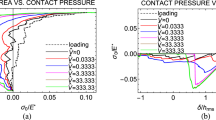
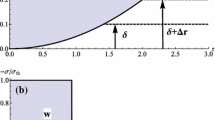
Abstract
In this work, a numerical method is developed to study the liquid-mediated adhesion between 3D rough surfaces. The presence of a wetting liquid between two rough surfaces generates a negative pressure inside the liquid film, which in turn induces tensile stresses in the contact region. Opposing these tensile stresses are the compressive stresses generated at solid–solid contact spots. An iterative deterministic contact model based on influence coefficients is employed to solve the equations of elasticity and capillarity simultaneously. Results for tensile (adhesive) force, wetted radius, average gap, and contact area between the rough surfaces are obtained. The results show that sudden changes in tensile force, average gap, and contact area occur with an increase in certain parameters, suggesting an elasto-capillary instability and surface collapse.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Radius of pressurized region (Eq. 8)
- A n :
-
Nominal contact area between two rough surfaces
- A r :
-
Real contact area between two rough surfaces
- A *r :
-
Normalized contact area
- C ijmn :
-
Influence coefficients
- d :
-
Distance between rigid flat and mean of undeformed rough surface
- Δp :
-
Capillary pressure drop
- Δx :
-
Grid spacing in x direction
- Δy :
-
Grid spacing in y direction
- E :
-
Elastic modulus
- \(E^{\prime }\) :
-
Reduced or effective elastic modulus
- F c :
-
Compressive force between rough surfaces
- F t :
-
Tensile force between rough surfaces
- \(F_{\text{t}}^{*}\) :
-
Normalized tensile force
- γ :
-
Surface tension of liquid
- Γ :
-
Adhesion parameter
- h fs :
-
Surface separation at the free surface of the liquid
- \(\bar{h}\) :
-
Average surface separation
- h * :
-
Normalized average surface separation
- l c :
-
Correlation length
- L :
-
Scan lengths in x and y directions
- N :
-
Number of nodal points in x and y directions
- υ :
-
Poisson’s ratio
- p :
-
Pressure
- p ij :
-
Nodal pressure
- P :
-
External load applied to rough surfaces
- P * :
-
Normalized external load
- r w :
-
Radius of wetted region
- R I,II :
-
Principal radii of curvature at the free surface of the liquid
- σ :
-
Root mean square of rough surface heights
- θ A,B :
-
Contact angles between the liquid and rough surfaces
- u :
-
Surface deformation
- u ij :
-
Nodal surface deformation
- V 0 :
-
Liquid volume
- V *0 :
-
Normalized liquid volume
- z 0ij :
-
Nodal surface height of undeformed surface
- z ij :
-
Nodal surface height of deformed surface
References
Adamson, A.W., Gast, A.P.: Physical chemistry of surfaces. (1967)
Bhushan, B., Dugger, M.: Liquid-mediated adhesion at the thin film magnetic disk/slider interface. ASME J. Tribol 112, 217–223 (1990)
Yang, S.H., Nosonovsky, M., Zhang, H., Chung, K.-H.: Nanoscale water capillary bridges under deeply negative pressure. Chem. Phys. Lett. 451(1), 88–92 (2008)
Yang, S.H., Zhang, H., Nosonovsky, M., Chung, K.-H.: Effects of contact geometry on pull-off force measurements with a colloidal probe. Langmuir 24(3), 743–748 (2008)
Grobelny, J., Pradeep, N., Kim, D.-I., Ying, Z.: Quantification of the meniscus effect in adhesion force measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(9), 091906 (2006)
Rabinovich, Y.I., Esayanur, M.S., Johanson, K.D., Adler, J.J., Moudgil, B.M.: Measurement of oil-mediated particle adhesion to a silica substrate by atomic force microscopy. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 16(7), 887–903 (2002)
Rabinovich, Y.I., Adler, J.J., Esayanur, M.S., Ata, A., Singh, R.K., Moudgil, B.M.: Capillary forces between surfaces with nanoscale roughness. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 96(1), 213–230 (2002)
Rabinovich, Y.I., Esayanur, M.S., Moudgil, B.M.: Capillary forces between two spheres with a fixed volume liquid bridge: theory and experiment. Langmuir 21(24), 10992–10997 (2005)
Tian, H., Matsudaira, T.: The role of relative humidity, surface roughness and liquid build-up on static friction behavior of the head/disk interface. J. Tribol. 115(1), 28–35 (1993)
Matthewson, M.J.: Adhesion of spheres by thin liquid films. Philos. Mag. A 57(2), 207–216 (1988)
Zheng, J., Streator, J.L.: A micro-scale liquid bridge between two elastic spheres: deformation and stability. Tribol. Lett. 15(4), 453–464 (2003)
Zheng, J., Streator, J.: A liquid bridge between two elastic half-spaces: a theoretical study of interface instability. Tribol. Lett. 16(1–2), 1–9 (2004)
Megias-Alguacil, D., Gauckler, L.J.: Capillary forces between two solid spheres linked by a concave liquid bridge: regions of existence and forces mapping. AIChE J. 55(5), 1103–1109 (2009)
Matthewson, M.J., Mamin, H.J.: Liquid mediated adhesion of ultra-flat solid surfaces. In: MRS Proceedings, vol. 119, pp. 87–92 (1988)
Poon, C.Y., Bhushan, B.: Numerical contact and stiction analyses of Gaussian isotropic surfaces for magnetic head slider/disk contact. Wear 202(1), 68–82 (1996)
Tian, X., Bhushan, B.: The micro-meniscus effect of a thin liquid film on the static friction of rough surface contact. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 29(1), 163 (1996)
Streator, J.: A model of mixed lubrication with capillary effects. Tribol. Ser. 40, 121–128 (2002)
Persson, B.: Capillary adhesion between elastic solids with randomly rough surfaces. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 20(31), 315007 (2008)
Streator, J.L., Jackson, R.L.: A model for the liquid-mediated collapse of 2-D rough surfaces. Wear 267(9), 1436–1445 (2009)
Streator, J.L.: A model of liquid-mediated adhesion with a 2D rough surface. Tribol. Int. 42(10), 1439–1447 (2009)
Rostami, A., Streator, J.L.: Study of liquid-mediated adhesion between 3D rough surfaces: a spectral approach. Tribol. Int. 84, 36–47 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2014.11.019
Rostami, A., Streator, J.L.: A model for capillary flow between rough surfaces. STLE annual meeting (2014)
Jackson, R.L., Streator, J.L.: A multi-scale model for contact between rough surfaces. Wear 261(11), 1337–1347 (2006)
Rostami, A., Jackson, R.L.: Predictions of the average surface separation and stiffness between contacting elastic and elastic–plastic sinusoidal surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J: J. Eng. Tribol. 227(12), 1376–1385 (2013)
Johnson, K.: Contact Mechanics, 1985. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1974)
Love, A.E.H.: The stress produced in a semi-infinite solid by pressure on part of the boundary. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A, Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Charact. 228, 377–420 (1929)
Webster, M., Sayles, R.: A numerical model for the elastic frictionless contact of real rough surfaces. J. Tribol. 108(3), 314–320 (1986)
Garcia, N., Stoll, E.: Monte Carlo calculation for electromagnetic-wave scattering from random rough surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52(20), 1798 (1984)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Science Foundation (NSF) for support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostami, A., Streator, J.L. A Deterministic Approach to Studying Liquid-Mediated Adhesion Between Rough Surfaces. Tribol Lett 58, 2 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0497-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0497-2