Abstract
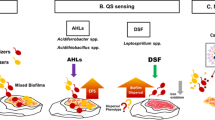
Aerobic granular sludge (AGS) has recently attracted attention because of its excellent settling ability and treatment efficiency compared with traditional activated sludge. This review provides recent advances on the formation process of AGS and mainly analyzes the function of quorum sensing (QS) and cell signaling during AGS formation. QS and cell signaling play important roles in the formation of AGS. QS can accelerate the synthesis of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) and increase microbial adhesion to the surface of AGS. Cell signaling can also promote the secretion of EPS and influence biofilm formation. Cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP), as a second messenger, acts an important role in granulation. C-di-GMP causes bacteria to adhere to each other and form a biofilm. Adding Ca2+ benefits bacterial growth and promotes c-di-GMP secretion. Adding Mn2+ reduces c-di-GMP content and triggers AGS disintegration. Finally, the review discusses the possible trends of AGS: QS and cell signaling can lay a theoretical foundation for the formation mechanism of AGS and would be of practical significance for its application in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rhman SH, El-Mahdy AM, El-Mowafy M (2015) Effect of tyrosol and farnesol on virulence and antibiotic resistance of clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biomed Res Int 2015:456463
Adav SS, Chen MY, Lee DJ, Ren NQ (2007a) Degradation of phenol by Acinetobacter strain isolated from aerobic granules. Chemosphere 67(8):1566–1572
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2007b) Effects of aeration intensity on formation of phenol-fed aerobic granules and extracellular polymeric substances. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77(1):175–182
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2007c) Activity and structure of stored aerobic granules. Environ Technol 28:1227–1235
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Show KY, Tay JH (2008a) Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 26(5):411–423
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2008b) Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule. Water Res 42(6–7):1644–1650
Adriana DRP, Maurilio Lopes M, Elza Fernandes DA, Hilário Cuquetto M, Vanetti MCD (2012) AiiA quorum-sensing quenching controls proteolytic activity and biofilm formation by Enterobacter cloacae. Curr Microbiol 65(6):758–763
Becvar JE, Tu SC, Hastings JW (1978) Activity and stability of the luciferase–flavin intermediate. Biochemistry 17(9):1807–1812
Blana VA, Nychas GJE (2014) Presence of quorum sensing signal molecules in minced beef stored under various temperature and packaging conditions. Int J Food Microbiol 173(3):1–8
Brackman G, Al Quntar AA, Enk CD, Karalic I, Nelis HJ, Van Calenbergh S (2013) Synthesis and evaluation of thiazolidinedione and dioxazaborocaneanalogues as inhibitors of AI-2 quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Bioorgan Med Chem 21(3):660–667
Bronesky D, Wu ZF, Marzi S, Walter P (2016) Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII and its regulon link quorum sensing, stress responses, metabolic adaptation, and regulation of virulence gene expression. Annu Rev Microbiol 70:299–316
Caudan C, Filali A, Spérandio M, Girbal-Neuhauser E (2014) Multiple EPS interactions involved in the cohesion and structure of aerobic granules. Chemosphere 117(1):262–270
Chen G, Strevett KA (2003) Impact of carbon and nitrogen conditions on E. coli surface thermodynamics. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 28:135–146
Chen MY, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2007a) Distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic granule. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73(6):1463–1469
Chen MY, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2007b) Staining of extracellular polymeric substances and cells in bioaggregates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:467–474
Dagkessamanskaia AMM, Henard V, Guiral S, Overweg K, Reuter M, Martin B (2004) Interconnection of competence, stress and CiaR regulons in Streptococcus pneumoniae: competence triggers stationary phase autolysis of ciaR mutant cells. Mol Microbiol 51(4):1071–1086
de Kreuk MK, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Selection of slow growing organisms as a means for improving aerobic granular sludge stability. Water Sci Technol 49:9–17
Dickschat JS (2010) Quorum sensing and bacterial biofilms. Nat Prod Rep 27(3):343–369
Diggle SP, Griffin AS, Campbell GS, West SA (2007) Cooperation and conflict in quorum-sensing bacterial populations. Nature 450(7168):411-U7
Ding C, Wang Z, Cai W, Zhou Q, Zhou J (2014) Biodegradation of phenol with Candida tropicalis isolated from aerobic granules. Fresen Environ Bull 23(3):887–895
Duanis-Assaf D, Steinberg D, Chai Y, Shemesh M (2016) The LuxS based quorum sensing governs lactose induced biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis. Front Microbiol 6(907):302–309
Frederick MR, Kuttler C, Hense BA, Eberl HJ (2011) A mathematical model of quorum sensing regulated EPS production in biofilm communities. Theor Biol Med Model 8(9):1293–1300
Galloway WRJD, Hodgkinson JT, Bowden SD, Welch M, Spring DR (2011) Quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: small-molecule modulation of AHL and Al-2 quorum sensing pathways. Chem Rev 111(1):28–67
García-Contreras R, Nuñez-López L, Jasso-Chávez R, Kwan BW, Belmont JA, Rangel-Vega A (2014) Quorum sensing enhancement of the stress response promotes resistance to quorum quenching and prevents social cheating. ISME J 9(7):115–125
Garnier C, Görner T, Lartiges BS, Abdelouhab S, De Donato P (2005) Characterization of activated sludge exopolymers from various origins: a combined size-exclusion chromatography and infrared microscopy study. Water Res 39:3044–3054
Han GS, Carman GM (2002) Phosphorylation of the yeast diacylglycerol pyrophosphate phosphatase. FASEB J 16(5):A1184
Hengge R, Gründling A, Jenal U, Ryan R, Yildiz F (2015) Bacterial signal transduction by c-di-GMP and other nucleotide second messengers. J Bacteriol 56(1):211–214
Hu SQ, Gao YG, Tajima K, Sunagawa N, Zhou Y, Kawano S (2010) Structure of bacterial cellulose synthase subunit D octamer with four inner passageways. PNAS 107:17957–17961
Huang BX, Whitchurch CB, Mattick JS (2003) FimX, a multidomain protein connecting environmental signals to twitching motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 185(24):7068–7076
Ionescu IA, Bumbac C, Cornea P (2015) Formation of aerobic granules in sequencing batch reactor SBR treating dairy industry wastewater. Sci Bull 7(2):121–124
Jenal U, Malone J (2006) Mechanisms of cyclic-di-GMP signaling in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet 40:385–407
Jiang B, Liu Y (2012) Roles of ATP-dependent N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in aerobic granulation. Chemosphere 88(9):1058–1064
Jiang B, Yu L (2013) Dependence of structure stability and integrity of aerobic granules on ATP and cell communication. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(11):5105–5112
Kalia VC (2013) Quorum sensing inhibitors: an overview. Biotechnol Adv 31(2):224–245
Kamegaya T, Kuroda K, Hayakawa Y (2011) Identification of a Streptococcus pyogenes SF370 gene involved in production of c-di-AMP. Nagoya J Med Sci 73(1–2):49–57
Leadbetter JR, Greenberg EP (2000) Metabolism of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Variovorax paradoxus. J Bacteriol 182(24):6921–6926
Li J, Ding LB, Cai A, Huang GX, Horn H (2014) Aerobic sludge granulation in a full-scale sequencing batch reactor. Biomed Res Int 10(2):687–689
Liang ZX (2015) The expanding roles of c-di-GMP in the biosynthesis of exopolysaccharides and secondary metabolites. Nat Prod Rep 32(5):140–144
Lin YM, de Kreuk M, van Loosdrecht Mark (2010) Characterization of alginate-like exopolysaccharides isolated from aerobic granular sludge in pilot-plant. Water Res 44(11):3355–3364
Liu Y, Liu QS (2006) Causes and control of filamentous growth in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol Adv 24:115–127
Liu Y, Tay JH (2002) The essential role of hydrodynamic shear force in the formation of biofilm and granular sludge. Water Res 36(7):1653–1665
Liu YQ, Tay JH (2015) Fast formation of aerobic granules by combining strong hydraulic selection pressure with overstressed organic loading rate. Water Res 80(1):256–266
Liu Y, Yang SF, Tan SF, Lin YM, Tay JH (2002) Aerobic granules: a novel zinc biosorbent. Lett Appl Microbiol 35(6):548–551
Liu Y, Yang SF, Liu QS, Tay JH (2003) The role of cell hydrophobicity in the formation of aerobic granules. Curr Microbiol 46:270–274
Liu Y, Yang SY, Tay JH, Liu QS, Qin L, Li Y (2004) Cell hydrophobicity is a triggering force of biogranulation. Enzyme Microb Technol 34:371–379
Liu YQ, Moy B, Kong YH (2010) Formation, physical characteristics and microbial community structure of aerobic granules in a pilot-scale sequencing batch reactor for real wastewater treatment. Enzyme Microb Technol 46(6):520–525
Liu X, Sun SP, Ma BY, Zhang C, Wan CL, Lee DJ (2016) Understanding of aerobic granulation enhanced by starvation in the perspective of quorum sensing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(8):3747–3755
Luo JH, Wei L, Hao TW (2015) Effect of l-tyrosine on aerobic sludge granulation and its stability. RSC Adv 5(105):86513–86521
Lv J, Wang Y, Zhong C (2014) The effect of quorum sensing and extracellular proteins on the microbial attachment of aerobic granular activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 152:53–58
Mañas A, Biscans B, Spérandio M (2011) Biologically induced phosphorus precipitation in aerobic granular sludge process. Water Res 45(12):3776–3786
Martinez P, Huedo P, Martinez-Servat S, Plane R (2015) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia responds to exogenous AHL signals through the LuxR solo SmoR (SmIt1839). Front Cell Infect Microbiol 5:41
Matsuyama BY, Krasteva PV, Baraquet C, Harwood CS, Sondermann H (2016) Mechanistic insights into c-di-GMP-dependent control of the biofilmregulator FleQ from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PNAS 113(2):E209–E218
Merritt JH, Ha DG, Cowles KN, Lu W, Morales DK, Rabinowitz J (2010) Specific control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa surface-associated behaviors by two c-di-GMP diguanylate cyclases. mBio 1(4):1–9
Mills E, Pultz IS, Kulasekara HD, Miller SI (2011) The bacterial second messenger c-di-GMP: mechanisms of signalling. Cell Microbiol 13:1122–1129
Ni BJ, Yu H (2009) Mathematical modeling of aerobic granular sludge: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28(6):895–909
Ni BJ, Sheng GP, LiXY YuHQ (2010) Quantitative simulation of the granulation process of activated sludgefor wastewater treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 49(6):2864–2873
Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Wexselblatt E, Katzhendler J, Yavin E, Ben-Yehuda S (2011) c-di-AMP reports DNA integrity during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO Rep 12(6):594–601
Palm JC, Jenkins D, Parker DS (1980) Relationship between organic loading, dissolved oxygen concentration and sludge settleability in the completely mixed activated sludge process. J Water Pollut Control Fed 52:2484–2506
Pei D, Zhu J (2004) Mechanism of action of S-ribosylhomocysteinase (LuxS). Curr Opin Chem Biol 8(5):492–497
Peterson SN, Sung CK, Cline R, Desai BV (2004) Identification of competence pheromone responsive genes in Streptococcus pneumoniae by use of DNA microarrays. Mol Microbiol 51(4):1051–1070
Pronk M, Kreuk MK, Bruin BD, Kamminga P, Kleerebezem R, Loosdrecht MCM (2015) Full scale performance of the aerobic granular sludge process for sewage treatment. Water Res 84(3):207–217
Rasmussen TB, Givskov M (2006) Quorum sensing inhibitors: a bargain of effects. Microbiol 152(4):895–904
Ren TT, Yu HQ, Li XY (2010) The quorum-sensing effect of aerobic granules on bacterial adhesion, biofilm formation, and sludge granulation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88(3):789–797
Rod MN, Lamont RJ (2003) Microbial dinner-party conversations: the role of LuxS in interspecies communication. J Med Microbiol 52(7):541–545
Rossetti S, Tomei MC, Nielsen PH, Tandoi V (2005) “Microthrix parvicella”, lamentous bacterium causing bulking and foaming in activated sludge systems: a review of current knowledge. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:49–64
Russell MH, Bible AN, Fang X, Gooding JR, Campagna SR, Gomelsky M (2014) Integration of the second messenger c-di-GMP into the chemotactic signaling pathway. Nagoya J Med Sci 41(1):74–78
Rutherford ST, Bassler BL (2012) Bacterial quorum sensing: its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. CSH Perspect Med 2(11):705–709
Sanin SL (2003) Effect of starvation on resuscitation and the surface characteristics of bacteria. J Environ Sci Health A 38:1517–1528
Schaefer AL, Greenberg EP, Oliver CM, Oda Y, Huang JJ (2008) A new class of homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals. Nature 454(7204):595-U6
Schumacher MA, Zeng WJ (2016) Structures of the activator of K. pneumonia biofilm formation, MrkH, indicates PilZ domains involved in c-di-GMP and DNA binding. PNAS 113(36):10067–10072
Schuster M, Greenberg EP (2006) A network of networks: quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Med Microbiol 296(2):73–81
Schwarzenbeck N, Borges JM, Wilderer PA (2005) Treatment of dairy effluents in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:711–718
Song Z, Ning T, Wang Q (2015) Cultivation and characteristics of aerobic nitrifying granules. Chin J Environ Eng 9(1):200–206
Soni D, Smoum R, Breuer A, Mechoulam R, Steinberg D (2014) Effect of the synthetic cannabinoid HU-210 on quorum sensing and on the production of quorum sensing-mediated virulence factors by Vibrio harveyi. BMC Microbiol 15(1):1–10
Sun SP, Liu X, Ma BY (2016) The role of autoinducer-2 in aerobic granulation using alternating feed loadings strategy. Bioresour Technol 201:58–64
Surette MG, Miller MB, Bassler BL (1999) Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Vibrio harveyi: anew family of genes responsible for autoinducer production. PNAS 96(4):1639–1644
Tan CH, Koh KS, Xie C, Tay M, Zhou Y (2014) The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. ISME J 8(6):1186–1197
Tay JH, Liu QS, Liu Y (2001) The role of cellular polysaccharides in the formation and stability of aerobic granules. Lett Appl Microbiol 33(3):222–226
Ulitzur S, Hastings JW (1978) Myristic acid stimulation of bacterial bioluminescence in “aldehyde” mutants. PNAS 75(1):266–269
Valle A, Bailey MJ, Whiteley AS, Manefield M (2004) N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones (AHLs) affect microbial community composition and function in activated sludge. Environ Microbiol 6(4):424–433
Wan C, Peng Z, Lee DJ, Xue Y, Xiang L, Sun S (2013) Disintegration of aerobic granules: role of second messenger cyclic di-GMP. Bioresour Technol 146(10):330–335
Wan C, Chen S, Wen L, Lee DJ (2015a) Formation of bacterial aerobic granules: role of propionate. Bioresour Technol 197:489–494
Wan C, Lee DJ, Yang X, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu X (2015b) Calcium precipitate induced aerobic granulation. Bioresour Technol 176(1):32–37
Wang XM (2005) Regulatory functions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Physiol 139(2):566–573
Wang XH, Zhang HM, Yang FL, Xia LP, Gao MM (2007) Improved stability and performance of aerobic granules under stepwise increased selection pressure. Enzyme Microb Technol 41(3):205–211
Wang S, Shi WX, Yu SL, Yi XS, Yang X (2012) Formation of aerobic granules by Mg2+ and Al3+ augmentation in sequencing batch airlift reactor at low temperature. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35(7):1049–1055
Waters CM, Bassler BL (2005) Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21(1):319–346
Wen Z, Lan L (2012) Research progress of bacterial quorum sensing-signal molecule. Chin J Antibiot 37(6):431–436
West SA, Griffin AS, Andy G, Diggle SP (2006) Social evolution theory for microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(8):597–607
Whiteley CG, Lee DJ (2015) Bacterial diguanylate cyclases: structure, function and mechanism in exopolysaccharide biofilm development. Biotechnol Adv 33:124–141
Whitney JC, Colvin KM, Marmont LS, Robinson H, Parsek MR, Howell PL (2012) Structure of the cytoplasmic region of PelD, a degenerate diguanylate cyclase receptor that regulates exopolysaccharide production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 287:23582–23593
Xiong Y, Liu Y (2010) Involvement of ATP and autoinducer-2 in aerobic granulation. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(1):51–58
Xiong Y, Liu Y (2012) Essential roles of eDNA and AI-2 in aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors operated at different settling times. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:2645–2651
Xue T, Zhao LP, Sun HP, Zhou XX, Sun BL (2009) LsrR-binding site recognition and regulatory characteristics in Escherichia coli AI-2 quorum sensing. Cell Res 19(11):1258–1268
Zhang WW, Li CH (2016) Exploiting quorum sensing interfering strategies in gram-negative bacteria for the enhancement of environmental applications. Front Microbiol 6:1–15
Zhang Y, Tay JH (2015) Toxic and inhibitory effects of trichloroethylene aerobic co-metabolism on phenol-grown aerobic granules. J Hazard Mater 286(1):204–210
Zhang LL, Feng XX, Zhu NW, Chen JM (2007) Role of extracellular protein in the formation and stability of aerobic granules. Enzyme Microb Technol 41(5):551–557
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51408264), the Practice Innovation Program (2015) for University Graduate Students of Jiangsu Province (No. SJLX15_0564), the State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse Foundation (No. PCRRF13022), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. JUSRP51512).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Shi, W., Tang, T. et al. Function of quorum sensing and cell signaling in the formation of aerobic granular sludge. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 16, 1–13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-017-9420-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-017-9420-7