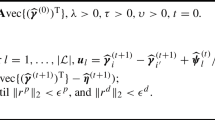Abstract
This article proposes a mixture modeling approach to estimating cluster-wise conditional distributions in clustered (grouped) data. We adapt the mixture-of-experts model to the latent distributions, and propose a model in which each cluster-wise density is represented as a mixture of latent experts with cluster-wise mixing proportions distributed as Dirichlet distribution. The model parameters are estimated by maximizing the marginal likelihood function using a newly developed Monte Carlo Expectation–Maximization algorithm. We also extend the model such that the distribution of cluster-wise mixing proportions depends on some cluster-level covariates. The finite sample performance of the proposed model is compared with some existing mixture modeling approaches as well as mixed effects models through the simulation studies. The proposed model is also illustrated with the posted land price data in Japan.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demidenko, E.: Mixed Models: Theory and Applications. Wiley, New York (2004)
Dempster, A., Laird, N., Rubin, D.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. B 39, 1–38 (1977)
Doornik, J.: Ox: Object Oriented Matrix Programming. Timberlake Consultants Press, London (2007)
Geweke, J., Keane, M.: Smoothly mixing regressions. J. Econom. 138, 252–290 (2007)
Hurn, M., Justel, A., Robert, C.P.: Estimating mixtures of regressions. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 12, 55–79 (2003)
Jacobs, R.A., Jordan, M.I., Nowlan, S.J., Hinton, G.E.: Adaptive mixtures of local experts. Neural Comput. 3, 79–87 (1991)
Jordan, M.I., Jacobs, R.A.: Hierarchical mixtures of experts and the EM algorithm. Neural Comput. 214, 181–214 (1994)
McLachlan, G.J., Peel, D.: Finite Mixture Models. Wiley, New York (2000)
Ng, S.K., McLachlan, G.J.: Extension of mixture-of-experts networks for binary classification of hierarchical data. Artif. Intell. Med. 41, 57–67 (2007)
Ng, S.K., McLachlan, G.J.: Mixture models for clustering multilevel growth trajectories. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 71, 43–51 (2014)
Nguyen, H.D., McLachlan, G.J.: Laplace mixture of linear experts. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 93, 177–191 (2016)
Rosen, O., Jiang, W., Tanner, M.A.: Mixtures of marginal models. Biometrika 87, 391–404 (2000)
Rubin, D.B., Wu, Y.: Modeling schizophrenic behavior using general mixture components. Biometrics 53, 243–261 (1997)
Shi, J.Q., Copas, J.: Publication bias and meta-analysis for 2\(\times \)2 tables: an average Markov chain Monte Carlo EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 64, 221–236 (2002)
Sun, Z., Rosen, O., Sampson, A.R.: Multivariate Bernoulli mixture models with application to postmortem tissue studies in schizophrenia. Biometrics 63, 901–909 (2007)
Tang, X., Qu, A.: Mixture modeling for longitudinal data. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 25, 1117–1137 (2016)
Vermunt, J.K.: A hierarchical mixture model for clustering three-way data sets. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 51, 5368–5376 (2007)
Villani, M., Kohn, R., Giordani, P.: Regression density estimation using smooth adaptive Gaussian mixtures. J. Econom. 153, 155–173 (2009)
Villani, M., Kohn, R., Nott, D.J.: Generalized smooth finite mixtures. J. Econom. 171, 121–133 (2012)
Wei, G.C.G., Tanner, M.A.: A Monte Carlo implementation of the EM algorithm and the poor man’s data augmentation algorithm. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 85, 699–704 (1990)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Nos. [16H07406, 15K17036, 16K17101, 18K12754, 18K12757]. The computational results were obtained using Ox version 6.21 (Doornik 2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugasawa, S., Kobayashi, G. & Kawakubo, Y. Latent mixture modeling for clustered data. Stat Comput 29, 537–548 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-018-9821-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-018-9821-7