Abstract
Introduction
Sleep plays an important role in cardiometabolic health. The sleep-wake cycle is partially driven by the endogenous circadian clock, which governs a range of metabolic pathways. The association between sleep and cardiometabolic health may be mediated by alterations of the human metabolome.
Objectives
To better understand the biological mechanism underlying the association between sleep and health, we examined human plasma metabolites in relation to sleep duration and sleep timing.
Methods
Using an untargeted approach, 329 fasting plasma metabolites were measured in 277 Chinese participants. We measured sleep timing (midpoint between bedtime and wake up time) using repeated time-use surveys (4 weeks during 1 year) and previous night sleep duration from questionnaires completed before sample donation.
Results
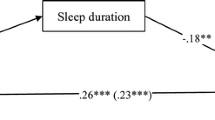
We found 64 metabolites that were associated with sleep timing with a false discovery rate of 0.2 or lower, after adjusting for potential confounders. Notably, we found that later sleep timing was associated with higher levels of multiple metabolites in amino acid metabolism, including branched chain amino acids and their gamma-glutamyl dipeptides. We also found widespread associations between sleep timing and numerous metabolites in lipid metabolism, including bile acids, carnitines and fatty acids. In contrast, previous night sleep duration was not associated with plasma metabolites in our study.
Conclusion
Sleep timing was associated with a large number of metabolites across a variety of biochemical pathways. Some metabolite associations are consistent with a relationship between late chronotype and adverse effects on cardiometabolic health.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S. H. (2011). Emerging perspectives on essential amino acid metabolism in obesity and the insulin-resistant state. Advances in Nutrition: An International Review Journal, 2(6), 445–456.
Ang, J. E., Revell, V., Mann, A., Mantele, S., Otway, D. T., Johnston, J. et al. (2012). Identification of human plasma metabolites exhibiting time-of-day variation using an untargeted liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry metabolomic approach. Chronobiology International, 29, 868–881.
Bailey, S. M., Udoh, U. S., & Young, M. E. (2014). Circadian regulation of metabolism. Journal of Endocrinology, 222, R75–R96.
Bass, J., & Takahashi, J. S. (2010). Circadian integration of metabolism and energetics. Science, 330, 1349–1354.
Batch, B. C., Hyland, K., & Svetkey, L. P. (2014). Branch chain amino acids: Biomarkers of health and disease. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 17, 86–89.
Bell, L. N., Kilkus, J. M., Booth, J. N., Bromley, L. E., 3rd, Imperial, J. G., & Penev, P. D. (2013). Effects of sleep restriction on the human plasma metabolome. Physiology and Behavior, 122, 25–31.
Brinton, E. A. (2008). Novel pathways for glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: Focus on bile acid modulation. Diabetes Obesity and Metabolism, 10, 1004–1011.
Cappuccio, F. P., Cooper, D., D’elia, L., Strazzullo, P., & Miller, M. A. (2011). Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. European Heart Journal, 32, 1484–1492.
Cappuccio, F. P., D’elia, L., Strazzullo, P., & MILLER, M. A. (2010). Quantity and quality of sleep and incidence of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care, 33, 414–420.
Dallmann, R., Viola, A. U., Tarokh, L., Cajochen, C., & Brown, S. A. (2012). The human circadian metabolome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 2625–2629.
Davies, S. K., Ang, J. E., Revell, V. L., Holmes, B., MANN, A., Robertson, F. P., et al. (2014). Effect of sleep deprivation on the human metabolome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111, 10761–10766.
Dehaven, C. D., Evans, A. M., Dai, H. P., & Lawton, K. A. (2010). Organization of GC/MS and LC/MS metabolomics data into chemical libraries. Journal of Cheminformatics, 2, 9.
Dinis-Oliveira, R. J. (2016). Oxidative and non-oxidative metabolomics of ethanol. Current Drug Metabolism, 17(4), 327–335.
Duffield, G. E., Best, J. D., Meurers, B. H., Bittner, A., Loros, J. J., & Dunlap, J. C. (2002). Circadian programs of transcriptional activation, signaling, and protein turnover revealed by microarray analysis of mammalian cells. Current Biology, 12, 551–557.
Evans, A. M., DeHaven, C. D., Barrett, T., Mitchell, M., & Milgram, E. (2009). Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Analytical Chemistry, 81(16), 6656–6667.
Farkkila, M. A., Kairemo, K. J., Taavitsainen, M. J., Strandberg, T. A., & Miettinen, T. A. (1996). Plasma lathosterol as a screening test for bile acid malabsorption due to ileal resection: Correlation with (75)SeHCAT test and faecal bile acid excretion. Clinical Science, 90, 315–319.
Ferrannini, E., Natali, A., Camastra, S., Nannipieri, M., Mari, A., Adam, K. P., et al. (2013). Early metabolic markers of the development of dysglycemia and type 2 diabetes and their physiological significance. Diabetes, 62, 1730–1737.
Gall, W. E., Beebe, K., Lawton, K. A., Adam, K. P., Mitchell, M. W., Nakhle, P. J., et al. (2010). Alpha-hydroxybutyrate is an early biomarker of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in a nondiabetic population. PLoS ONE, 5, e10883.
Gan, Y., Yang, C., Tong, X., Sun, H., Cong, Y., Yin, X., et al. (2015). Shift work and diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 72, 72–78.
Gooley, J. J., & Chua, E. C. P. (2014). Diurnal regulation of lipid metabolism and applications of circadian lipidomics. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 41(5), 231–250.
Guertin, K. A., Loftfield, E., Boca, S. M., Sampson, J. N., Moore, S. C., Xiao, Q., & Sinha, R. (2015). Serum biomarkers of habitual coffee consumption may provide insight into the mechanism underlying the association between coffee consumption and colorectal cancer. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 101(5), 1000–1011.
Guertin, K. A., Moore, S. C., Sampson, J. N., Huang, W. Y., Xiao, Q., Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. Z., et al. (2014). Metabolomics in nutritional epidemiology: Identifying metabolites associated with diet and quantifying their potential to uncover diet-disease relations in populations. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 100(1), 208-217.
Hughes, M. E., Ditacchio, L., Hayes, K. R., Vollmers, C., Pulivarthy, S., Baggs, J. E., et al. (2009). Harmonics of circadian gene transcription in mammals. PLoS Genetics, 5, e1000442.
Kantermann, T., Sung, H., & Burgess, H. J. (2015). Comparing the morningness-eveningness questionnaire and munich chronotype questionnaire to the dim light melatonin onset. Journal of Biological Rhythms, 30, 449–453.
Lynch, C. J., & Adams, S. H. (2014). Branched-chain amino acids in metabolic signalling and insulin resistance. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 10(12), 723–736.
Matthan, N. R., Zhu, L., Pencina, M., D’Agostino, R. B., Schaefer, E. J., & Lichtenstein, A. H. (2013). Sex-specific differences in the predictive value of cholesterol homeostasis markers and 10-year cardiovascular disease event rate in framingham offspring study participants. Journal of the American Heart Association, 2(1), e005066.
McCoin, C. S., Knotts, T. A., & Adams, S. H. (2015). Acylcarnitines [mdash] old actors auditioning for new roles in metabolic physiology. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 11, 617–625.
Moore, S. C., Matthews, C. E., Sampson, J. N., Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. Z., Zheng, W., Cai, Q., et al. (2014). Human metabolic correlates of body mass index. Metabolomics, 10, 259–269.
Natale, V., Plazzi, G., & Martoni, M. (2009). Actigraphy in the assessment of insomnia: A quantitative approach. Sleep, 32, 767–771.
Panda, S., Antoch, M. P., Miller, B. H., Su, A. I., Schook, A. B., Straume, M., et al. (2002). Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell, 109(3), 307–320.
Peters, T. M., Moore, S. C., Xiang, Y. B., Yang, G., Shu, X. O., Ekelund, U., et al. (2010). Accelerometer-measured physical activity in Chinese adults. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 38(6), 583–591.
Roehrs, T., & Roth, T. (2008). Caffeine: Sleep and daytime sleepiness. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 12(2), 153–162.
Roenneberg, T., Kuehnle, T., Juda, M., Kantermann, T., Allebrandt, K., Gordijn, M., et al. (2007). Epidemiology of the human circadian clock. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 11(6), 429–438.
Roenneberg, T., Wirz-Justice, A., & Merrow, M. (2003). Life between clocks: Daily temporal patterns of human chronotypes. Journal of Biological Rhythms, 18(1), 80–90.
Sampson, J. N., Boca, S. M., Shu, X. O., Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. Z., Matthews, C. E., Hsing, A. W., et al. (2013). Metabolomics in epidemiology: Sources of variability in metabolite measurements and implications. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention Biomarkers, 22(4), 631–640.
Shan, Z., Ma, H., Xie, M., Yan, P., Guo, Y., Bao, W., et al. (2015). Sleep duration and risk of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetes care, 38(3), 529–537.
Shu, X. O., Li, H., Yang, G., Gao, J., Cai, H., Takata, Y., et al. (2015). Cohort profile: The shanghai men’s health study. International Journal of Epidemiology, 44(3), 810–818.
Tom, A., & Nair, K. S. (2006). Assessment of branched-chain amino acid status and potential for biomarkers. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 324S–330S.
Van Drongelen, A., Boot, C. R., Merkus, S. L., Smid, T., & Van Der Beek, A. J. (2011). The effects of shift work on body weight change—a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment and Health, 37, 263–275.
Vyas, M. V., Garg, A. X., Iansavichus, A. V., Costella, J., Donner, A., Laugsand, L. E., et al. (2012). Shift work and vascular events: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clinical Research ed.), 345, e4800.
Wang, F., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., He, Y., Xie, S., et al. (2014). Meta-analysis on night shift work and risk of metabolic syndrome. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 71(1), A78–A78.
Weljie, A. M., Meerlo, P., Goel, N., Sengupta, A., Kayser, M. S., Abel, T., et al. (2015). Oxalic acid and diacylglycerol 36:3 are cross-species markers of sleep debt. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(8), 2569–2574.
Wittmann, M., Dinich, J., Merrow, M., & Roenneberg, T. (2006). Social jetlag: Misalignment of biological and social time. Chronobiology International, 23(1–2), 497–509.
Wong, P. M., Hasler, B. P., Kamarck, T. W., Muldoon, M. F., & Manuck, S. B. (2015). Social jetlag, chronotype, and cardiometabolic risk. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 100(12), 4612–4620.
Wu, Y., Zhai, L., & Zhang, D. (2014). Sleep duration and obesity among adults: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sleep Medicine, 15(12), 1456–1462.
Xiao, Q., Moore, S. C., Keadle, S. K., Xiang, Y. B., Zheng, W., Peters, T. M., et al. (2016). Objectively measured physical activity and plasma metabolomics in the Shanghai Physical Activity Study. International Journal of Epidemiology, 45(5), 1433-1444.
Zheng, W., Chow, W.H., Yang, G., Jin, F., Rothman, N., Blair, A., et al. (2005). The Shanghai Women’s Health Study: Rationale, study design, and baseline characteristics. American Journal of Epidemiology, 162, 1123–1131.
Zou, H., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2006). Sparse principal component analysis. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 15, 265–286.
Funding
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Department of Health and Human Services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q., Derkach, A., Moore, S.C. et al. Habitual sleep and human plasma metabolomics. Metabolomics 13, 63 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1205-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1205-z