobiol Dis 15:601–609
Gerhard A, Neumaier B, Elitok E et al (2000) In vivo imaging of activated microglia using [11C]PK11195 and positron emission tomography in patients after ischemic stroke. Neuroreport 11:2957–2960
Venneti S, Lopresti BJ, Wiley CA (2006) The peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (translocator protein 18 kDa) in microglia: from pathology to imaging. Prog Neurobiol 80:308–322
Yota F, Paul MH, Hugh T III et al (2008) Increased peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in arterial plaque of patients with atherosclerosis: an autoradiographic study with [3H]PK 11195. Atherosclerosis 201:108–111
Camsonne R, Crouzel C, Comar D et al (1984) Synthesis of N-(11C)Methyl, N-(methyl-1-propyl), (chloro-2-phenyl)-1-isoquinoleine carboxamide-3 (PK-11195): a new ligand for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 21:985–991
James ML, Selleri S, Kassiou M (2006) Development of ligands for the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Curr Med Chem 13:1991–2001
Okubo T, Yoshikawa R, Chaki S, Okuyama S, Nakazato A (2004) Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of novel tetracyclic compounds as peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Bioorg Med Chem 12:3569–3580
Fujita M, Imaizumi M, Zoghbi SS et al (2008) Kinetic analysis in healthy humans of a novel positron emission tomography radioligand to image the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor, a potential biomarker for inflammation. Neuroimage 40:43–52
Boutin H, Chauveau F, Thominiaux C et al (2007) [11C]-DPA-713: a novel peripheral benzodiazepine receptor PET ligand for in vivo imaging of neuroinflammation. J Nucl Med 48:573–581
Wilson AA, Garcia A, Parkes J et al (2008) Radiosynthesis and initial evaluation of [18F]-FEPPA for PET imaging of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Nucl Med Biol 35:305–314
Rusjan PM, Wilson AA, Bloomfield PM et al (2011) Quantitation of translocator protein binding in human brain with the novel radioligand [18F]-FEPPA and positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1807–1816
Owen DR, Yeo AJ, Gunn RN et al (2012) An 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1–5
Owen DR, Gunn RN, Rabiner EA et al (2011) Mixed-affinity binding in humans with 18-kDa translocator protein ligands. J Nucl Med 52:24–32
Mizrahi R, Rusjan PM, Kennedy J, et al. (2012) Translocator protein (18 kDa) polymorphism (rs 6971) explains in-vivo brain binding affinity of the PET radioligand [18F]-FEPPA. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metabol 32:968–972
Brambilla M, Secco C, Dominietto M et al (2005) Performance characteristics obtained for a new 3-dimensional lutetium oxyorthosilicate-based whole-body PET/CT scanner with the National Electrical Manufacturers Association NU 2-2001 standard. J Nucl Med 46:2083–2091
Defrise M, Kinahan PE, Townsend DW et al (1997) Exact and approximate rebinning algorithms for 3-D PET data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16:145–158
Hudson HM, Larkin RS (1994) Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 13:601–609
Hamill J (1995) Evaluating a frequency-space SPECT reconstruction algorithm. Proc Opt Eng Midwest SPIE 2622:785–791
ICRP (2002) ICRP Publication 89: Basic anatomical and physiological data for use in radiological protection: reference values. A report of age- and gender-related differences in the anatomical and physiological characteristics of reference individuals. Ann ICRP 32:5–265
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E (2005) OLINDA/EXM: the second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 46:1023–1027
Lahiri DK, Nurnberger JI Jr (1991) A rapid non-enzymatic method for the preparation of HMW DNA from blood for RFLP studies. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5444
Brown AK, Fujita M, Fujimura Y et al (2007) Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution in monkey and man of 11C-PBR28: a PET radioligand to image inflammation. J Nucl Med 48:2072–2079
Fujimura Y, Kimura Y, Simeon FG et al (2010) Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry in humans of a new PET ligand, (18)F-PBR06, to image translocator protein (18 kDa). J Nucl Med 51:145–149
Hirvonen J, Roivainen A, Virta J et al (2010) Human biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of 11C-(R)-PK11195, the prototypic PET ligand to image inflammation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:606–612
Owen DR, Howell OW, Tang SP et al (2010) Two binding sites for [3H]PBR28 in human brain: implications for TSPO PET imaging of neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1608–1618
Takano A, Gulyas B, Varrone A et al (2011) Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) radioligand [18F]FEDAA1106: a human whole-body PET study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:2058–2065
Mejia AA, Nakamura T, Masatoshi I et al (1991) Estimation of absorbed doses in humans due to intravenous administration of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in PET studies. J Nucl Med 32:699–706
Vesselle H, Grierson J, Peterson LM et al (2003) 18F-Fluorothymidine radiation dosimetry in human PET imaging studies. J Nucl Med 44:1482–1488
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by Canada Foundation for Innovation and the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation. Dr. Mizrahi is supported by the New Investigator Award from CIHR and the Ontario Mental Health Foundation New Investigator Fellowship. We thank Armando Garcia, Winston Stableford, and Ming Wong for their excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Romina Mizrahi and Pablo M. Rusjan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizrahi, R., Rusjan, P.M., Vitcu, I. et al. Whole Body Biodistribution and Radiation Dosimetry in Humans of a New PET Ligand, [18F]-FEPPA, to Image Translocator Protein (18 kDa). Mol Imaging Biol 15, 353–359 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-012-0589-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-012-0589-4