Abstract
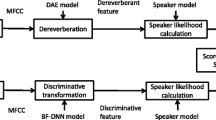
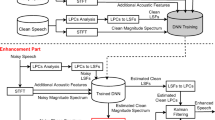
In this paper, we propose a robust distant-talking speech recognition by combining cepstral domain denoising autoencoder (DAE) and temporal structure normalization (TSN) filter. As DAE has a deep structure and nonlinear processing steps, it is flexible enough to model highly nonlinear mapping between input and output space. In this paper, we train a DAE to map reverberant and noisy speech features to the underlying clean speech features in the cepstral domain. For the proposed method, after applying a DAE in the cepstral domain of speech to suppress reverberation, we apply a post-processing technology based on temporal structure normalization (TSN) filter to reduce the noise and reverberation effects by normalizing the modulation spectra to reference spectra of clean speech. The proposed method was evaluated using speech in simulated and real reverberant environments. By combining a cepstral-domain DAE and TSN, the average Word Error Rate (WER) was reduced from 25.2 % of the baseline system to 21.2 % in simulated environments and from 47.5 % to 41.3 % in real environments, respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
W i and \(W_{{i^{T}_{1}}}\) correspond to f L in Eq. 1
References
Yoshioka, T., Sehr, A., Delcroix, M., Kinoshita, K., Maas, R., Nakatani, T., & Kellermann, W. (2012). Making machines understand us in reverberant rooms: robustness against reverberation for automatic speech recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 29(6), 114–126.
Wu, M., & Wang, D. (2006). A two-stage algorithm for one-microphone reverberant speech enhancement. IEEE Transactions on ASLP, 14(3), 774–784.
Jin, Q., Schultz, T., & Waibel, A. (2007). Far-field speaker recognition. IEEE Transactions on ASLP, 15 (7), 2023–2032.
Delcroix, M., & Hikichi, T. (2007). M.Miyoshi, Precise dereverberation using multi-channel linear prediction. IEEE Transactions on ASLP, 15(2), 430–440.
Wang, L., Zhang, Z., & Kai, A. (2013). Hands-free speaker identification based on spectral subtraction using a multi-channel least mean square approach. Proceedings of ICASSP, 2013, 7224–7228.
Habets, E. A. (2005). Multi-channel speech dereverberation based on a statistical model of late reverberation. Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP, 173–176.
Wang, L., Kitaoka, N., & Nakagawa, S. (2006). Robust Distant Speech Recognition by Combining Multiple Microphone-array Processing with Position-dependent CMN. Eurasip Journal on Applied Signal Processing, 2006 (95491), 1–11.
Wang, L., Kitaoka, N., & Nakagawa, S. (2011). Distant-talking speech recognition based on spectral subtraction by multi-channel LMS algorithm. IEICE Transactions on Information Systems, E94-D(3), 659–667.
Wang, L., Odani, K., & Kai, A. (2012). Dereverberation and denoising based on generalized spectral subtraction by nutil-channel LMS algorithm using a small-scale microphone array. Eurasip Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2012(12), 1–11.
Li, W., Wang, L., Zhou, F., & Liao, Q. (2013). Joint sparse representation based cepstral-domain dereverberation for distant-talking speech recognition. Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP, 7117–7120.
Hirsch, H., & Finster, H. (2008). A new approach for the adaptation of HMMs to reverberation and background noise. Speech Communication, 50(3), 244–263.
Sehr, A., Maas, R., & Kellermann, W. (2010). Reverberation model-based decoding in the logmelspec domain for robust distant-talking speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on ASLP, 18(7), 1676–1691.
Sadjadi, S.O., & Hasnen, J.H.L. (2011). Hilbert envelope based features for robust speaker identification under reverberant mismatched conditions. In Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP (pp. 5448–5451).
Kinoshita, K., Delcroix, M., Nakatani, T., & Miyoshi, M. (2006). Spectral subtraction steered by multistep forward linear prediction for single channel speech dereverberation. In Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP (Vol. 2006, pp. 817–820).
Wang, L., Odani, K., & Kai, A. (2012). Dereverberation and denoising based on generalized spectral subtraction by multi-channel LMS algorithm using a small-scale microphone array. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2012, 12.
Wang, L., Kitaoka, N., & Nakagawa, S. (2011). Distant-talking speech recognition based on spectral subtraction by multi-channel LMS algorithm. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, E94-D(3), 659–667.
Wang, L., Zhang, Z., & Kai, A. (2013). Hands-free speaker identification based on spectral subtraction using a multi-channel least mean square approach. Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP, 2013, 7224–7228.
Furui, S. (1981). Cepstral Analysis Technique for automatic speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 29(2), 254–272.
Liu, F., Stern, R., Huang, X., & Acero, A. (1993). Efficient cepstral normalization for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of ARPA Speech Natural Language Workshop (pp. 69–74).
Wang, L., Kitaoka, N., & Nakagawa, S. (2007). Robust distant speech recognition by combining position-dependent CMN with conventional CMN. Proceedings of ICASSP, 817–820.
Boll, S. (1979). Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 27(2), 113–120.
Wolfel, M (2009). Enhanced speech features by single-channel joint compensation of noise and reverberation. IEEE Transactions on Audio Speech Language Processing, 17(2), 312–323.
Konig, Y., Heck, L., Weintraub, M., & Sonmez, K. (1998). Nonlinear discriminant feature extraction for robust text-independent speaker recognition. In Proceedings of RLA2C: ESCA workshop on speaker recognition and its commercial and forensic applications (pp. 72–75).
Zhu, Q., Stolcke, A., Chen, B.Y., & Morgan, N. (2005). Using MLP features in SRI’s conversational speech recognition system. INTERSPEECH, 2005, 2141–2144.
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., Bengio, Y., & Manzagol, P. A. (2010). Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 11, 3371–3408.
Lu, X., Tsao, Y., Matsuda, S., & Hori, C. (2013). Speech enhancement based on deep denoising autoencoder, In Proceedings of Interspeech (pp. 436–440).
Ishii, T., Komiyama, H., Shinozaki, T., Horiuchi, Y., & Kuroiwa, S. (2013). Reverberant speech recognition based on denoising autoencoder. In Proceedings of Interspeech (pp. 3512– 3516).
Itou, K., Yamamoto, M., Takeda, K., Kakezawa, T., Matsuoka, T., Kobayashi, T., Shikano, K., & Itahashi, S. (1999). JNAS: Janpanese speech corpus for large vocabulary continuous speech recognition research. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. (E), 20(3), 199– 206.
Hinton, G., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2006). Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 313(5786), 504–507.
Yamada, T., Wang, L., & Kai, A. (2013). Improvement of distant-talking speaker identification using bottleneck features of DNN. In Proceedings of Interspeech (pp. 3661– 3664).
Xiao, X., Chng, E.S., & Li, H. (2008). Normalization of the speech modulation spectra for robust speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Audio Speech, and Language Processing, 16(8), 1662–1674.
Xiao, X., Chng, E.S., & Li, H. (2007). Temporal structure normalization of speech feature for robust speech recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 14(7), 500–503.
Kinoshita, K., Delcroix, M., Yoshioka, T., Nakatani, T., Habets, E., Haeb-Umbach, R., Leutnant, V., Sehr, A., Kellermann, W., Maas, R., Gannot, S., & Raj, B (2013). The REVERB challenge: A common evaluation framework for dereverberation and recognition of reverberant speech. In Proceedings of the IEEE workshop on applications of signal processing to audio and acoustics (WASPAA-13).
Robinson, T., Fransen, J., Pye, D., Foote, J., & Renals, S. (1995). Wsjcam0: A british english speech corpus for large vocabulary continuous speech recognition. In Proceedings of ICASSP (Vol. 95, pp. 81–84).
Lincoln, M., McCowan, I., Vepa, I., & Maganti, H. K. (2005). The multi-channel wall street journal audio visual corpus (MC-WSJ-AV): Specification and initial experiments. In Proceedings of ASRU (pp. 357–362).
Young, S., Kershow, D., Odell, J., Ollason, D., Valtchev, V., & Woodland, P. (2000). The HTK book (for HTK version 3.0): Cambridge University.
Gales, M.J.F., & Woodland, P.C. (1996). Mean and variance adaptation within the MLLR framework. Computer Speech & Language, 10, 249–264.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by a research grant from the Research Foundation for the Electrotechnology of Chubu (REFEC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, Y., Wang, L., Kai, A. et al. Single-channel Dereverberation for Distant-Talking Speech Recognition by Combining Denoising Autoencoder and Temporal Structure Normalization. J Sign Process Syst 82, 151–161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1007-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1007-3