Abstract
Background and Aims
Interspecific differences have been clearly shown in the contribution of endogenous spatial autocorrelation (caused by dispersal) to the spatial structure of undisturbed vegetation. However, this phenomenon has not been studied in industrially polluted areas, where heavy metals’ excess is traditionally considered to be the main driver of ecosystem processes. We compare the contributions of endogenous autocorrelation and environmental parameters to the distribution of herbaceous plants in open and forested sites heavily polluted with copper smelter emissions.
Methods
Principal coordinates of neighbour matrices were used to create spatial predictors that were incorporated into beta regression models together with environmental predictors. Their importance for species’ spatial structure was assessed using multimodel inference and variation partitioning approach.
Results
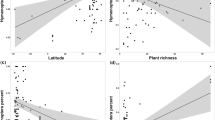
Equisetum sylvaticum, Leucanthemum vulgare, Tussilago farfara, Carex rostrata, Scirpus sylvaticus and Deschampsia cespitosa responded strongly to soil toxicity, while Agrostis capillaris and Lychnis flos-cuculi, to microtopography and tree disposition. Endogenous autocorrelation was strongly pronounced in L. flos-cuculi distribution across all study sites and was substantial for A. capillaris in open areas.
Conclusion
Despite the extreme level of soil toxicity, the importance of other environmental parameters and endogenous autocorrelation remarkably differed among species, resulting from interspecific differences in ecological preferences and dispersal mode.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba M, Takafumi H, Hiura T (2012) Interspecific differences in determinants of plant species distribution and the relationships with functional traits. J Ecol 100:950–957. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2012.01959.x
Alameda D, Villar R, Iriondo JM (2012) Spatial pattern of soil compaction: trees’ footprint on soil physical properties. For Ecol Manag 283:128–137. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2012.07.018
Andersen R, Poulin M, Borcard D, Laiho R, Laine J, Vasander H, Tuittila ET (2011) Environmental control and spatial structures in peatland vegetation. J Veg Sci 22:878–890. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2011.01295.x
Antonovics J, Bradshaw AD, Turner RG (1971) Heavy metal tolerance in plants. In: Cragg JB (ed) Advances in Ecological Research. Academic Press 7:1–85. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60202-0
Baker AJM (1987) Metal tolerance. New Phytol 106:93–111. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1987.tb04685.x
Borcard D, Legendre P (2002) All-scale spatial analysis of ecological data by means of principal coordinates of neighbour matrices. Ecol Model 153:51–68. doi:10.1016/S0304-3800(01)00501-4
Borcard D, Legendre P, Drapeau P (1992) Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation. Ecology 73:1045–1055. doi:10.2307/1940179
Bowman G, Perret C, Hoehn S, Galeuchet DJ, Fischer M (2008) Habitat fragmentation and adaptation: a reciprocal replant-transplant experiment among 15 populations of Lychnis flos-cuculi. J Ecol 96:1056–1064. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2008.01417.x
Bradshaw AD (1960) Population differentiation in Agrostis tenuis Sibth. III. Populations in varied environments. New Phytol 59:92–103. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1960.tb06206.x
Bramley H, Tyerman SD, Turner DW, Turner NC (2011) Root growth of lupins is more sensitive to waterlogging than wheat. Funct Plant Biol 38:910–918. doi:10.1071/Fp11148
Brown SL, Chaney RL, Angle JS, Baker AJM (1994) Phytoremediation potential of Thlaspi caerulescens and bladder campion for zinc-contaminated and cadmium-contaminated soil. J Environ Qual 23:1151–1157
Buckland ST, Burnham KP, Augustin NH (1997) Model selection: an integral part of inference. Biometrics 53:603–618. doi:10.2307/2533961
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Burnham KP, Anderson DR, Huyvaert KP (2011) AIC model selection and multimodel inference in behavioral ecology: some background, observations, and comparisons. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 65:23–35. doi:10.1007/s00265-010-1029-6
Calcagno V, de Mazancourt C (2010) Glmulti: an R package for easy automated model selection with (generalized) linear models. J Stat Softw 34:1–29
Chaloupecká E, Lepš J (2004) Equivalence of competitor effects and tradeoff between vegetative multiplication and generative reproduction: case study with Lychnis flos-cuculi and Myosotis nemorosa. Flora 199:157–167
Chiapella J, Probatova NS (2003) The Deschampsia cespitosa complex (Poaceae: Aveneae) with special reference to Russia. Bot J Linn Soc 142:213–228. doi:10.1046/j.1095-8339.2003.00167.x
Cox RM, Hutchinson TC (1980) Multiple metal tolerances in the grass Deschampsia cespitosa (L.) Beauv. from the Sudbury smelting area. New Phytol 84:631–647. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1980.tb04777.x
Cribari-Neto F, Zeileis A (2010) Beta regression in R. J Stat Softw 34:1–24
Davy AJ (1980) Biological flora of the British Isles. Deschampsia caespitosa (L.) Beauv. J Ecol 62:367–378
Desjardins D, Nissim WG, Pitre FE, Naud A, Labrecque M (2014) Distribution patterns of spontaneous vegetation and pollution at a former decantation basin in southern Québec, Canada. Ecol Eng 64:385–390. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.01.003
Dray S, Legendre P, Peres-Neto PR (2006) Spatial modelling: a comprehensive framework for principal coordinate analysis of neighbour matrices (PCNM). Ecol Model 196:483–493. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.02.015
Dray S et al (2012) Community ecology in the age of multivariate multiscale spatial analysis. Ecol Monogr 82:257–275. doi:10.1890/11-1183.1
Dulya OV, Mikryukov VS, Vorobeichik EL (2013) Strategies of adaptation to heavy metal pollution in Deschampsia caespitosa and Lychnis flos-cuculi: analysis based on dose–response relationship. Russ J Ecol 44:271–281. doi:10.1134/S1067413613040036
Ferrari SLP, Cribari-Neto F (2004) Beta regression for modelling rates and proportions. J Appl Stat 31:799–815. doi:10.1080/0266476042000214501
Flinn KM, Gouhier TC, Lechowicz MJ, Waterway MJ (2010) The role of dispersal in shaping plant community composition of wetlands within an old-growth forest. J Ecol 98:1292–1299. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2010.01708.x
Fortin M-J, Dale MRT (2005) Spatial analysis: a guide for ecologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Foster BL, Gross KL (1998) Species richness in a successional grassland: effects of nitrogen enrichment and plant litter. Ecology 79:2593–2602. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(1998)079[2593:Sriasg]2.0.Co;2
Gallardo A, Parama R, Covelo F (2006) Differences between soil ammonium and nitrate spatial pattern in six plant communities. Simulated effect on plant populations. Plant Soil 279:333–346. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-8552-7
Gelman A (2008) Scaling regression inputs by dividing by two standard deviations. Stat Med 27:2865–2873. doi:10.1002/Sim.3107
Halpern CB, Haugo RD, Antos JA, Kaas SS, Kilanowski AL (2012) Grassland restoration with and without fire: evidence from a tree-removal experiment. Ecol Appl 22:425–441
Haugo RD, Halpern CB (2010) Tree age and tree species shape positive and negative interactions in a montane meadow. Botany 88:488–499. doi:10.1139/B10-018
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69:373–386. doi:10.2307/3545850
Kaigorodova SY, Vorobeichik EL (1996) Changes in certain properties of grey forest soil polluted with emissions from a copper-smelting plant. Russ J Ecol 27:177–183
Kleyer M et al (2008) The LEDA Traitbase: a database of life-history traits of the Northwest European flora. J Ecol 96:1266–1274. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2008.01430.x
Kuhn I, Durka W, Klotz S (2004) BiolFlor—a new plant-trait database as a tool for plant invasion ecology. Divres Distrib 10:363–365. doi:10.1111/j.1366-9516.2004.00106.x
Lazarus BE, Richards JH, Claassen VP, O’Dell RE, Ferrell MA (2011) Species specific plant-soil interactions influence plant distribution on serpentine soils. Plant Soil 342:327–344. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0698-2
Legendre P, Borcard D, Roberts DW (2012) Variation partitioning involving orthogonal spatial eigenfunction submodels. Ecology 93:1234–1240. doi:10.1890/11-2028.1
Levine JM, Murrell DJ (2003) The community-level consequences of seed dispersal patterns. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 34:549–574. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.011802.132400
Marmottant P, Ponomarenko A, Bienaime D (2013) The walk and jump of Equisetum spores. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 280:20131465. doi:10.1098/Rspb.2013.1465
Moeslund JE, Arge L, Bøcher PK, Dalgaard T, Ejrnæs R, Odgaard MV, Svenning JC (2013) Topographically controlled soil moisture drives plant diversity patterns within grasslands. Biodivers Conserv 22:2151–2166. doi:10.1007/s10531-013-0442-3
Moore KA, Elmendorf SC (2006) Propagule vs. niche limitation: untangling the mechanisms behind plant species’ distributions. Ecol Lett 9:797–804. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00923.x
Murray K, Conner MM (2009) Methods to quantify variable importance: implications for the analysis of noisy ecological data. Ecology 90:348–355. doi:10.1890/07-1929.1
Nesterkov AV, Vorobeichik EL (2009) Changes in the structure of chortobiont invertebrate community exposed to emissions from a copper smelter. Russ J Ecol 40:286–296. doi:10.1134/S1067413609040109
Oksanen J et al (2015) Vegan: community ecology package. http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/vegan/. Accessed 8 March 2015
Rapson GL, Wilson JB (1988) Non-adaptation in Agrostis capillaris L. (Poaceae). Funct Ecol 2:479–490. doi:10.2307/2389391
R Core Team (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 8 March 2015
Reichman S (2002) The responses of plants to metal toxicity: a review focusing on copper, manganese & zinc. Australian Minerals & Energy Environment Foundation, Melbourne
Revelle W (2015) Psych: procedures for personality and psychological research. Northwestern University. http://cran.r-project.org/package=psych. Accessed 8 March 2015
Simas AB, Barreto-Souza W, Rocha AV (2010) Improved estimators for a general class of beta regression models. Comput Stat Data Anal 54:348–366. doi:10.1016/j.csda.2009.08.017
Sotek Z (2010) Distribution patterns, history, and dynamics of peatland vascular plants in Pomerania (NW Poland). Biodiv Resour Conserv 18:1–82. doi:10.2478/v10119-010-0020-4
Stuefer J, De Kroon H, During H (1996) Exploitation of environmental hetergeneity by spatial division of labor in a clonal plant. Funct Ecol 10:328–334
Von Frenckell-Insam BAK, Hutchinson TC (1993a) Nickel and zinc tolerance and co-tolerance in populations of Deschampsia cespitosa (L.) Beauv. subject to artificial selection. New Phytol 125:547–553. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1993.tb03902.x
Von Frenckell-Insam BAK, Hutchinson TC (1993b) Occurrence of heavy metal tolerance and co-tolerance in Deschampsia cespitosa (L.) Beauv. from European and Canadian populations. New Phytol 125:555–564. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1993.tb03903.x
Vorobeichik EL, Pishchulin PG (2009) Effect of individual trees on the pH and the content of heavy metals in forest litters upon industrial contamination. Eur Soil Sci 42:861–873. doi:10.1134/S1064229309080043
Vorobeichik EL, Pozolotina VN (2003) Microscale spatial variation in forest litter phytotoxicity. Russ J Ecol 34:381–388. doi:10.1023/A:1027308400182
Vorobeichik EL, Trubina MR, Khantemirova EV, Bergman IE (2014) Longterm dynamic of forest vegetation after the reduction of copper smelter emission. Russ J Ecol 45:498–507. doi:10.1134/S1067413614060150
Wilkinson L (2012) Exact and approximate area-proportional circular Venn and Euler diagrams. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 18:321–331. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2011.56
Wilson JB (1988) The cost of heavy-metal tolerance—an example. Evolution 42:408–413. doi:10.2307/2409246
Xiong SJ, Nilsson C (1999) The effects of plant litter on vegetation: a meta-analysis. J Ecol 87:984–994. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2745.1999.00414.x
Zvereva EL, Kozlov MV (2004) Facilitative effects of top-canopy plants on four dwarf shrub species in habitats severely disturbed by pollution. J Ecol 92:288–296. doi:10.1111/j.0022-0477.2004.00854.x
Acknowledgments
We appreciate E.L. Vorobeichik for discussion of the results, and anonymous referees for their helpful comments. We thank I.E. Bergman and T.Yu. Gabershtein for the help in data collection. This study was supported by Russian Foundation for Basic Research (14-04-31345; 12-04-32116), the Scientific School Support Program (NSh-2840.2014.4) and the Program of Basic Research of the Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences (12-P-4-1026).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Henk Schat.
O. V. Dulya and V. S. Mikryukov contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1477 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dulya, O.V., Mikryukov, V.S. & Hlystov, I.A. Interspecific differences in determinants of plant distribution in industrially polluted areas: Endogenous spatial autocorrelation vs. environmental parameters. Plant Soil 394, 329–342 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2538-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2538-x