Abstract
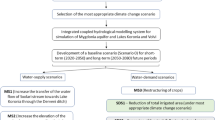
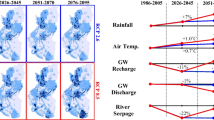
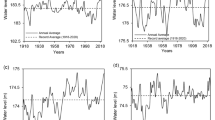
The joint effect of changes in climate and land use on the future availability of water resources was assessed under the SRES A1B and A2 climate scenarios as well as five land use scenarios for the 2080–2100 time-frame in an Italian coastal watershed. The study area is a small coastal polder (100 km2) characterized by irrigated agriculture, urban expansion, drainage, quarrying and sensitivity to salt-water intrusion. The hydroclimatic budget and the GALDIT index have been computed for assessing water resources availability and groundwater vulnerability to salinization, respectively. The methodology developed is integrated into a tool based on Excel™, which supported the development of scenarios in participatory processes. The conclusions emerged from the analysis are the following: (1) climate change is more effective than land use change in controlling future freshwater availability and amplifies the imbalance between winter surplus and summer deficits, (2) freshwater availability in the summer will likely be affected by an increase in evaporation from open water surfaces due to increased temperature, whereas winter surplus would increase, (3) the vulnerability of the coastal aquifer to salinization will probably moderately increase but an inherent limitation of the GALDIT index to land use change parameters prevents a sound assessment. Strategies that may be proposed to administrators and stakeholders are based on increasing storage of seasonal water surplus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulla F, Eshtawi T, Assaf H (2009) Assessment of the impact of potential climate change on the water balance of a semi-arid watershed. Water Resour Manag 23:2051–2068
Allen RG, Pruitt WO (1991) FAO-24 reference evapotranspiration factors. J Irrig Drain E-ASCE 117:758–773
Allen RG, Smith M, Perrier A, Pereira LS (1994) An update for the definition of reference evapotranspiration. ICID Bull 43:1–34
Antonellini M, Mollema PN, Giambastiani B, Bishop K, Caruso L, Minchio A, Pellegrini L, Sabia M, Ulazzi E, Gabbianelli G (2008) Salt water intrusion in the coastal aquifer of the southern Po Plain, Italy. Hydrogeol J 16:1541–1556
Antonellini M, Mollema PN (2010) Impact of ground water salinity on vegetation species richness in the coastal pine forests and wetlands of Ravenna, Italy. Ecol Eng 36:1201–1211
Badon Ghijben W (1888) Nota in verband met de voorgenomen putboring nabij Amsterdam [Notes on the probable results of a well drilling near Amsterdam]. Tijdschrift Koninklijk Instit Ing 1988/1989:8–22
Barrocu G, Muscas L, Sciabica MG (2001) GIS and modeling for studying saltwater intrusion in the Capoterra Alluvial plain (Sardinia, Italy). Proc. SWICA-M3, Essaouira, Morocco, April 2001
Barrocu G (2003) Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of Italy. In: Calaferra J (ed) State of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of the mediterranean coast, Alicante, 207–223
Baruffi F, Cisotto A, Cimolino A et al (2012) Climate change impact assessment on Veneto and Friuli plain groundwater. Part I: an integrated modeling approach for hazard scenario construction. Sci Total Environ 440:154–166
Bekele EG, Knapp HV (2010) Watershed modeling to assessing impacts of potential climate change on water supply availability. Water Resour Manag 24:3299–3320
Belvederi G, Bocci A, Campiani E, Corticelli S, Garberi ML, Guandalini B, Mariani MC, Masi S, Salvestrini L (2010) Il nuovo database dell’uso del suolo della Regione Emilia-Romagna. Proceedings 14° ASITA Conference, Brescia, 229–233
Börjeson L, Höjer K, Dreborg H, Ekvall T, Finnveden G (2006) Scenario types and techniques: towards a user’s guide. Futures 38:723–739
Campiani E, Corticelli S, Garberi M L, Gavagni A, Guandalini B (2006) Uso del suolo 2003 Regione Emilia-Romagna, Servizio Sistemi informativi geografici
Cau P, Lecca G, Muscas, Barrocu G, Uras G (2002) Saltwater intrusion in the plain of Oristano (Sardinia), 17th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Delft, The Netherlands, 6–10 May 2002, pp 435–444
Chachadi AG, Lobo-Ferreira JP (2005) Assessing aquifer vulnerability to sea-water intrusion using GALDIT method: part 2 – GALDIT indicator descriptions. IAHS and LNEC, Proceedings of the 4th The Fourth Inter Celtic Colloquium on Hydrology and Management of Water Resources, held at Universidade do Minho, Guimarães, Portugal, July 11–13, 2005
Custodio E (2010) Coastal aquifers of Europe: an overview. Hydrogeol J 18:269–280
De Luca A, Preziosi E, Giuliano G, Mastroianni D, Falconi F (2005) First evaluation of the saltwater intrusion in the Tiber delta area (Rome, central Italy). 18th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Cartagena, Spain, 31 May–3 June 2004, 34 pp
Ehlers L, Herrmanna F, Blaschek M, Duttmannb R, Wendland F (2015) Sensitivity of mGROWA-simulated groundwater recharge to changes in soil and land use parameters in a Mediterranean environment and conclusions in view of ensemble-based climate impact simulations. Sci Total Environ. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.122
Ertürk A, Ekdal A, Gürel M, Karakaya N, Guzel C, Gönenç E (2014) Evaluating the impact of climate change on groundwater resources in a small Mediterranean watershed. Sci Total Environ 499:437–447
European Commission EC (2009) Integrated coastal zone management protocol. Off J Eur Union L34:19–28
European Commission EC (2010) EU Focus on the coastal zone. Bruxelles, 36
European Environment Agency EEA (2012) Climate change, impacts and vulnerability in Europe 2012 - an indicator-based report. EEA Report No 12/2012, Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Union, ISBN 978-92-9213-346-7, doi:10.2800/66071
Fetter CW (2001) Applied hydrogeology, fourthth edn. Prentice hall, New Jersey, p 598
Fung F, Watts G, Lopez A, Orr HG, New M, Extence C (2013) Using large climate ensembles to plan for the hydrological impact of climate change in the freshwater environment. Water Resour Manag 27:1063–1084
Giambastiani BMS, Antonellini M, Oude Essink GHP, Roelof J, Stuurman RJ (2007) Saltwater intrusion in the unconfined coastal aquifer of Ravenna (Italy): a numerical model. J Hydrol 340:91–104
Giupponi C, Mordechai S (2003) Climate change in the mediterranean. Edward Elgar Publishing, ISBN 1-84376-154-8, 332 pp
Goderniaux P, Brouyère S, Wildemeersch S, Therrien R, Dassargues A (2015) Uncertainty of climate change impact on groundwater reserves – application to a chalk aquifer. J Hydrol 528:108–121
Graveline N, Aunay B, Fusillier JL, Rinaudo JD (2014) Coping with urban & agriculture water demand uncertainty in water management plan design: the interest of participatory scenario analysis. Water Resour Manag 28:3075–3093. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0656-5
Healy RW (2011) Estimating groundwater recharge. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, p 256
Herzberg A (1901) Die Wasserversorgung einiger Nordseebaeder [The water supply of selected North Sea towns]. Z F Gasbeleucht Wasserversorg 44:815–844
Höjer M, Ahlroth S, Dreborg KH, Ekvall T, Finnveden G, Hjelm O, Hochschorner E, Nilsson M, Palm V (2008) Scenarios in selected tools for environmental systems analysis. J Clean Prod 16:1958–1970
Huang B, Zhang L, Wu B (2009) Spatio-temporal analysis of rural–urban land conversion. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 23:379–398
IPCC (2000) Nakicenovic N, Swart R (eds) Cambridge University Press, UK. pp 570 ISBN: 92-9169-113-5. http://www.ipcc.ch/ipccreports/sres/emission/index.php?idp=0
IPCC (2007) Climate Change 2007, the Fourth IPCC Assessment Report. Geneve
Lavalle C, Mubareka S, Perpiña Castillo C, Jacobs-Crisioni C, Baranzelli C, Batista Silva F, Vandecasteele I (2013) Configuration of a reference scenario for the land use modelling platform. Technical report, European Commission – Joint Research Center – Institute for the Environment and Sustainability, ISBN 978-92-79-32349-2
Lee KS, Chung ES (2007) Hydrological effects of climate change, groundwater withdrawal, and land use in a small Korean watershed. Hydrol Process 21:3046–3056
Lobo-Ferreira JP, Chachadi AG, Diamantino C, Henriques MJ (2007) Assessing aquifer vulnerability to seawater intrusion using the GALDIT method. Part 1: application to the Portuguese Monte Gordo aquifer. In: Lobo Ferreira JP, Viera JMP (eds) Water in Celtic countries: quantity, quality and climatevariability. IAHS 310, Wallingford, pp 161–171
Marconi V, Antonellini M, Balugani E, Dinelli E (2011) Hydro-geochemical characterization of small coastal wetlands and forests in the Southern Po plain (Northern Italy). Ecohydrology 4:597–607
Mizyed N (2009) Impacts of climate change on water resources availability and agricultural water demand in the west bank. Water Resour Manag 23:2015–2029
Mollema PN, Antonellini M, Gabbianelli G, Laghi M, Marconi V, Minchio A (2012) Climate and water budget change of a Mediterranean coastal watershed, Ravenna, Italy. Env Earth Sci 65:257–276
Mollema PN, Antonellini M, Gabbianelli G, Galloni E (2013) Water budget management of a coastal pine forest in a Mediterranean catchment (Marina Romea, Ravenna, Italy). Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1862-1
Monteith JL (1973) Principles of environmental physics. Edward Arnold, London, p 350
Morgan LK, Werner AD (2014) Seawater intrusion vulnerability indicators for freshwater lenses in strip islands. J Hydrology 508:322–327
Mujumdar PP (2013) Climate change: a growing challenge for water management in developing countries. Water Resour Manag 27:953–954
Müller D, Munroe DK (2007) Issues in spatially explicit statistical land-use/cover change (LUCC) models: examples from western Honduras and the Central Highlands of Vietnam. Land Use Policy 24:521–530
Neupane RP, Kumar S (2015) Estimating the effects of potential climate and land use changes on hydrologic processes of a large agriculture dominated watershed. J Hydrol 529:418–429
Pranzini G (2002) Groundwater salinization in Versilia (Italy). 17th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Delft, The Netherlands, 6–10 May 2002, pp 412–421
Post VEA (2005) Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: is our technology ready for the problems ahead? Hydrogeol J 13:120–123
Rahman Z, Gago da Silva A, Moran Tejeda E, Gobiet A, Beniston M, Lehmann A (2015) An independent and combined effect analysis of land use and climate change in the upper Rhone River watershed, Switzerland. Appl Geogr 63:264–272
Recinos N, Kallioras A, Pliakas F, Schuth C (2014) Application of GALDIT index to assess the intrinsic vulnerability to seawater intrusion of coastal granular aquifers. Env Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3452-x
Santha Sophiya M, Syed TH (2013) Assessment of vulnerability to seawater intrusion and potential remediation measures for coastal aquifers: a case study from eastern India. Env Earth Sci 70:1197–1209
Scheidleger A, Grath J, Lininger H (2004) Saltwater intrusion due to groundwater overexploitation – EEA Inventory throughout Europe. 18th Saltwater Intrusion Meeting. Cartagena, Spain, p 125
Serpa D, Nunes JP, Santos J et al (2015) Impacts of climate and land use changes on the hydrological and erosion processes of two contrasting Mediterranean catchments. Sci Total Environ 538:64–77
Shi P, Ma X, Hou Y et al (2013) Effects of land-Use and climate change on hydrological processes in the upstream of Huai river, china. Water Resour Manag 27:1263–1278
Simonneaux V, Cheggour A, Deschamps A et al (2015) Land use and climate change effects on soil erosion in a semi-arid mountainous watershed (High Atlas, Morocco). J Arid Environ 122:64–75
Silveira P, Silva V, Dentinho TP (2009) Spatial interaction model with land and water use: an application to Terceira Island, 45th ISOCARP Congress, p 171
Small C, Nicholls RJ (2003) A global analysis of human settlements in coastal zones. J Coast Res 19:584–599
Smith M, Allen RG, Monteith JL, Perrier A, Pereira L, Segeren A (1992) Report of the expert consultation on procedures for revision of FAO guidelines for prediction of crop water requirements. UN-FAO, Rome, Italy, p 54
Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (2007) Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, p 996
Sophocleous M (2010) Review: groundwater management practices, challenges, and innovations in the high plains aquifer, USA-lessons and recommended actions. Hydrogeol J 18(3):559–575
Teatini P, Ferronato M, Gambolati G, Bertoni W, Gonella M (2005) A century of land subsidence in Ravenna, Italy. Environ Geol 47:831–846
Tu J (2009) Combined impact of climate and land use changes on streamflow and water quality in eastern Massachusetts, USA. J Hydrol 379:268–283
Ty TV, Sunada K, Ichikawa Y, Oishi S (2012) Scenario-based impact assessment of land use/cover and climate changes on water resources and demand: a case study in the Srepok River basin, Vietnam, Cambodia. Water Resour Manag 26:1387–1407
Verburg PH, Soepboer W, Veldkamp A, Limpiada R, Espaldon V, Mastura SSA (2002) Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: the CLUE-S model. Environ Manag 30:391–405
Werner AD, Ward JD, Morgan LK, Simmons CT, Robinson NI, Teubner MD (2012) Vulnerability indicators of sea water intrusion. Ground Water 50:48–58
Werner AD, Zhang Q, Xue L, Smerdon BD, Li X, Zhu X, Yu L, Li L (2013) An initial inventory and indexation of groundwater mega-depletion cases. Water Resour Manag 27:507
Zhang L, Nan Z, Yu W, Ge Y (2015) Modeling land-Use and land-cover change and hydrological responses under consistent climate change scenarios in the Heihe river basin, China. Water Resour Manag 29(13):4701–4717
Websites
ARPA http://www.arpa.emr.it/sim/?osservazioni_e_dati/dexter consulted on 14/06/2011
WATERKNOW http://www.circle-med.net/index.php?pagename=WATERKNOW&itemid=110&PHPSESSID=f3d5398d94d31fcf38703723c6134271 consulted on 14/06/2011
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by a CIRCLEMED grant to the WATERKNOW project. We thank Andrea Minchio and Elizabeth General Diaz for helping in data elaboration as well as two anonymous reviewers who helped in improving the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 521 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benini, L., Antonellini, M., Laghi, M. et al. Assessment of Water Resources Availability and Groundwater Salinization in Future Climate and Land use Change Scenarios: A Case Study from a Coastal Drainage Basin in Italy. Water Resour Manage 30, 731–745 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1187-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1187-4