Abstract
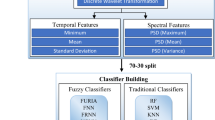
Epilepsy is a severe neurological disease which is diagnosed by analyzing Electroencephalogram. The epileptic seizure detection technique based on multiscale entropies and complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition (CEEMD) is proposed in this paper. CEEMD is used for the estimation of sub-bands and two multiscale entropies; multiscale dispersion entropy (MDE) and refined composite MDE are extracted from the sub-bands. The feature selection method, configured by hybridizing the filter based and wrapper based method, is used to select relevant multiscale entropies. The hybrid method has not only reduced features but also improved classification performance. An artificial neural network is trained with relevant features and performance is measured using classification accuracy, sensitivity and specificity. Five clinically relevant classification problems are used to assess the proposed technique. The performance is also compared with the state of the art techniques. The proposed technique has shown an improvement in detection of seizures and can be used to build the clinical system for epileptic seizure detection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epilepsy. (2017). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs999/en/. Accessed October 25, 2017.
Dastidar, S. G., Adeli, H., & Dadmehr, N. (2007). Mixed band wavelet chaos neural network methodology for epilepsy and epileptic seizure detection. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 54, 1545–1551. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2007.891945.
Motamedi, G., & Meador, K. (2003). Epilepsy and cognition. Epilepsy & Behavior, 4, 25–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2003.07.004.
Electroencephalogram. (2018). https://www.healthline.com/health/eeg. Accessed January 2, 2018.
Shoeb, A. H. (2009). Application of machine learning to epileptic seizure onset detection and treatment. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Patnaik, L. M., & Manyam, O. K. (2008). Epileptic EEG detection using neural networks and post-classification. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 91, 100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2008.02.005.
Güler, I., & Ubeyli, E. D. (2005). Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for classification of EEG signals using wavelet coefficients. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 148, 113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.04.013.
Übeyli, E. D. (2008). Wavelet/mixture of experts network structure for EEG signals classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 34, 1954–1962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.02.006.
Ocak, H. (2008). Optimal classification of epileptic seizures in EEG using wavelet analysis and genetic algorithm. Signal Processing, 88, 1858–1867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.01.026.
Ocak, H. (2009). Automatic detection of epileptic seizures in EEG using discrete wavelet transform and approximate entropy. Expert Systems with Applications, 36, 2027–2036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.12.065.
Song, Y., & Zhang, J. (2013). Automatic recognition of epileptic EEG patterns via extreme learning machine and multiresolution feature extraction. Expert Systems with Applications, 40, 5477–5489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.04.025.
Kumar, Y., Dewal, M. L., & Anand, R. S. (2014). Epileptic seizures detection in EEG using DWT-based ApEn and artificial neural network. Signal, Image Video Process, 8, 1323–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-012-0362-9.
Kumar, Y., Dewal, M. L., & Anand, R. S. (2014). Epileptic seizure detection using DWT based fuzzy approximate entropy and support vector machine. Neurocomputing, 133, 271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.11.009.
Guo, L., Rivero, D., Dorado, J., Rabunal, J. R., & Pazos, A. (2010). Automatic epileptic seizure detection in EEGs based on line length feature and artificial neural networks. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 191, 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.05.020.
Singh, G., Kaur, M., & Singh, D. (2016). Detection of epileptic seizure using wavelet transformation and spike based features. In 2015 2nd international conference on recent advances in engineering computing science RAECS 2015, pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/raecs.2015.7453376.
Subasi, A., Kevric, J., & Abdullah, Canbaz M. (2017). Epileptic seizure detection using hybrid machine learning methods. Neural Computing and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3003-y.
Guo, L., Rivero, D., & Pazos, A. (2010). Epileptic seizure detection using multiwavelet transform based approximate entropy and artificial neural networks. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 193, 156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.08.030.
Bhattacharyya, A., Pachori, R., Upadhyay, A., & Acharya, U. (2017). Tunable-Q wavelet transform based multiscale entropy measure for automated classification of epileptic EEG signals. Applied Science, 7, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040385.
Sharma, M., & Pachori, R. B. (2017). A novel approach to detect epileptic seizures using a combination of tunable-Q wavelet transform and fractal dimension. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 17, 1740003. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219519417400036.
Huang, N. E., Shen, Z., Long, S. R., Wu, M. C., Shih, H. H., Zheng, Q., et al. (1998). The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceeding of Royal Society of London, 454, 903–995. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193.
Pachori, R. B., & Varun, B. (2011). Analysis of normal and epileptic seizure EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 104, 373–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2011.03.009
Sharma, R., & Pachori, R. B. (2015). Classification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals based on phase space representation of intrinsic mode functions. Expert Systems with Applications, 42, 1106–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.08.030.
Pachori, R. B. (2008). Discrimination between ictal and seizure-free EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. Research Letters in Signal Processing, 2008, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/293056.
Bajaj, V., & Pachori, R. B. (2012). Classification of seizure and nonseizure EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 16, 1135–1142. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2011.2181403.
Kaur, M., & Singh, G. (2017). Classification of seizure prone EEG signal using amplitude and frequency based parameters of intrinsic mode functions. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 37, 540–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-017-0275-8.
Alam, S. M. S., & Bhuiyan, M. I. H. (2013). Detection of seizure and epilepsy using higher order statistics in the EMD domain. IEEE Journal of Biomedical Health Informatics, 17, 312–318. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2012.2237409.
Pachori, R. B., & Patidar, S. (2014). Epileptic seizure classification in EEG signals using second-order difference plot of intrinsic mode functions. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 113, 494–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.11.014.
Djemili, R., Bourouba, H., & Amara Korba, M. C. (2016). Application of empirical mode decomposition and artificial neural network for the classification of normal and epileptic EEG signals. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 36, 285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2015.10.006.
Wu, Z., & Huang, N. E. (2005). Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 1, 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000047.
Bizopoulos, P. A., Tsalikakis, D. G., Tzallas, A. T., Koutsouris, D. D., & Fotiadis, D. I. (2013). EEG epileptic seizure detection using k-means clustering and marginal spectrum based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition. In 13th IEEE international conference on bioinformatics and bioengineering, pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/bibe.2013.6701528.
Colominas, M. A., Schlotthauer, G., & Torres, M. E. (2014). Improved complete ensemble EMD: a suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 14, 19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2014.06.009.
Sree, S. V., Ang, P. C. A., Yanti, R., & Suri, J. S. (2012). Application of non-linear and wavelet based features for the automated identification of epileptic EEG signals. International Journal of Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065712500025.
Gao, Z.-K., Cai, Q., Yang, Y.-X., Dong, N., & Zhang, S.-S. (2017). Visibility graph from adaptive optimal kernel time-frequency representation for classification of epileptiform EEG. International Journal of Neural Systems, 27, 1750005. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065717500058.
Acharya, U. R., Sree, S. V., Chattopadhyay, S., Yu, W., & Ang, P. C. A. (2011). Application of recurrence quantification analysis for the automated identification of epileptic EEG signals. International Journal of Neural Systems, 21, 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065711002808.
Al Ghayab, H. R., Li, Y., Abdulla, S., Diykh, M., & Wan, X. (2016). Classification of epileptic EEG signals based on simple random sampling and sequential feature selection. Brain Informatics, 3, 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40708-016-0039-1.
Redelico, F. O., Traversaro, F., García M del, C., Silva, W., Rosso, O. A., & Risk, M. (2017). Classification of normal and pre-ictal EEG signals using permutation entropies and a generalized linear model as a classifier. Entropy, 1, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19020072.
Joshi, V., Pachori, R. B., & Vijesh, A. (2014). Classification of ictal and seizure-free EEG signals using fractional linear prediction. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 9, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2013.08.006.
Tiwari, A. K., Pachori, R. B., Kanhangad, V., & Panigrahi, B. K. (2017). Automated diagnosis of epilepsy using key-point based local binary pattern of EEG signals. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 21, 888–896. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2016.2589971.
Sharma, R., Pachori, R. B., & Rajendra, Acharya U. (2015). An integrated index for the identification of focal electroencephalogram signals using discrete wavelet transform and entropy measures. Entropy, 17, 5218–5240. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17085218.
Shannon, C. E. (2001). A mathematical theory of communication. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications, 5, 3–55. https://doi.org/10.1145/584091.584093.
Costa, M., Goldberger, A. L., & Peng, C. (2002). Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Physical Review Letters, 89, 068102. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.068102.
Morabito, F. C., Labate, D., La Foresta, F., Bramanti, A., Morabito, G., & Palamara, I. (2012). Multivariate multi-scale permutation entropy for complexity analysis of Alzheimer’s disease EEG. Entropy, 14, 1186–1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14071186.
De, Wu S, Wu, C. W., & Humeau-Heurtier, A. (2016). Refined scale-dependent permutation entropy to analyze systems complexity. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 450, 454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2016.01.044.
De, Wu S, Wu, C. W., Lin, S. G., Lee, K. Y., & Peng, C. K. (2014). Analysis of complex time series using refined composite multiscale entropy. Physics Letters, Section A: General, Atomic and Solid State Physics, 378, 1369–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2014.03.034.
Azami, H., Rostaghi, M., Abasolo, D., & Escudero, J. (2017). Refined composite multiscale dispersion entropy and its application to biomedical signals. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 64, 2872–2879. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2017.2679136.
Mainardi, L. T., Bianchi, L. M., & Cerutti, S. (2012). Digital biomedical signal acquisition and processing. In H. Liang, J. D. Bronzino, & D. R. Peterson (Eds.), Biosignal processing principles and practice. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Rostaghi, M., & Azami, H. (2016). Dispersion entropy: A measure for time series analysis. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 23, 610–614. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2016.2542881.
Andrzejak, R. G., Lehnertz, K., Mormann, F., Rieke, C., David, P., & Elger, C. E. (2001). Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: Dependence on recording region and brain state. Physical Review E, 64, 061907. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.64.061907.
Torres, M. E., Colominas, M., Schlotthauer, G., & Flandrin, P. (2011). A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, pp. 4144–4147. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2011.5947265.
Richman, J., & Moorman, J. (2000). Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory, 278, H2039–H2049. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.2000.278.6.H2039.
Sanei, S., & Chambers, J. (2007). EEG signal processing. Hoboken: Wiley.
Costa, M., Goldberger, A. L., & Peng, C.-K. (2005). Multiscale entropy analysis of biological signals. Physical Review E: Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 71, 21906. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.71.021906.
Jain, A., & Zongker, D. (1997). Feature selection: Evaluation, application, and small sample performance. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 19, 153–158. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.574797.
Peng, Y., Wu, Z., & Jiang, J. (2010). A novel feature selection approach for biomedical data classification. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 43, 15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2009.07.008.
Tiwari, S., Singh, B., & Kaur, M. (2017). An approach for feature selection using local searching and global optimization techniques. Neural Computing and Applications, 28, 2915–2930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2959-y.
Sebban, M., & Nock, R. (2013). A hybrid filter/wrapper approach of feature selection using information theory. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 53, 1689–1699. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Kira, K., & Rendell, L. (1992). A practical approach to feature selection. In Proceedings of ninth international workshop on machine learning, pp. 249–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-55860-247-2.50037-1.
Kira, K., & Rendell, L. (1992). The feature selection problem: Traditional methods and a new algorithm. In Proceedings of tenth national conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 129–34.
Kononenko, I. (1994). Estimating attributes: Analysis and extensions of RELIEF. In Proceedings of 7th European conference of machine learning, pp. 171–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-57868-4_57.
Hall, M. (1999). Correlation-based feature selection for machine learning. Hamilton: University of Waikato.
Guo, P. T., Wu, W., Sheng, Q. K., Li, M. F., Liu, H. B., & Wang, Z. Y. (2013). Prediction of soil organic matter using artificial neural network and topographic indicators in hilly areas. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 95, 333–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-013-9566-9.
Singh, G., Kaur, M., & Singh, D. (2015). Detection of epileptic seizure using wavelet transformation and spike based features. In 2015 2nd international conference on recent advances engineering and computer science, pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/raecs.2015.7453376.
Shoeb, A. H., & Guttag, J. V. (2010). Application of machine learning to epileptic seizure detection. In Proceedings of 27th international conference on machine learning, pp. 975–82.
Samiee, K., Kovács, P., & Gabbouj, M. (2015). Epileptic seizure classification of EEG time-series using rational discrete short-time fourier transform. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 62, 541–552. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2014.2360101.
Zheng, Y., Yuting, Z., Wang, J., & Zheng, X. (2015). Comparison of classification methods on EEG signals based on wavelet packet decomposition. Neural Computing and Applications, 26, 1217–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1786-7.
Peker, M., Sen, B., & Delen, D. (2016). A novel method for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using complex-valued classifiers. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 20, 108–118. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2014.2387795.
Chen, G., Xie, W., Bui, T. D., & Krzyżak, A. (2017). Automatic epileptic seizure detection in EEG using nonsubsampled wavelet-Fourier features. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 37, 123–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-016-0214-0.
Bhati, D., Pachori, R. B., & Gadre, V. M. (2017). A novel approach for time–frequency localization of scaling functions and design of three-band biorthogonal linear phase wavelet filter banks. Digital Signal Processing A Review Journal, 69, 309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2017.07.008.
Li, M., Chen, W., & Zhang, T. (2017). Application of MODWT and log-normal distribution model for automatic epilepsy identification. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 37, 679–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2017.08.003.
Sharma, M., Bhurane, A. A., & Acharya, U. R. (2018). MMSFL-OWFB: A novel class of orthogonal wavelet filters for epileptic seizure detection. Knowledge-Based Systems, 160, 265–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.07.019.
Zhang, T., Chen, W., & Li, M. (2018). Fuzzy distribution entropy and its application in automated seizure detection technique. Biomedical Signal Process Control, 39, 360–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.08.013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Kaur, M. & Singh, B. Detection of Epileptic Seizure EEG Signal Using Multiscale Entropies and Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Wireless Pers Commun 116, 845–864 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07742-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07742-z