Abstract
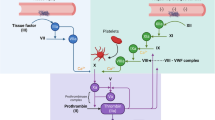
Monocytes and monocyte-derived microparticles (MMPs) play a major role in acute coronary syndrome (ASC). Activated monocytes (ac-M) and MMPs support thrombin generation via tissue factor (TF). The aim of this study was to evaluate the inhibitory effect of fondaparinux, a selective Xa inhibitor, on thrombin generation supported by activated monocytes and MMPs. Monocytes were purified by elutriation. They were activated by LPS, allowing to obtain both ac-M and MMPs. Thrombin generation was performed using Fluoroscan® in these two cell models, in comparison with a cell-free model (TF 5 pM final). Two concentrations of ac-M (0.2 × 106 and 1 × 106/well) and four concentrations of MMPs (40,000; 80,000; 120,000 and 160,000/well) were tested. TGT was evaluated for increasing fondaparinux concentrations (0, 0.1, 0.4, 0.7 and 1.2 μg/ml). Without fondaparinux, 0.2 × 106 ac-M and 160,000 MMPs induced comparable results. Fondaparinux inhibited thrombin generation in the three models. Inhibition was fondaparinux concentration dependent. Rate index was the most sensitive parameter, compared to lag-time, peak and endogenous thrombin potential. The rate index IC50 were 0.69 ± 0.03 μg/ml for ac-M, 0.20 ± 0.03 μg/ml for MMPs, and 0.22 ± 0.02 μg/ml for cell-free model. Fondaparinux exerted an inhibitory effect at all concentrations, including the lowest (0.1 μg/ml). The extend of inhibition was similar between MMPs and cell-free models, and stronger than ac-M model. We assume that the efficacy of fondaparinux 2.5 mg once daily in ACS patients may be in part attributed to its inhibitory effect on MMPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shantsila E, Lip GY (2009) Monocytes in acute coronary syndromes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1433–1438
Methe H, Kim JO, Kofler S, Weis M, Nabauer M, Koglin J (2005) Expansion of circulating toll-like receptor 4-positive monocytes in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Circulation 111:2654–2661
Leatham EW, Bath PM, Tooze JA, Camm AJ (1995) Increased monocyte tissue factor expression in coronary disease. Br Heart J 73:10–13
Ott I, Andrassy M, Zieglgänsberger D, Geith S, Schömig A, Eumann FJ (2001) Regulation of monocyte procoagulant activity in acute myocardial infraction: role of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor-1. Blood 97:3721–3726
Matsumoto N, Nomura S, Kamihata H, Kimura Y, Iwasaka T (2004) Increased level of oxidized LDL-dependent monocyte-derived microparticles in acute coronary syndrome. Thromb Haemost 91:146–154
Mallat Z, Hugel B, Ohan J, Lesèche G, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A (1999) Shed membrane microparticles with procoagulant potential in human atherosclerotic plaques: a role for apoptosis in plaque thrombogenicity. Circulation 99:348–353
Leroyer AS, Isobe H, Lesèche G, Castier Y, Wassef M, Mallat Z, Binder BR, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM (2007) Cellular origins and thrombogenic activity of microparticles isolated from human atherosclerotic plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:772–777
Bonderman D, Teml A, Jakowitsch J, Adlbrecht C, Gyöngyösi M, Sperker W, Lass H, Mosgoeller W, Glogar DH, Probst P, Maurer G, Nemerson Y, Lang IM (2002) Coronary no-reflow is caused by shedding of active tissue factor from dissected atherosclerotic plaque. Blood 99:2794–2800
Bauer KA (2004) Fondaparinux: a new synthetic and selective inhibitor of factor Xa. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 17:89–104
Mehta SR, Granger CB, Eikelboom JW, Bassand JP, Wallentin L, Faxon DP, Peters RJG, Budaj A, Afzal R, Chrolavicius S, Fox KAA, Yusuf S (2007) Efficacy and safety of fondaparinux versus enoxaparin in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Results from the OASIS-5 trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 50:1742–1751
Yusuf S, Mehta SR, Chrolavicius S, Afzal R, Pogue J, Granger CB, Budaj A, Peters RJG, Bassand JP, Wallentin L, Joyner C, Fox KAA (2006) Effects of fondaparinux on mortality and reinfarction in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the OASIS-6 randomized trial. JAMA 295:1519–1530
Nguyen P, Nguyen P, Broussas M, Cornillet-Lefebvre P, Potron G (1999) Coexpression of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor by human monocytes purified by leukapheresis and elutriation. Response of nonadherent cells to lipopolysaccharide. Transfusion 39:975–982
Poitevin S, Cochery-Nouvellon E, Dupont A, Nguyen P (2007) Monocyte IL-10 produced in response to lipopolysaccharide modulates thrombin generation by inhibiting tissue factor expression and release of active tissue factor-bound microparticles. Thromb Haemost 97:598–607
Hemker HC, Giesen P, AlDieri R, Regnault V, Smed ED, Wagenvoord R, Lecompte T, Béguin S (2002) The calibrated automated thrombogram (CAT): a universal routine test for hyper- and hypocoagulability. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 32:249–253
Petros S, Siegemund T, Siegemund A, Engelmann L (2006) The effect of different anticoagulants on thrombin generation. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 17:131–137
Gerotziafas GT, Petropoulou AD, Verdy E, Samama MM (2007) Effect of the anti-factor Xa and anti-factor IIa activities of low-molecular-weight heparins upon the phases of thrombin generation. J Thromb Haemost 5:955–962
Robert S, Ghiotto J, Pirotte B, David JL, Masereel B, Pochet L, Dogné JM (2009) Is thrombin generation the new rapid, reliable and relevant pharmacological tool for the development of anticoagulant drugs? Pharmacol Res 59:160–166
Hemker HC, Beguin S (2000) Phenotyping the clotting system. Thromb Haemost 84:747–751
Satta N, Toti F, Feugeas O, Bohbot A, Dachary-Prigent J, Eschwège V, Hedman H, Freyssinet JM (1994) Monocyte vesiculation is a possible mechanism for dissemination of membrane-associated procoagulant activities and adhesion molecules after stimulation by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 153:3245–3255
Biasucci LM, Biasillo G, Stefanelli A (2009) Procalcitonin and acute coronary syndromes: a new biomarker for old disease. Intern Emerg Med 4:363–365
Aharon A, Tamari T, Brenner B (2008) Monocyte-derived microparticles exosomes induce procoagulant and apoptotic effects on endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 100:878–885
Del Conde I, Shrimpton CN, Thiagarajan P, Lopez JA (2005) Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood 106:1604–1611
Osterud B (2001) The role of platelets in decrypting monocyte tissue factor. Semin Hematol 38:2–5
Shaw AW, Pureza VS, Sligar SG, Morrissey JH (2007) The local phospholipid environment modulates the activation of blood clotting. J Biol Chem 282:6556–6563
Morrissey JH, Pureza V, Davis-Harrison RL, Sligar SG, Ohkubo YZ, Tajkhorshid E (2008) Blood clotting reactions on nanoscale phospholipid bilayers. Thromb Res 122:23–26
Simoons ML, Bobbink IW, Boland J, Gardien M, Klootwijk P, Lensing AW, Ruzyllo W, Umans VA, Vahanian A, Van De Werf F, Zeymer U, PENTUA Investigators (2004) A dose-finding study of fondaparinux in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: the Pentasaccharide in Unstable Angina (PENTUA) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:2183–2190
Turpie AG, Eriksson BI, Lassen MR, Bauer KA (2002) A meta-analysis of fondaparinux versus enoxaparin in the prevention of venous thromboembolism after major orthopaedic surgery. J South Orthop Assoc 11:182–188
Büller HR, Davidson BL, Decousus H, Gallus A, Gent M, Piovella F, Prins MH, Raskob G, van den Berg-Segers AE, Cariou R, Leeuwenkamp O, Lensing AW, Matisse Investigators (2003) Subcutaneous fondaparinux versus intravenous unfractionated heparin in the initial treatment of pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 349:1695–1702
Anderson JAM, Hirsh J, Yusuf S, Johnston M, Afzal R, Mehta SR, Fox KAA, Budaj A, Eikelboom JW (2010) Comparison of the anticoagulant intensities of fondaparinux and enoxaparin in the organisation to assess strategies in acute ischemic syndromes (OASIS)-5 trial. J Thromb Haemost 8:243–249
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the excellent laboratory assistance from G. Simon. We also thank C. Mace for her expertise in statistics.
Disclosure and conflict of interests statement
The authors state they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Hadj-Khalifa-Kechiche, S., Hezard, N., Poitevin, S. et al. Differential inhibitory effect of fondaparinux on the procoagulant potential of intact monocytes and monocyte-derived microparticles. J Thromb Thrombolysis 30, 412–418 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-010-0490-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-010-0490-4