Abstract
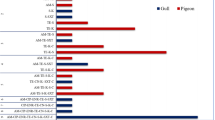
The antibiotic resistance profile of 17 poultry isolates of Salmonella was studied against 24 different antibiotics. 69–88% of the Salmonella isolates displayed a high level of resistance, particularly against penicillin, rifampicin, erythromycin, clarithromycin, clindamycin, sulphamethoxazole and vancomycin. In contrast, a relatively low or moderate level of resistance was observed against furazolidone, spectinomycin, ciprofloxacin, chloramphenicol, cefepime, carbenicillin, nalidixic acid, streptomycin, oxacillin and cephalothin (11–59%). Moreover, resistance to multiple antibiotics (2–5) was also observed among the Salmonella strains, and none of the isolates was found susceptible to all the antibiotics used. Similarity coefficient among Salmonella strains by RAPD-PCR analysis varied from 0.60 to 0.86, and all the salmonellae could be classified into seven groups on the basis of dendrogram analysis. Generally, a very high level of concordance between RAPD-PCR profile and antibiotic profile was not observed, which indicates that genes for antibiotic resistance may not always be present on genomic DNA rather may be plasmid-borne.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajaj BK, Sharma V, Koul S, Thakur RL (2003a) Incidence of Salmonella in poultry and meats and growth inhibition of Salmonella enteritidis by organic acids. J Food Sci Technol 40:556–558
Bajaj BK, Sharma V, Thakur RL (2003b) Prevalence and antibiotic resistance profiles of Salmonella sp. in poultry eggs. J Food Sci Technol 40:682–684
Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am Clin Pathol 45:493–496
Betancor L, Schelotto F, Martinez A, Pereira M, Algorta G, Rodríguez A, Vignoli R, Chabalgoity JA (2004) Random amplified polymorphic DNA and phenotyping analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolates collected from humans and poultry in Uruguay from 1995 to 2002. J Clin Microbiol 42:1155–1162
Carraminana JJ, Rota C, Agustín I, Herrera A (2004) High prevalence of multiple resistance to antibiotics in Salmonella serovars isolated from a poultry slaughterhouse in Spain. Vet Microbiol 104:133–139
Fluit AC (2005) Towards more virulent and antibiotic-resistant Salmonella? FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 43:1–11
Landeras E, Gonzalez Hevia MA, Mendoza MC (1998) Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis: relationship between food, water and pathogenic strains. Int J Food Microbiol 43:81–90
Le Minor L (1984) Salmonella lignieres. In: Kreig NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergeyȁ9s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 427–458. ISBN 0683041088
Ling JM, Koo IC, Kam KM, Cheng AF (1998) Antimicrobial susceptibilities and molecular epidemiology of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis strains isolated in Hong Kong from 1986 to 1996. J Clin Microbiol 36:1693–1699
Mare L, Dicks LMT, Vander Walt ML (2001) Characterization of South African isolaletes of Salmonella enteritidis by phage typing, numerical analysis of RAPD-PCR banding patterns and plasmid profiles. Int J Food Microbiol 64:237–245
Mikolajczyk A, Radkowski M (2002) Salmonella spp. on chicken carcasses in processing plants in Poland. J Food Protect 65:1475–1479
Miyamoto T, Tian HZ, Okabe T, Trevanich S, Asoh K, Tomoda S, Honjoh K, Shoji H (1998) Application of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis for detection of Salmonella spp. in foods. J Food Protect 61:785–791
Mrema N, Mpuchane S, Gashe BA (2006) Prevalence of Salmonella in raw minced meat, raw fresh sausages and raw burger patties from retail outletsin Gaborone, Botswana. Food Control 17:217–212
Smith OS, Smith JSC, Bowen SL, Tenbor RA, Wall SJ (1990) Similarities among a group of elite maize inbreds as measured by pedigree, F1grain yield, heterosis and RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 80:833–840
Soto SM, Gonzalez-Hevia MA, Mendoza MC (2003) Antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis: relationships between mutations conferring quinolone resistance, integrons, plasmids and genetic types. J Antimicrob Agents Chemoth 51:1287–1291
White DG, Zhao S, Simjee S, Wagner DD, McDermott PF (2002) Antimicrobial resistance of food borne pathogens. Microbes Infect 4:405–412
Wilson K (1987) Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore BD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current protocols in molecular biology. John and Wiley & Sons, New York. pp 2.4.1–2.4.2. ISBN 0471632481
Acknowledgement
Authors thank the Head, Department of Biotechnology, University of Jammu, Jammu, for providing all the necessary laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, Y.R., Bajaj, B.K. Antibiotic resistance and molecular characterization of poultry isolates of Salmonella by RAPD-PCR. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 1177–1183 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9159-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9159-8