Abstract
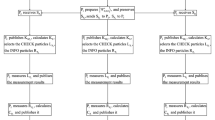
A secure multiparty quantum key agreement protocol using single-qubit states is proposed. The agreement key is computed by performing exclusive-OR operation on all the participants’ secret keys. Based on the commutative property of the commutative encryption, the exclusive-OR operation can be performed on the plaintext in the encrypted state without decrypting it. Thus, it not only protects the final shared key, but also reduces the complexity of the computation. The efficiency of the proposed protocol, compared with previous multiparty QKA protocols, is also improved. In the presented protocol, entanglement states, joint measurement and even the unitary operations are not needed, and only rotation operations and single-state measurement are required, which are easier to be realized with current technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121 (1992)
Goldenberg, L., Vaidman, L.: Quantum cryptography based on orthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 1239 (1995)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Shor, Pw, Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441 (2000)
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22, 644–654 (1976)
Shor P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logrithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134 (1994)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Du, R.G., Sun, Z.W., Wang, B.H., Long, D.Y.: Quantum secret sharing of secure direct communication using one-time pad. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 2727–2736 (2012)
Sun, Z.W., Du, R.G., Long, D.Y.: Quantum secure direct communication with quantum identification. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 10, 1250008 (2012)
Sun, Zw, Du, R.G., Long, D.Y.: Quantum secure direct communication with two-photon four-qubit cluster state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 1946–1952 (2012)
Chen, X.B., Xu, G., Niu, X.X., Wen, Q.Y., Yang, Y.X.: An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on the triplet entangled state and single-particle measurement. Opt. Commun. 283, 1561–1565 (2010)
Sun, Zw, Long, D.Y.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 212–218 (2013)
Sun, Z.W., Yu, J.P., Wang, P., Xu, L.L., Wu, C.H.: Quantum private comparison with a malicious third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(6), 2125–2133 (2015)
Sun, Zhiwei, Jianping, Yu., Wang, Ping, Lingling, Xu: Symmetrically private information retrieval based on blind quantum computing. Phys. Rev. A 91, 052303 (2015)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40(18), 1149 (2004)
Tsai, C., Hwang, T.: On quantum key agreement protocol. R.O.C, Technical Report, C-S-I-E, NCKU, Taiwan (2009)
Chong, S.K., Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: Improvement on quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(6), 1793–1802 (2011)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Commun. 283(6), 1192–1195 (2010)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Sun, Y.: Quantum key agreement with EPR pairs and single particle measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(3), 649–663 (2014)
Dongsu, Shen, Wenping, Ma., Lili, Wang: Two-party quantum key agreement with four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2313 (2014)
Sun, Zhiwei, Jianping, Yu., Wang, Ping: Efficient multiparty quantum key agreement by cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(1), 373–384 (2016)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with bell states and bell measurements. Quantum Inf. Process 12(2), 921–932 (2013)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(4), 1797–1805 (2013)
Sun, Z., Wang, B., Li, Q., Long, D.: Improvements on multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 3411 (2013)
Yin, X.R., Ma, W.P., Liu, W.Y.: Three-party quantum key agreement with two-photon entanglement. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 3915–3921 (2013)
Chitra, S., Nasir, A., Anirban, P.: Protocols of quantum key agreement solely using bell states and bell measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2391–2405 (2014)
Kanamori, Yoshito, Yoo, Seong-Moo, Gregory, Don A., Sheldon, Frederick T.: Authentication protocol using quantum superposition states. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 9(2), 101–108 (2009)
Hwang, Won-Young: Quantum key distribution with high loss: toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 057901 (2003)
Lo, Hoi-Kwong, Ma, Xiongfeng, Chen, Kai: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230504 (2005)
Wang, Xiang-Bin: Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230503 (2005)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., Zhang, Z.J.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against Trojan horse attack. Phys. Rev. A 72, 044302 (2005)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Improving the security of secure direct communication based on the secret transmitting order of particles. Phys. Rev. A 74, 054302 (2006)
Cai, Q.Y.: Eavesdropping on the two-way quantum communication protocols with invisible photons. Phys. Lett. A 351, 23–25 (2006)
Lin, J., Hwang, T.: New circular quantum secret sharing for remote agents. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 685 (2013)
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5633–5638 (2000)
Liu, W.-J., Liu, C., Chen, H.-W., Liu, Z.-H., Yuan, M.-X., Lu, J.-S.: Improvement on “an efficient protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with W state”. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 12(01), 1450001 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the anonymous referees for their valuable comments and suggestions that help to improve the paper. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61402293, 61300204), Seed Funding from Scientific and Technical Innovation Council of Shenzhen Government (No. 827-000035), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (2015A030313630), Opening Project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Integrated Administration Technologies for Information Security, the Science and Technology Innovation Projects of Shenzhen (Nos. JCYJ20150324141711665 and JCYJ20150324141711694), Natural Science Foundation of SZU (No. 201435), Shenzhen R&D Program (GJHZ20140418191518323) and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (No. 2015M572360).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Huang, J. & Wang, P. Efficient multiparty quantum key agreement protocol based on commutative encryption. Quantum Inf Process 15, 2101–2111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1253-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1253-8