Abstract
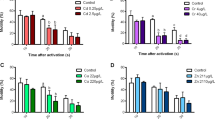
Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) embryos were electroporated with sterilization constructs targeting primordial germ cell proteins or with buffer. Some embryos then were treated with repressor compounds, cadmium chloride, copper sulfate, sodium chloride or doxycycline, to prevent expression of the transgene constructs. Promoters included channel catfish nanos and vasa, salmon transferrin (TF), modified yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae copper transport protein (MCTR) and zebrafish racemase (RM). Knock-down systems were the Tet-off (nanos and vasa constructs), MCTR, RM and TF systems. Knock-down genes included shRNAi targeting 5′ nanos (N1), 3′ nanos (N2) or dead end (DND), or double-stranded nanos RNA (dsRNA) for overexpression of nanos mRNA. These constructs previously were demonstrated to knock down nanos, vasa and dead end, with the repressors having variable success. Exogenous DNA affected percentage hatch (% hatch), as all 14 constructs, except for the TF dsRNA, TF N1 (T), RM DND (C), vasa DND (C), vasa N1 (C) and vasa N2 (C), had lower % hatch than the control electroporated with buffer. The MCTR and RM DND (T) constructs resulted in delayed hatch, and the vasa and nanos constructs had minimal effects on time of hatch (P < 0.05). Cadmium chloride appeared to counteract the slow development caused by the TF constructs in two TF treatments (P < 0.05). The 4 ppt sodium chloride treatment for the RM system decreased % hatch (P < 0.05) and slowed development. In the case of nanos constructs, doxycycline greatly delayed hatch (P < 0.05). Adverse effects of the transgenes and repressors continued for several treatments for the first 6 days after hatch, but only in a few treatments during the next 10 days. Repressors and gene expression impacted the yield of putative transgenic channel catfish fry, and need to be considered and accounted for in the hatchery phase of producing transgenically sterilized catfish fry and their fertile counterparts. This fry output should be considered to ensure that sufficient numbers of transgenic fish are produced for future applications and for defining repressor systems that are the most successful.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong JB, Duhon ST, Malacinski GM (1989) Raising the axolotl in captivity. In: Armstrong JB, Malacinski GM (eds) Developmental biology of the axolotl. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 220–227
Bart AN, Dunham RA (1996) Effects of sperm concentration and egg number on fertilization efficiency with channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) eggs and blue catfish (I. furcatus) spematozoa. Theriogenology 45:673–682
Bridge AJ, Pebernard S, Ducraux A, Nicoulaz AL, Iggo R (2003) Induction of an interferon response by RNAi vectors in mammalian cells. Nat Genet 34:263–264
Cao HB, Wang A, Martin B, Koehler DR, Zeitlin PL, Tanawell AK, Hu J (2005) Down-regulation of IL-8 expression in human airway epithelial cells through helper-dependent adenoviral-mediated RNA interference. Cell Res 15:111–119
Carginale V, Capasso C, Scudiero R, Parisi E (2002) Identification of cadmium-sensitive genes in the Antarctic fish Chionodraco hamatus by messenger RNA differential display. Gene 299:117–124
Chaimongkol A (2009) Disruption of embryonic development in common carp, Cyprinus carpio, and channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, via knock down of bmp2 gene for repressible transgenic sterilization. Dissertation, Auburn University, Auburn, AL
Cheng Q, Su B, Qin Z, Weng CC, Yin F, Zhou Y, Fobes M, Perera DA, Shang M, Silva F, Shi Z, Davis A, Dunham RA (2014) Interaction of diet and the masou salmon Δ5-desaturase transgene on Δ6-desaturase and stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene expression and n-3 fatty acid level in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Transgenic Res 23:729–742
Collares T, Campos VF, Seixas FK, Cavalcanti PV, Dellagostin OA, Moreira HL, Deschamps JC (2010) Transgene transmission in South American catfish (Rhamdia quelen) larvae by sperm-mediated gene transfer. J Biosci 35:39–47
Dunham RA (2011) Aquaculture and fisheries biotechnology: genetic approaches, 2nd edn. CABI Publishing, Cambridge, pp 93–127
Dunham RA, Smitherman RO (1984) Ancestry and breeding of catfish in the United States. Cir 273, Alabama Agricultural Experiment Station, Auburn University, Auburn, AL
Dunham RA, Winn RN (2014) Production of transgenic fish. In: Pinkert CA (ed) Transgenic animal technology: a laboratory handbook, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 308–336
Dunham RA, Ramboux AC, Duncan PL, Hayat M, Chen TT, Lin CM, Kight K, Gonzalez-Villasenor I, Powers DA (1992) Transfer, expression and inheritance of salmonid growth hormone genes in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, and effects on performance traits. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 1:380–389
Dunham RA, Lambert DM, Argue BJ, Ligeon C, Yant DR, Liu Z (2000) Comparisons of manual stripping and pen spawning for production of channel catfish X blue catfish hybrids and aquarium spawning of channel catfish. N Am J Aquacult 62:260–265
Fish RJ, Kruithof EK (2004) Short-term cytotoxic effects and long-term instability of RNAi delivered using lentiviral vectors. BMC Mol Biol 5:9
Gama Sosa MA, De Gasperi R, Elder GA (2010) Animal transgenesis: an overview. Brain Struct Funct 214:91–109
Gama Sosa MA, De Gasperi R, Elder GA (2012) Modeling human neurodegenerative diseases in transgenic systems. Hum Genet 131:535–563
Gibbs PD, Schmale MC (2000) GFP as a genetic marker scorable throughout the life cycle of transgenic zebra fish. Mar Biotechnol 2:107–125
Gossen M, Bujard H (1992) Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5547–5551
GraphPad Software (2007) Prism 5 for Mac OS X, version 5.02. San Diego, California. www.graphpad.com
Grimm D, Streetz KL, Jopling CL, Storm TA, Pandey K, Davis CR, Marion P, Salazar F, Kay MA (2006) Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature 441:537–541
Hatch U, Hebicha H, Dunham RA (1990) Optimal product combinations of channel catfish egg, fry, fingerling and food fish production in west Alabama catfish farms. In: Smitherman RO, Tave D (eds) Proceedings auburn symposium on fisheries and aquaculture, Sept 19–23, 1984. Brown Printing Co., Montgomery, pp 313–320
Houdebine LM, Chourrout D (1991) Transgenesis in fish. Experientia 47:891–897
Inoue K, Yamashita S, Hata J, Kabeno S, Asada S, Nagahisa E, Fujita T (1990) Electroporation as a new technique for producing transgenic fish. Cell Differ Dev 29:123–128
Kang J, Yoshizaki G, Homma O, Strüssmann CA, Takashima F (1999) Effect of an osmotic differential on the efficiency of gene transfer by electroporation of fish spermatozoa. Aquaculture 173:297–307
Karpala AJ, Doran TJ, Bean AG (2005) Immune responses to dsRNA: implications for gene silencing technologies. Immunol Cell Biol 83:211–216
Köprunner M, Thisse C, Thisse B, Raz E (2001) A zebrafish nanos-related gene is essential for the development of primordial germ cells. Genes Dev 15:2877–2885
Kristanto AH, Umali G, Beam R, Dunham RA (2009) Effect of postmanufacturing processing and shipping of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone analog on induced ovulation for production of channel catfish female × blue catfish male hybrid fry. N Am J Aquac 71:307–311
Labbé S, Zhu Z, Thiele DJ (1997) Copper-specific transcriptional repression of yeast genes encoding critical components in the copper transport pathway. J Biol Chem 272:15951–15958
Lambert DM, Argue BJ, Liu Z, Dunham RA (1999) Effects of seasonal variations, thyroid and steroid hormones and carp pituitary extract on the artificial production of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) × blue catfish (I. furcatus) hybrid embryos. J World Aquac Soc 30:80–89
Mansuy IM, Bujard H (2000) Tetracycline-regulated gene expression in the brain. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:593–596
McDonald JH (2009) Handbook of biological statistics, 2nd edn. Sparky House Publishing, Baltimore, pp 70–75. http://udel.edu/~mcdonald/statfishers.html
Muir WM, Howard RD (1999) Possible ecological risks of transgenic organism release when transgenes affect mating success: sexual selection and the Trojan gene hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13853–13856
Pezzullo JC (2013) 2-Way contingency table analysis. http://statpages.org/ctab2x2.html
Phelps RP, Walser CA (1993) Effect of sea salt on the hatching of channel catfish eggs. J Aquat Anim Health 5:205–207
Powers DA, Hereford L, Cole T, Chen TT, Lin CM, Kight K, Creech K, Dunham RA (1992) Electroporation: a method for transferring genes into the gametes of zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio), channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus), and common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 1:301–308
Richardson BE, Lehmann R (2010) Mechanisms guiding primordial germ cell migration: strategies from different organisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:37–49
Saito T, Fujimoto T, Maegawa S, Inoue K, Tanaka M, Arai K, Yamaha E (2006) Visualization of primordial germ cells in vivo using GFP-nos1 3′UTR mRNA. Intl J Dev Biol 50:691–699
SAS Institute (2010) SAS 9.3, SAS for windows, Windows version 6.1.7601. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Sauter S, Buxton KS, Macek KJ, Petrocelli SR (1976) Effects of exposure to heavy metals on selected freshwater fish. Toxicity of copper, cadmium, chromium and lead to eggs and fry of seven fish species. Env Res Lab., US Env Protection Agency, Rep. EPA-600/3-76-105 Duluth, Minnesota
Singh S, Narang AS, Mahato RI (2011) Subcellular fate and off-target effects of siRNA, shRNA, and miRNA. Pharm Res 28:2996–3015
Slanchev K, Stebler J, Cueva-Méndez G, Raz E (2005) Development without germ cells: the role of the germ line in zebrafish sex differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:4074–4079
Steeby JA, Avery J (2005) Channel catfish broodfish and hatchery management. Southern Regional Aquaculture Center, SRAC Pub. 1803, Stoneville, Mississippi. http://www.extension.org/mediawiki/files/5/55/Channel_Catfish_broodfish_and_hatchery_mgt.pdf
Straus DL, Mitchell AJ, Carter RR, McEntire ME, Steeby JA (2012) Safety of copper sulfate to channel catfish eggs. N Am J Aquac 74:60–64
Struhsaker JW, Hashimoto DY, Girard SM, Prior FT, Cooney TD (1973) Effect of antibiotics on survival of carangid fish larvae (Caranx mate), reared in the laboratory. Aquaculture 2:53–88
Su B (2012) Reproductive confinement of common carp, Cyprinus carpio, and channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, via transgenic sterilization. Dissertation, Auburn University, Auburn
Su B, Perera DA, Mu XJ, Dunham RA (2013a) Effect of sodium chloride on hatching rate on channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, embryos. J Appl Aquac 25:283–292
Su B, Perera DA, Zohar Y, Abraham E, Stubblefield J, Fobes M, Beam R, Argue B, Ligeon C, Padi J, Waters P, Umali-Maceina G, Chatakondi N, Kristanto A, Hutson A, Templeton C, Ballenger J, Chaimongkol A, Gima A, Gima M, Zuberi A, Lambert DM, Kim S, Mandour M, Dunham RA (2013b) Relative effectiveness of carp pituitary extract, LHRHa injections and LHRHa implants for producing hybrid catfish fry. Aquaculture 372–375:133–136
Su B, Peatman E, Shang M, Thresher R, Grewe P, Patil J, Pinkert C, Irwin M, Li C, Perera D, Duncan PL, Fobes M, Dunham RA (2014) Expression and knockdown of primordial germ cell genes, vasa, nanos and dead end in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) embryos for transgenic sterilization and reduced sexual maturity. Aquaculture 420–421:S72–S84
Svoboda P (2007) Off-targeting and other non-specific effects of RNAi experiments in mammalian cells. Curr Opin Mol Ther 9:248–257
Szczerbik P, Mikołajczyk T, Sokołowska-Mikołajczyk M, Socha M, Chyb J, Epler P (2008) The influence of cadmium on Prussian carp oocyte maturation, development of eggs and hatching. Czech J Anim Sci 53:36–44
Thresher R, Hinds LA, Hardy C, Whyard S, Vignarajan S, Grewe P, Patil J (2005) Repressible sterility of animals. USA Patent Application Publication. Pub. No.: US2005/0071891 A1
Thresher R, Grewe P, Patil JG, Whyard S, Templeton CM, Chaimongol A, Hardy C, Hinds LA, Dunham RA (2009) Development of repressible sterility to prevent the establishment of feral populations of exotic and genetically modified animals. Aquaculture 290:104–109
Van Eenennaam AL, Olin PG (2006) Careful risk assessment needed to evaluate transgenic fish. Calif Agric 60:126–131
Weidinger G, Stebler J, Slanchev K, Dumstrei K, Wise C, Lovell-Badge R, Thisse C, Thisse B, Raz E (2003) Dead end, a novel vertebrate germ plasma component, is required for zebrafish primordial germ cell migration and survival. Curr Biol 13:1429–1434
Weirich CR, Tiersch TR (1997) Effects of environmental sodium chloride on percent hatch, yolk utilization, and survival of channel catfish fry. J World Aquac Soc 28:289–296
Witeck L, Bombardelli RA, Sanches EA, Oliveira JDS, Baggio DM, Souza BE (2011) Sperm motility, oocyte fertilization and egg hatching on jundiá catfish in cadmium contaminated water. Rev Bras Zootecn 40:477–481
Witeska M, Jezierska B, Chaber J (1995) The influence of cadmium on common carp embryos and larvae. Aquaculture 129:129–132
Wong AC, Van Eenennaam AL (2008) Transgenic approaches for the reproductive containment of genetically engineered fish. Aquaculture 275:1–12
Yoon C, Kawakami K, Hopkins N (1997) Zebrafish vasa homologue RNA is localized to the cleavage planes of 2- and 4-cell-stage embryos and is expressed in the primordial germ cells. Development 124:3157–3165
Zeh JA, Bonilla MM, Adrian AJ, Mesfin S, Zeh DW (2012) From father to son: transgenerational effect of tetracycline on sperm viability. Sci Rep 2:375
Acknowledgments
This work was partially funded by the USDA-Biotechnology Risk Assessment Program (Grant No: 2009-33522-05774) and the Alabama Agricultural Experiment Station. The authors would like to thank Dr. Ron Thresher at CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia for the review and comments on the first draft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Baofeng Su and Mei Shang are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, B., Shang, M., Li, C. et al. Effects of transgenic sterilization constructs and their repressor compounds on hatch, developmental rate and early survival of electroporated channel catfish embryos and fry. Transgenic Res 24, 333–352 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-014-9846-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-014-9846-4