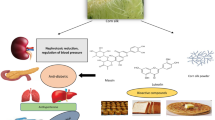
Abstract
Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. has a relatively wide geographical distribution and biological diversity; various lotus parts have excellent food and medicinal values. Lotus seeds, which are currently the oldest known plant seeds, contain many functional ingredients. They can be eaten raw or cooked, and are often added to foods as ingredients or supplements. Many naturally occurring ingredients isolated from lotus seeds are certified to be multiple functional compounds, such as polyphenols, protein, polysaccharides. Proteins and carbohydrates are the main nutrients of lotus seeds. Low fat content and good proportion of amino acids confer to lotus seeds unique nutritional values that have attracted increasing attention around the world: multiple studies have assessed the functional components of lotus seeds. The bioactivity of ingredients from lotus seeds in vitro and in vivo include antioxidant activity, hypoglycemic, immunomodulatory, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effects as well as gastrointestinal regulation. Lotus seeds show prospective application in function food area and traditional medicine research. Furthermore, structure–activity relationship of functional compounds from lotus seeds will attracts much more interests in recent years. This work briefly reviews the nutrition composition, physiological functions and processing methods of lotus seeds, describing the impact of the latter on nutrient preservation. In addition, this review addresses the recent progresses made in this area and discusses the potential applications and limitations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat R, Karim AA (2009) Effect of ionizing radiation on some quality attributes of nutraceutically valued lotus seeds. Int J Food Sci Nutr 60:9–20
Bhat R, Sridhar KR (2008) Nutritional quality evaluation of electron beam-irradiated lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seeds. Food Chem 107:174–184
Bhat R, Sridhar KR, Karim AA, Young CC, Arun AB (2009) Influence of γ-radiation on the nutritional and functional qualities of lotus seed flour. J Agric Food Chem 57:9524–9531
Bhat R, Sridhar KR, Karim AA (2010) Microbial quality evaluation and effective decontamination of nutraceutically valued lotus seeds by electron beams and gamma irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 79:976–981
Bi Y, Yang G, Li H, Zhang G, Guo Z (2006) Characterization of the chemical composition of lotus plumule oil. J Agric Food Chem 54:7672–7677
Cai D (2012) Contents of heavy metals in lotus seed from rees mining area. J Saudi Chem Soc 16:175–176
Cai L, Zeng H, Wang Y, Liao X, Zhang J (2010) Amino acid contents of lotus seed protein and its nutritional evaluation. Acta Nutr Sin 32:503–506
Cai L, Zeng H, Cai X, Wang Y (2011) Second structure of the protein faction from lotus seeds. Spectrosc Spect Anal 31:2394–2398
Chakravarthi PV, Gopakumar N, Nair AMC, Joy AD (2009) Assessment of analgesic activity of red and white lotus seeds (Nelumbo nucifera) in albino rats. J Nat Remed 9:224–227
Chen X, Zhou J (2011) Preliminary analysis of the chemical composition of lotus seed skin. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 20:139–141
FAO Joint, WHO (1973) Energy and protein requirements: report of a joint FAO/WHO ad hoc expert committee (meeting held in Rome from 22 March to 2 April 1971)
Gao J, Chen Y (2003) Isolation, purification of glycoproteins from Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. seed and its effects on scavenging free radicals. J Wuhan Bot Res 21:175–178
Gao H, Gao Y, Xu H (2013) Antioxidant and anti-browning activities of ethanol extract from lotus seed skin. Food Sci 34:83–87
Guo Z, Liu W, Zeng S, Zheng B (2013) Effect of ultra high pressure processing on the particle characteristics of lotus-seed starch. Chin J Struct Chem 32:525–532
Guo Z, Zeng S, Zhang Y, Lu X, Tian Y, Zheng B (2015) The effects of ultra-high pressure on the structural, rheological and retrogradation properties of lotus seed starch. Food Hydrocoll 44:285–291
He J, Cheng W, Chen X, Wen S, Zhang G, Xiong G, Ye L, Chen Y (2006) Study on the vacuum sublimation freezing-drying of lotus seeds. Hubei Agric Sci 45:240–244
Hua H, Zhao C, Wang Q, Yan S, Li J (2012) Study on processing technology of crunchy lotus seed. Sci Technol Food Ind 33:264–265
Huang S, Zheng B (2010) Antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds in lotus seed. J Fujian Agric For Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 39:94–97
Kim M, Shin H (2012) Antioxidative effect of lotus seed and seedpod extracts. Food Sci Biotechnol 21:1761–1766
Kim DW, Hwang IK, Yoo K, Li H, Kang I, Moon W, Won M, Kim SJ, Han D, Kim D (2008) Aqueous extracts of walnut (Juglans Regia L.) and Nelumbo nucifera seeds reduce plasma corticosterone levels, gastric lesions, and c-fos immunoreactivity in chronic restraint-stressed mice. Food Sci Biotechnol 17:713–717
Kuo Y, Lin Y, Liu C, Tsai W (2005) Herpes simplex virus type 1 propagation in hela cells interrupted by Nelumbo nucifera. J Biomed Sci 12:1021–1034
Li Z (2008) Nutrient value and processing of lotus seed. Acad Period Agric Prod Process 2008:42–43
Li Y, Wei Y, Xu B (2000) Study on the ABA content and SOD activity in ancient lotus and modern lotus seeds. Chin Bull Bot 17:439–442
Li L, Liu Z, Cen J, Yang X, Hao S, Zhou W, Chen S (2013) Research on purification conditions of superoxide dismutase from tilapia blood by ion exchange chromatography. Sci Technol Food Ind 34:137–139
Li Y, Smith T, Yang J, Jin J, Li C (2014) Paleobiogeography of the lotus plant (Nelumbonaceae: Nelumbo) and its bearing on the paleoclimatic changes. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol 399:284–293
Lin Y, Zeng S, Zheng B (2009) Study on the in vitro digestibility of edible lotus-seed starch film. Chin Agric Sci Bull 25:100–103
Ling Z, Xie B, Yang E (2005) Isolation, characterization, and determination of antioxidative activity of oligomeric procyanidins from the seedpod of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. J Agric food Chem 53:2441–2445
Liu C, Tsai W, Lin Y, Liao J, Chen C, Kuo Y (2004) The extracts from Nelumbo nucifera suppress cell cycle progression, cytokine genes expression, and cell proliferation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Life Sci 75:699–716
Lu L, Chen F, Tan Y (2013) Lotus seed Fe-SOD extraction and high temperature resistant ability. Biotechnol World 2:65–66
Ma Z, Wang H, Liu L, Xin D, Zhang H, Shen J (1995) Experimental study on the antiaging effect of powdered Hindu lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seed. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 26:81–82
Man J, Cai J, Cai C, Xu B, Huai H, Wei C (2012) Comparison of physicochemical properties of starches from seed and rhizome of lotus. Carbohydr Polym 88:676–683
Mani SS, Subramanian IP, Pillai SS, Muthusamy K (2010) Evaluation of hypoglycemic activity of inorganic constituents in Nelumbo nucifera seeds on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 138:226–237
Miao S, Xu Y, Fang X (2005) Antioxidation of semen Nelumbinis polysaccharide on aging mice. Chin J Mod Drug Appl 22:11–12
Miao S, Yang Y, Fang X (2008) Effect of Semen nelumbinis polysaccharide on the immune function of cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppressed mice. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res 12:10477–10480
Mukherjee PK, Mukherjee D, Maji AK, Rai S, Heinrich M (2009) The sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)-phytochemical and therapeutic profile. J Pharm Pharmacol 61:407–422
Mukherjee D, Khatua TN, Venkatesh P, Saha BP, Mukherjee PK (2010) Immunomodulatory potential of rhizome and seed extracts of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. J Ethnopharmacol 128:490–494
Pan L, Liang H, Guo G (1993) Nutritional value and processing technology of lotus seed. Sci Technol Food Ind 1:29–32
Pan Y, Cai B, Yang G, Cao L, Shen A (2005) Screening of active components of plumula Nelumbinis nucifera for lowering blood sugar. J Nanjing TCM Univ 21:243–244
Pan Y, Cai B, Wang K, Wang S, Zhou S, Yu X, Xu B, Chen L (2009) Neferine enhances insulin sensitivity in insulin resistant rats. J Ethnopharmacol 124:98–102
Porfire AS, Leucuţa SE, Kiss B, Loghin F, Pârvu AE (2014) Investigation into the role of Cu/Zn-SOD delivery system on its antioxidant and antiinflammatory activity in rat model of peritonitis. Pharm Rep 66:670–676
Qi S, Zhou D (2013) Lotus seed epicarp extract as potential antioxidant and anti-obesity additive in chinese cantonese sausage. Meat Sci 93:257–262
Rai S, Wahile A, Mukherjee K, Saha BP, Mukherjee PK (2006) Antioxidant activity of Nelumbo nucifera (sacred lotus) seeds. J Ethnopharmacol 104:322–327
Shad MA, Nawaz H, Siddique F, Zahra J, Mushtaq A (2013) Nutritional and functional characterization of seed kernel of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera): application of response surface methodology. Food Sci Technol Res 19:163–172
Su B, Deng F, Liu S (2010) The research on the characteristics of lotus seed starch. Innovat Edit Agric Prod Process 2:52–54
Sun Q, Zhou J, Cheng L, Yu W (2010) The development of the lotus seed millet noodles. Food Process 35:72–74
Sung J, Sung J, Shin H (2011) Cytoprotective effects of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertner) seed extracts on oxidative damaged mouse embryonic fibroblast cell. Food Sci Biotechnol 20:1533–1537
Tang P, Jiang Z, Mei C, Jiang H (1998) The composition, solubility and quality of lotus seed. J Beijing Norm Univ (Nat Sci) 34:532–537
Tian J, Hu J, Zhou F, Xu Q, Liu Y (2005) The influence of adding yam, lotus seed food for 46 cases of type 2 diabetes. Shaanxi J Tradit Chin Med 26:198–200
Tian Y, Lu X, Zheng B (2012a) Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of oligosaccharidefrom lotus seeds using response surface methodology. J Beijing Technol Bus Univ (Nat Sci Edit) 30:17–21
Tian Y, Zhang Y, Zeng S, Zheng Y, Chen F, Guo Z, Lin Y, Zheng B (2012b) Optimization of microwave vacuum drying of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds by response surface methodology. Food Sci Technol Int 18:477–488
Tian Y, Zheng B, Chen C, Zheng Y (2012c) Ultrasound-assisted extraction, preliminary characterization, and antioxidant activity of a novel water-soluble polysaccharide from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds. Sep Sci Technol 47:2408–2416
Wang G, Xu W (2013) Research on fresh-keeping packaging and respirationrate of the peeled fresh lotus seed. J Wuhan Polytech Univ 32:16–18
Wang J, Zhang G (2010) The yield and chemical composition of lotus seed on different culture conditions. Hubei J TCM 32:75–76
Wang Z, Zhao Q, Li C, Pan N, Liu S (2005) The advance on the ancient sacred lotus. J Cap Norm Univ (Nat Sci Edit) 26:55–58
Wang X, Zheng T, Li Q (2009) Optimization of ethanol extraction conditions of antioxidant compounds from lotus seeds using responsesurface methodology. Food Sci 30:34–38
Wu W (2008) Study on processing technology of quick-frozen fresh white lotus. J Anhui Agric Sci 36:16135–16137
Wu F, Xiao G (2013) Nutritional properties of lotus seeds and its application in functional foods. Subtrop Agric Res 8:274–278
Wu X, Chen J, Wang J, Lin J (2005) Modulatory role of lotus-seed milk fermented product on gastrointestinal motility and absorption in mice. World Chin J Digestol 13:2535–2539
Wu J, Zheng Y, Chen T, Yi J, Qin L, Rahman K, Lin W (2007) Evaluation of the quality of lotus seed of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. from outer space mutation. Food Chem 105:540–547
Wu C, Xia Y, Tang X (2013) Optimization of fermentation process for lotus rice-wine production by response surface methodology. Mod Food Sci Technol 29:1675–1679
Xia Y (2012) Effect of germination on chemical and functional properties of lotus seeds. Food Sci 33:91–98
Xie R (2010) The development of candied lotus-seeds with soft-packaging. Food Ind 5:36–38
Xu Y (1992) Study on the content and composition of phospholipids in semen of Nelumbo nucifera. Chin Bull Bot 9:46–47
Yen G, Chen H, Lee C (1999) Measurement of antioxidative activity in metal ion-induced lipid peroxidation systems. J Sci Food Agric 79:1213–1217
Yen G, Duh P, Su H (2005) Antioxidant properties of lotus seed and its effect on DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Food Chem 89:379–385
Yen G, Duh P, Su H, Yeh C, Wu C (2006) Scavenging effects of lotus seed extracts on reactive nitrogen species. Food Chem 94:596–602
Yi F (2007) Food and drug of lotus seed. Food Health 8:29–29
You JS, Lee YJ, Kim KS, Kim SH, Chang KJ (2014) Anti-obesity and hypolipidaemic effects of Nelumbo nucifera seed ethanol extract in human pre-adipocytes and rats fed a high-fat diet. J Sci Food Agric 94:568–575
Yuan D, Zhou W, Niu X (2011) Processing technology and formulationsof tremella lotus juice. China Food Addit 1:172–177
Zeng S, Zhang Y, Liang J, Zheng B (2007) Studies on appearance quality and starch quality of 22 kinds of lotus-seed. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol 7:74–78
Zeng S, Lin Y, Zheng B (2009a) Proliferation effect of lotus-seed and lotus-seed starch on bifidobacterium. J Fujian Agri For Univ (Nat Sci Edit) 38:417–419
Zeng S, Zheng B, Lin Y, Zhuo X (2009b) Granular characteristics of lotus-seed starch. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc 8:62–64
Zeng H, Cai L, Cai X, Wang Y, Li Y (2011) Structure characterization of protein fractions from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seed. J Mol Struct 1001:139–144
Zeng S, Chen B, Guo Z, Zheng B (2012) Advances in the bioactivity of lotus-seed. Chin J Trop Crops 33:2110–2114
Zeng H, Cai L, Cai X, Wang Y, Li Y (2013) Amino acid profiles and quality from lotus seed proteins. J Sci Food Agric 93:1070–1075
Zhang L, Zhang H, Huang J (1994) Measure the elements in lotus seed by ICP-AES. J Nanchang Univ (Nat Sci) 18:410–412
Zhang F, Lin Y, Zheng B (2012a) Study on influence of preparation technology on film-forming properties of lotus-seed starch modified by dry heating. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc 26:39–44
Zhang Y, Zheng B, Tian Y, Huang S (2012b) Microwave-assisted extraction and anti-oxidation activity of polyphenols from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds. Food Sci Biotechnol 21:1577–1584
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zheng B, Lu X, Zhuang W (2013) The in vitro effects of retrograded starch (resistant starch type 3) from lotus seed starch on the proliferation of Bifidobacterium adolescentis. Food Funct 4:1609–1616
Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wang Y, Zeng S, Zheng B (2014) Structural characteristics and crystalline properties of lotus seed resistant starch and its prebiotic effects. Food Chem 155:311–318
Zheng Y, Wu J (2004) Measure the sugar content in the lotus seed by DNS colorimetry. J Fujian Coll TCM 14:32–34
Zheng B, Zheng J (2004) Lactobacillus zymotechnics of lotus seed. J Fujian Agric For Univ (Nat Sci Edit) 33:254–257
Zheng B, Zheng J, Zeng S (2003) Analysis of the nutritional compositionin chinese main lotus seed varieties. Acta Nutr Sin 25:153–156
Zheng B, Zheng J, Zeng C (2004) Study on three functional components of Chinese main lotus seed varieties. Acta Nutr Sin 26:158–160
Zhou L, Xu Y (1992) The determination of the phospholipid content in egg yolk, pine nuts, lotus seed by infrared spectrometry. Food Res Dev 3:40–43
Zhou D, Gao J, Yang Y, Chen A, Mai Z (2011) Analysis on the nutrient components of lotus seed shell and study on the antioxidation activity of flavonoid. J Anhui Agric Sci 39:3968–3970
Acknowledgments
This research is financially supported by the China State “11th Five-Year Plan” Scientific and Technological Support Scheme (2007BAD07B05), the Special Major Science and Technology in Fujian Province (2008N0007), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (T0650021), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2012J01081), the Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education (20133515110013), the National Spark Program (2010GA720045), the National Natural Science Fund (31301441) and the Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University Outstanding Youth fund (No. xjp201204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yi Zhang and Xu Lu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Lu, X., Zeng, S. et al. Nutritional composition, physiological functions and processing of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds: a review. Phytochem Rev 14, 321–334 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-015-9401-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-015-9401-9