Abstract
Clonal propagation of Quercus suber via somatic embryogenesis is an alternative to conventional tree propagation methods; however, complete maturation of somatic embryos is considered the major bottleneck for mass propagation of Quercus species. During somatic embryogenesis, embryo development and maturation are controlled by signaling pathways that integrate information from genetic and epigenetic programs as well as hormonal signals. Therefore, in this study genes were identified related to epigenetic regulation and the abscisic acid (ABA) pathway during development and maturation of cork oak somatic embryos. A total of eight expressed sequence tags were obtained of genes encoding a 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED), two histone deacetylases (HDA6 and HDA19), two histone monoubiquitinases (HUB1 and HUB2), a histone H3 kinase (AUR3) as well as genes related to chromatin remodeling processes PICKLE and VP1/ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 3-LIKE 1 (VAL1). The analysis of the expression patterns of selected genes during different developmental stages indicated that QsNCED3 may play a role in ABA synthesis during embryogenesis. The change in the expression levels for all seven genes associated with epigenetic regulation showed that QsHUB1 and QsHUB2 may have a role in ABA signalling while QsHDA6 and QsHDA19 could act in different pathways than in Arabidopsis. Furthermore, expression levels of QsAUR3 indicated that histone phosphorylation is an early epigenetic mark in Q. suber somatic embryos while QsPICKLE and QsVAL1 may be necessary for the correct development of cork oak somatic embryos.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aichinger E, Villar CBR, Di Mambro R, Sabatini S, Köhler C (2011) The CHD3 chromatin remodeler PICKLE and polycomb group proteins antagonistically regulate meristem activity in the Arabidopsis root. Plant Cell 23:1047–1060
Bassel GW, Fung P, Freeman Chow TF, Foong JA, Provart NJ, Cutler SR (2008) Elucidating the germination transcriptional program using small molecules. Plant Physiol 1476(1):143–155
Bueno MA, Gómez A, Manzanera JA (2000) Somatic and gametic embryogenesis in Quercus suber L. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, forestry sciences, vol 6. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 470–508
Chaves I, Passarinho JAP, Capitão C, Chaves MM, Fevereiro P, Ricardo CPP (2011) Temperature stress effects in Quercus suber leaf metabolism. J Plant Physiol 168:1729–1734
Chernys JT, Zeevaart JAD (2000) Characterization of the 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene family and the regulation of abscisic acid biosynthesis in avocado. Plant Physiol 124:343–353
Chinnusamy V, Zhu JK (2009) Epigenetic regulation of stress responses in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(2):133–139
Chinnusamy V, Gong Z, Zhu JK (2008) Abscisic acid-mediated epigenetic processes in plant development and stress responses. J Integr Plant Biol 50(10):1187–1195
Demidov D, Van Damme D, Geelen D, Blattner FR, Houben A (2005) Identification and dynamics of two classes of aurora-like kinases in Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant Cell 17:836–848
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797
Fleury D, Himanen K, Cnops G, Nelissen H, Boccardi TM, Maere S, Beemster GTS, Neyt P, Anami S, Robles P, Micol JL, Inzé D, van Lijsebettens M (2007) The Arabidopsis thaliana homolog of yeast BRE1 has a function in cell cycle regulation during early leaf and root growth. Plant Cell 19:417–432
Gao MJ, Gropp G, Wei S, Hegedus DD, Lydiate DJ (2012) Combinatorial networks regulating seed development and seed filling. In: Sato KI (ed) Embryogenesis. InTech, Rijeka. doi:10.5772/35960
Gutierrez L, Van Wuytswinkel O, Castelain M, Bellini C (2007) Combined networks regulating seed maturation. Trends Plant Sci 12(7):294–300
Kawabe A, Matsunaga S, Nakagawa K, Kurihara D, Yoneda A, Hasezawa S, Uchiyama S, Fukui K (2005) Characterization of plant aurora kinases during mitosis. Plant Mol Biol 58:1–13
Kermode AR (2005) Role of abscisic acid in seed dormancy. J Plant Growth Regul 24:319–344. doi:10.1007/s00344-005-0110-2
Kim JM, To TK, Seki M (2012) An epigenetic integrator: new insights into genome regulation, environmental stress responses and developmental controls by HISTONE DEACETYLASE 6. Plant Cell Physiol 53(5):794–800
Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128(4):693–705
Lauria M, Rossi V (2011) Epigenetic control of gene regulation in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1809:369–378
Le BH, Cheng C, Bui AQ, Wagmaister JA, Henry KF, Pelletier J, Kwong L, Belmonte M, Kirkbride R, Horvath S, Drews GN, Fischer RL, Okamuro JK, Harada JJ, Goldberg RB (2010) Global analysis of gene activity during Arabidopsis seed development and identification of seed-specific transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:8063–8070
Liu Y, Koornneef M, Soppe WJJ (2007) The abscense of Histone H2B Monoubiquitination in the Arabidopsis hub1 (rdo4) mutant reveals a role for chromatin remodeling in seed dormancy. Plant Cell 19:433–444
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Long JA, Ohno C, Smith ZR, Meyerowitz EM (2006) TOPLESS regulates apical embryonic fate in Arabidopsis. Science 312:1520–1523
Marchler-Bauer A, Lu S, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C, Fong JH, Geer LY, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Lanczyzki CJ, Lu F, Marchler GH, Mullokandov M, Omelchenko MV, Robertson CL, Dong JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zhang N, Zheng C, Bryant SH (2011) CDD: a conserved domain database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acid Res 39:D225–D229
Marum L, Miguel A, Ricardo CP, Miguel C (2012) Reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in Quercus suber. PLoS ONE 7(4):e35113. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035113
Neelakandan AK, Wang K (2012) Recent progress in the understanding of tissue culture-induced genome level changes in plants and potential applications. Plant Cell Rep 31:597–620. doi:10.1007/s00299-011-1202-z
Pérez M, Viejo M, Lacuesta M, Toorop P, Cañal MJ (2015) Epigenetic and hormonal profile during maturation of Quercus suber L. somatic embryos. J Plant Physiol 173:51–61. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2014.07.028
Puigderrajols P, Jofré A, Mir G, Pla M, Verdaguer D, Huguet G, Molinas M (2002) Developmentally and stress-induced small heat shock proteins in cork oak somatic embryos. J Exp Bot 53(373):1445–1452
Rai MK, Shehawat NS, Harish Gupta AK, Phulwaria M, Ram K, Jaiswal U (2011) The role of abscisic acid in plant tissue culture: a review of recent progress. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 106:179–190. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-9923-9
Ramakers C, Ruitjer JM, Lekanne Deprez RH, Moorman AFM (2003) Assumption-free analysis of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) data. Neurosci Lett 13:62–66
Rodríguez-Gacio MC, Matilla-Vázquez MA, Matilla AJ (2009) Seed dormancy and ABA signaling. Plant Signal Behav 4(11):1035–1048
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 365–386
Ruijter JM, Ramakers C, Hoogaars WMH, Karlen Y, Bakker O, van den Hoff MJB, Moorman AFM (2009) Amplification efficiency: linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res 37(6):e45. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp045
Santamaría ME, Rodríguez R, Cañal MJ, Toorop PE (2011) Transcriptome analysis of chesnut (Castanea sativa) tree buds suggests a putative role for epigenetic control of bud dormancy. Ann Bot 108:485–498
Seo M, Koshiba T (2002) Complex regulation of ABA biosynthesis in plants. Trends Plant Sci 7(1):41–48
Soler M, Serra O, Molinas M, García-Berthou E, Caritat A, Figueras M (2008) Seasonal variation in transcript abundance in cork tissue analyzed by real time RT-PCR. Tree Physiol 28:743–751
Šunderlíková V, Wilhem E (2002) High accumulation of legumin and Lea-like mRNAs during maturation is associated with increased conversion frequency of somatic embryos from pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.). Protoplasma 220:97–103. doi:10.1007/s00709-002-0025-8
Šunderlíková V, Salaj J, Kopecky D, Salaj T, Wilhem E, Matušiková I (2009a) Dehydrin genes and their expression in recalcitrant oak (Quercus robur) embryos. Plant Cell Rep 28:1011–1021
Šunderlíková V, Salaj J, Matušiková I, Wilhem E (2009b) Isolation and characterization of an embryo-specific Em-like gene of pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.) and its temporal and spatial expression patterns during somatic and zygotic embryo development. Trees 23:135–144
Suzuki M, McCarty DR (2008) Functional symmetry of the B3 network controlling seed development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:548–553
Suzuki M, Wang H, McCarty DR (2007) Repression of the LEAFY COTYLEDON 1/B3 regulatory network in plant embryo development by VP1/ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 3-LIKE B3 genes. Plant Physiol 143:902–911
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tan BC, Joseph LM, Deng WT, Liu L, Li QB, Cline K, McCarty DR (2003) Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene family. Plant J 35:44–56
Tanaka M, Kikuchi A, Kamada H (2008) The Arabidopsis histone deacetylases HDA6 and HDA19 contribute to the repression of embryonic properties after germination. Plant Physiol 146:149–161
Tsukagoshi H, Morikami A, Nakamura K (2007) Two B3 domain transcriptional repressors prevent sugar-inducible expression of seed maturation genes in Arabidopsis seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(7):2543–2547
Van Damme D, De Rybel B, Gudesblat G, Demidov D, Grunewald W, De Smet I, Houben A, Beeckman T, Russinova E (2011) Arabidopsis α Aurora Kinases function in formative cell división plane orientiation. Plant Cell 23(11):4013–4024
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0034
Verdier J, Thompson RD (2008) Transcriptional regulation of storage protein synthesis during dicotyledon seed filing. Plant Cell Physiol 49(9):1263–1271
Vieitez AM, Corredoira E, Martínez MT, San-José MC, Sánchez C, Valladares S, Vidal N, Ballester A (2012) Application of biotechnological tools to Quercus improvement. Eur J Forest Res 131:519–539. doi:10.1007/s10342-011-0526-0
Viejo M, Santamaría ME, Rodríguez JL, Valledor L, Meijón M, Pérez M et al (2012) Epigenetics, the role of DNA methylation in tree development. In: Loyola-Vargas VM, Ochoa-Alejo N (eds) Plant cell culture methods, methods in molecular biology, vol 877. Springer, Netherlands, pp 277–301
Wilhem E (2000) Somatic embryogenesis in oak (Quercus spp.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 36:349–357
Winter D, Vinegar B, Nahal H, Ammar R, Wilson GV, Provart NJ (2007) An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2:e718
Yadav RK, Girke T, Pasala S, Xie M, Reddy GV (2009) Gene expression map of the Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem stem cell niche. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4941–4946
Zhang H, Ogas J (2009) An epigenetic perspective on developmental regulation of seed genes. Mol Plant 2(4):610–627
Zhou Y, Tan B, Luo M, Li Y, Liu C, Chen C, Yu CW, Yang S, Dong S, Ruan J, Yuan L, Zhang X, Zhao L, Li C, Chen H, Cui Y, Wu K, Huang S (2013) HISTONE DEACETYLASE19 interacts with HSL1 and participates in the repression of seed maturation genes in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 25:134–148
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Victor Granda (University of Oviedo) for his design of degenerated primers of NCED3. This work was supported by Spanish national projects AGL2007-62907/FOR and AGL2010-22351-C03-01. FICYT foundation supported the fellowship of M. Pérez.
Conflict of Interest
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11240_2014_706_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
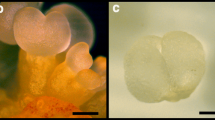
Online resource 1 Developmental stages defined during somatic embryogenesis procedure. Proliferative stages composed by white callogenic structures with globular embryos (PS), immature translucent cotyledonary embryos (E1); white opaque cotyledonary embryos (E2), cotyledonary embryos after one month onto maturation medium in darkness at 25 °C (E3), cotyledonary E3 embryos after cold stratification for 2 months in darkness (E4). (bars = 1 mm) (PDF 2536 kb)
11240_2014_706_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Online resource 3 List of EST sequences obtained after amplification with degenerated primers. The similarity (BLAST score, query coverage) is provided to the Arabidopsis orthologue and to the best hit for each gene in an NCBI BLAST search (PDF 105 kb)
11240_2014_706_MOESM5_ESM.pdf
Online resource 5 Arabidopsis thaliana embryo development gene expression levels. Taken from the Arabidopsis eFP Browser (http://bar.utoronto.ca/efp/cgi-bin/efpWeb.cgi) (Winter et al. 2007; Bassel et al. 2008). Embryo stages according to Le et al. (2010). Pre-globular-stage embryo (PGLOB), globular stage embryo (GLOB), heart-stage embryo (HRT), linear cotyledon-stage seed (LCOT), mature-green-stage seed (MG), Spearman correlation coefficient (rs)Correlations between Q. suber gene expression levels at stages E1–E2 were compared with A. thaliana embryos expression patterns LCOT and MG. A negative coefficient indicates an inverse proportion correlation. *indicates significant differences (p ≤ 0.01). (PDF 1395 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez, M., Cañal, M.J. & Toorop, P.E. Expression analysis of epigenetic and abscisic acid-related genes during maturation of Quercus suber somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 121, 353–366 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0706-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0706-y