Abstract
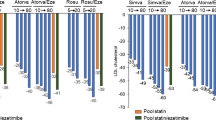
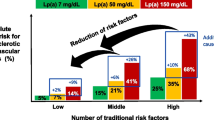
Micro and macrovascular complications occurring during hyperlipidemia are mostly attributed to haemostatic impairment and vascular endothelial dysfunction. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitors have been emerged recently as promising hypocholesterolemic agents to confer protection against lipid-mediated atherosclerosis. Therefore, 10-dehydrogingerdione (DHGD), a novel CETP inhibitor isolated from ginger rhizomes, was selected as a natural product in the present study to illustrate its effect on haemostatic impairment associated with hyperlipidemia as compared to a currently used hypocholesterolemic agent, atorvastatin (ATOR). Rabbits were fed a high cholesterol diet (HCD) and divided into three groups. One group served as control group while the other groups received DHGD or ATOR. Dyslipidemic rabbits showed a significant increase in serum endothelin-1, ischemia modified albumin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, prothrombin fragments (1+2) and plasma fibrinogen along with a decrease of nitric oxide level in serum. Daily administration of ATOR or DHGD significantly decreased the aforementioned coagulation and ischemia biomarkers and increased serum nitric oxide. DHGD (natural) results seem to be more remarkable as compared to ATOR (synthetic).



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABSU:
-
Absorbance units
- ADMA:
-
Asymmetric dimethyl arginine
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ATOR:
-
Atorvastatin
- CETP:
-
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- DHGD:
-
10-Dehydrogingerdione
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- ET-1:
-
Endothelin-1
- FIB:
-
Fibrinogen
- HCD:
-
High cholesterol diet
- HDL-C:
-
High density lipoprotein cholesterol
- IMA:
-
Ischemia modified albumin
- LDL-C:
-
Low density lipoprotein cholesterol
- NC:
-
Normal control
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- ox-LDL:
-
Oxidized low density lipoprotein
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- PF1+2:
-
Prothrombin fragment (1+2)
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
References
Lusis AJ (2000) Atherosclerosis. Nature 407:233–241
Sobel BE, Taatjes DJ, Schneider DJ (2003) Intramural plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 and coronary atherosclerosis. Artherioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:1979–1989
Smith A, Patterson C, Yarnell J et al (2005) Which hemostatic markers add to the predictive value of conventional risk factors for coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke? The Caerphilly study. Circulation 112:3080–3087
Berberoğlu M, Evliyaoğlu O, Adiyaman P et al (2006) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) gene polymorphism (-675 4G/5G) associated with obesity and vascular risk in children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 19:741–748
Kuniyasu A, Tokunaga M, Yamamoto T et al (2011) Oxidized LDL and lyso-phosphatidyl choline stimulate plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expres-sion through reactive oxygen species generation and ERK1/2 activation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1811:153–162
Hansson GK (2005) Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 352:1685–1695
Eriksson EE (2004) Mechanisms of leukocyte recruitment to atherosclerotic lesions: future prospects. Curr Opin Lipidol 15:553–558
Bhandary B, Lee GH, Marahatta A et al (2012) Water extracts of immature Rubus coreanus regulate lipid metabolism in liver cells. Biol Pharm Bull 35:1907–1913
Akalin A, Temiz G, Akcar N, Sensoy B (2008) Short term effects of atorvastatin on endothelial functions and oxidized LDL levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr J 55:861–866
Ishihara Y, Ohmori K, Mizukawa M et al (2010) Beneficial direct adipotropic actions of pitavastatin in vitro and their manifestations in obese mice. Atherosclerosis 212:131–138
Lee SH, Cho KI, Kim JY et al (2012) Non-lipideffects of rosuvastatin-fenofibrate combination therapy in high-risk Asian patients with mixed hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis 221:169–175
Forrester JS, Makkar R, Shah PK (2005) Increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in dyslipidemia by cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibition: an update for clinicians. Circulation 111:1847–1854
Mohammadpour AH, Akhlaghi F (2013) Future of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitors: a pharmacological perspective. Clin Pharmacokinet 52(8):615–626
Jin S, Cho KH (2011) Water extracts of cinnamon and clove exhibits potent inhibition of protein glycation and anti-atherosclerotic activity in vitro and in vivo hypolipidemic activity in zebrafish. Food Chem Toxicol 49:1521–1529
Ghorai M, Mandal SC, Pal M et al (2000) A comparative study on hypocholesterolaemic effect of allicin, whole germinated seeds of bengal gram and guggulipid of gum gugglu. Phytother Res 14:200–202
Choi SY, Park GS, Lee SY et al (2011) The conformation and CETP inhibitory activity of [10]-dehydrogingerdione isolated from Zingiber officinale. Arch Pharm Res 34:727–731
El-Seweidy MM, Abdallah FR, Eldohmy S et al (2013) 10-Dehydrogingerdione raises HDL-cholesterol through a CETP inhibition and wards off oxidation and inflammation in dyslipidaemic rabbits. Atherosclerosis 213:334–340
Chapman MJ (1980) Animal lipoproteins: chemistry, structure, and comparative aspects. J Lipid Res 21:789–853
Fan J, Challah M, Watanabe T (1999) Transgenic rabbit models for biomedical research: current status, basic methods and future perspectives. Pathol Int 49:583–594
Madhumathi BG, Venkataranganna MV, Gopumadhavan S et al (2006) Induction and evaluation of atherosclerosis in New Zealand white rabbits. Indian J Exp Biol 44:203–208
Kitahara M, Kanaki T, Ishii I, Saito Y (2010) Atherosclerosis induced by chronic inhibition of the synthesis of nitric oxide in moderately hypercholesterolaemic rabbits is suppressed by pitavastatin. Br J Pharmacol 159:1418–1428
Siempos II, Maniatis NA, Kopterides P et al (2010) Pretreatment with atorvastatin attenuates lung injury caused by high-stretch mechanical ventilation in an isolated rabbit lung model. Crit Care Med 38:1321–1328
Bar-Or D, Lau E, Winkler JV (2000) A novel assay for cobalt-albumin binding and its potential as a marker for myocardial ischemia: a preliminary report. J Emerg Med 19:311–315
Moshage H, Kok B, Heuzenga JR, Jansen PL (1995) Nitrite and nitrate determination in plasma: a critical evaluation. Clin Chem 41:892–896
Clauss A (1957) Rapid physiological coagulation method in determination of fibrinogen. Acta Haematol 17:237–246
Wei J, Ma C, Wang X (2006) Simvastatin inhibits tissue factor and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression of glomerular mesangial cells in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Biomed Res 27:149–155
Stoll LL, McCormick ML, Denning GM, Weintraub NL (2004) Antioxidant effects of statins. Drug Today 40:975–990
Hogue JC, Lamarche B, Tremblay AJ et al (2008) Differntial effect of ator-vastatin and fenofibrate on plasma oxidized low-density lipoprotein, inflammation markers, and cell adhesion molecules in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 57:380–386
Song CY, Kim BC, Lee HS (2008) Lovastatin inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor and transforming growth factor-β1 expression via a decrease in Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity in mesangial cells. Transl Res 151:27–35
Nomura S, Taniura T, Shouzu A et al (2012) Effects of pitavastatin on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in hyperlipidemic patients. Int J Gen Med 5:535–540
Deguchi H, Fernández JA, Griffin JH (2007) Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein and blood coagulability. Thromb Haemost 98:1160–1164
Deguchi H, Pecheniuk NM, Elias DJ et al (2005) High-density lipoprotein deficiency and dyslipoproteinemia associated with venous thrombosis in men. Circulation 112(6):893–899
Verma SK, Singh M, Jain P, Bordia A (2004) Protective effect of ginger, Zingiber officinale Rosc on experimental atherosclerosis in rabbits. Indian J Exp Biol 42:736–738
Böger RH, Lentz SR, Bode-Böger SM et al (2001) Elevation of asymmetrical dimethylarginine may mediate endothelial dysfunction during experimental hyperhomocysteinaemia in humans. Clin Sci (Lond) 100:161–167
Szilvássy Z, Csont T, Páli T et al (2001) Nitric oxide, peroxynitrite and cGMP in atherosclerosis-induced hypertension in rabbits: beneficial effects of cicletanine. J Vasc Res 38:39–46
Bolayirli IM, Aslan M, Balci H et al (2007) Effects of atorvastatin therapy on hypercholesterolemic rabbits with respect to oxidative stress, nitric oxide pathway and homocysteine. Life Sci 81:121–127
Maeso R, Aragoncillo P, Navarro-Cid J et al (2000) Effect of atorvastatin on endothelium-dependent constrictor factors in dyslipidemic rabbits. Gen Pharmacol 34:263–272
Hernández-Perera O, Pérez-Sala D, Navarro-Antolín J et al (1998) Effects of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors, atorvastatin and simvastatin, on the expression of endothelin-1 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 101:2711–2719
Rasmusen C, Cynober L, Couderc R (2005) Arginine and statins: relationship between the nitric oxide pathway and the atherosclerosis development. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 63:443–455
Rajamannan NM, Subramaniam M, Stock SR et al (2005) Atorvastatin inhibits calcification and enhances nitric oxide synthase production in the hypercholesterolaemic aortic valve. Heart 91:806–810
Vassalle C, Pratali L, Boni C et al (2008) An oxidative stress score as a combined measure of the pro-oxidant and anti-oxidant counterparts in patients with coronary artery disease. Clin Biochem 41:1162–1167
Roy D, Quiles J, Gaze DC et al (2006) Role of reactive oxygen species on the formation of the novel diagnostic marker ischemia modified albumin. Heart 92:113–114
Sbarouni E, Georgiadou P, Voudris V (2011) Ischemia modified albumin changes: review and clinical implications. Clin Chem Lab Med 49:177–184
Duarte MM, Rocha JB, Moresco RN et al (2009) Association between ischemia-modified albumin, lipids and inflammation biomarkers in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Clin Biochem 42:666–671
Bogavac-Stanojević N, Jelić-Ivanović Z, Spasojević-Kalimanovska V et al (2007) Lipid and inflammatory markers for the prediction of coronary artery disease: a multi-marker approach. Clin Biochem 40:1000–1006
Abramson JL, Hooper WC, Jones DP et al (2005) Association between novel oxidative stress markers and C-reactive protein among adults without clinical coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 178:115–121
Conflict of interest
The authors had no conflict of interest to disclose and declare that they did not receive any financial support for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Seweidy, M.M., Asker, M.ES., Eldahmy, S.I. et al. Haemostatic risk factors in dyslipidemic rabbits: role of 10-dehydrogingerdione as a new hypolipemic agent. J Thromb Thrombolysis 39, 196–202 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1150-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1150-x