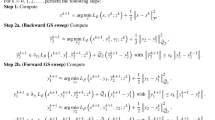Abstract
Since sparse unmixing has emerged as a promising approach to hyperspectral unmixing, some spatial-contextual information in the hyperspectral images has been exploited to improve the performance of the unmixing recently. The total variation (TV) has been widely used to promote the spatial homogeneity as well as the smoothness between adjacent pixels. However, the computation task for hyperspectral sparse unmixing with a TV regularization term is heavy. Besides, the convergence of the primal alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) for the hyperspectral sparse unmixing with a TV regularization term has not been explained in detail. In this paper, we design an efficient and convergent dual symmetric Gauss-Seidel ADMM (sGS-ADMM) for hyperspectral sparse unmixing with a TV regularization term. We also present the global convergence and local linear convergence rate analysis for this algorithm. As demonstrated in numerical experiments, our algorithm can obviously improve the efficiency of the unmixing compared with the state-of-the-art algorithm. More importantly, we can obtain images with higher quality.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We have to emphasize that in [15] the authors deal with problem (1) in three blocks instead of two blocks when they applied the primal ADMM. In fact, the problem can be regarded as two blocks. So Algorithm 1 in this paper is a little different from Algorithm 1 in [15]. It not only is faster but also has mathematically guaranteed convergence theory. Actually, the code for the algorithm in [15] is in accordance with our two-block primal ADMM.
In Algorithm 2, V3 is updated twice because we use the sGS decomposition to solve the subproblem. For more details, one may refer to [28].
downloaded from http://www.lx.it.pt/~bioucas/publications.html.
Since the SRE value will get worse after the KKT residual is smaller than some value, and Algorithm 2 is obviously faster than Algorithm 1 according to the experiments behind, the settings of the maximal iterations are not the same.
Available online: http://speclab.cr.usgs.gov/spectral.lib06.
Available online: http://aviris.jpl.nasa.gov/html/aviris.freedata.html
References
Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A., Dobigeon, N., Parente, M., Du, Q., Gader, P., Chanussot, J.: Hyperspectral unmixing overview: geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 5(2), 354–379 (2012)
Nascimento, J.P., Bioucas-Dias, J.M.: Vertex component analysis: a fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 43(4), 898–910 (2005)
Boardman, J.W., Kruse, F.A., Green, R.O.: Mapping target signatures via partial unmixing of AVIRIS data. In: Proc. J.L Airborne Earth Sci. Workshop, pp. 23–26 (1995)
Chang, C.-I., Wu, C.-C., Liu, W., Ouyang, Y.-C.: A new growing method for simplex-based endmember extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 44(10), 2804–2819 (2006)
Chan, T.-H., Chi, C.-Y., Huang, Y.-M., Ma, W.-K.: Convex analysis based minimum-volume enclosing simplex algorithm for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(11), 4418–4432 (2009)
Berman, M., Kiiveri, H., Lagerstrom, R., Ernst, A., Dunne, R., Huntington, J.F.: ICE: A statistical approach to identifying endmembers in hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 42(10), 2085–2095 (2004)
Miao, L., Qi, H.: Endmember extraction from highly mixed data using minimum volume constrained nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 45(3), 765–777 (2007)
Dobigeon, N., Moussaoui, S., Coulon, M., Tourneret, J.-Y., Hero, A.O.: Joint Bayesian endmember extraction and linear unmixing for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(11), 4355–4368 (2009)
Bruckstein, A.M., Donoho, D.L., Elad, M.: From sparse solutions of systems of equations to sparse modeling of signals and images. SIAM Rev. 51 (1), 34–81 (2009)
Iordache, M.-D., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A., Somers, B.: MUSIC-CSR: hyperspectral unmixing via multiple signal classification and collaborative sparse regression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52(7), 4364–4382 (2014)
Iordache, M.-D., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A.: Sparse unmixing of hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 49(6), 2014–2039 (2011)
Rudin, L.I., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 60(1-4), 259–268 (1992)
Zhao, X.-L., Wang, W., Zeng, T.-Y., Huang, T.-Z., Ng, M.K.: Total variation structured total least squares method for image restoration. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 35(6), 1304–1320 (2013)
Zakharova, A.: Total variation reconstruction from quadratic measurements. Numer. Algorith. 75(1), 81–92 (2017)
Iordache, M.-D., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A.: Total variation spatial regularization for sparse hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 50(11), 4484–4502 (2012)
Zhang, S., Li, J., Liu, K., Plaza, A.: Hyperspectral unmixing based on local collaborative sparse regression. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 13(5), 631–635 (2016)
Zhang, L., Wei, W., Zhang, Y., Yan, H., Li, F., Tian, C.: Locally similar sparsity-based hyperspectral compressive sensing using unmixing. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imag. 2(2), 86–100 (2016)
Iordache, M.-D., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A.: Collaborative sparse regression for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52(1), 341–354 (2014)
Chen, Y.-J., Ge, W.-D., Sun, L.: A novel linear hyperspectral unmixing method based on collaborative sparsity and total variation. Acta Auto. Sinica. 44(1), 116–128 (2018)
Glowinski, R., Marroco, A.: Sur l’approximation, par éléments finis d’ordre un, et la résolution, par pénalisation-dualité d’une classe de problémes de Dirichlet non linéaires, Revue Francaise d’Automatique. Informatique et Recherche Opérationelle 2(R-2), 41–76 (1975)
Gabay, D., Mercier, B.: A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2(1), 17–40 (1976)
Eckstein, J., Yao, W.: Understanding the convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers: Theoretical and computational perspectives. Pac. J. Optim. 11(4), 619–644 (2015)
Glowinski, R.: On alternating direction methods of multipliers: a historical perspective. In: Fitzgibbon, W., Kuznetsov, Y.A., Neittaanmaki, P., Pironneau, O. (eds.) Modeling Simulation and Optimization for Science and Technology 59–82 (2014)
Fazel, M., Pong, T.K., Sun, D., Tseng, P.: Hankel matrix rank minimization with applications to system identification and realization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 34(3), 946–977 (2013)
Han, D., Sun, D., Zhang, L.: Linear rate convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers for convex composite programming. arXiv:1508.02134 (2015)
Chen, C., He, B., Ye, Y., Yuan, X.: The direct extension of ADMM for multi-block convex minimization problems is not necessarily convergent. Math. Program. 155(1-2), 57–79 (2016)
Li, X., Sun, D., Toh, K.-C.: A Schur complement based semi-proximal ADMM for convex quadratic conic programming and extensions. Math. Program. 155(1-2), 333–373 (2016)
Li, X., Sun, D., Toh, K.-C.: A block symmetric Gauss-Seidel decomposition theorem for convex composite quadratic programming and its applications. Math. Program. 175(1-2), 395–418 (2019)
Chen, L., Sun, D., Toh, K.-C.: An efficient inexact symmetric Gauss-Seidel based majorized ADMM for high-dimensional convex composite conic programming. Math. Program. 161(1-2), 237–270 (2017)
Chen, L., Sun, D., Toh, K.-C., Zhang, N.: A unified algorithmic framework of symmetric Gauss-Seidel decomposition based proximal ADMMs for convex composite programming, Math. Program. arXiv:1812.06579 (2018)
Beck, A., Teboulle, M.: Fast gradient-based algorithms for constrained total variation image denoising and deblurring problems. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18(11), 2419–2434 (2009)
Zuo, W., Lin, Z.: A generalized accelerated proximal gradient approach for total-variation-based image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20 (10), 2748–2759 (2011)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Convex Analysis. University of Princeton, USA (1970)
Horn, R.A., Johnson, C.R.: Matrix Analysis, university of cambridge UK (1985)
Sun, J.: On monotropic piecewise quadratic programming, Ph.D. dissertation, University of Washington USA (1986)
Robinson, S.M.: Some contimuity properties of polyhedral multifuntions. Math. Program. Study 14, 206–214 (1981)
Dontchev, A., Rockafellar, R.T.: Implicit Function and Solution Mappings. Springer, USA (2009)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.-B.: Variational Analysis. Springer, USA (1998)
Wang, R., Li, H.-C., Liao, W., Huang, X., Philips, W.: Centralized collaborative sparse unmixing for hyperspectral images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 10(5), 1949–1962 (2017)
Condat, L.: A direct algorithm for 1-D total variation denoising. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(11), 1054–1057 (2013)
Kozintsev, B.: Computations with Gaussian random fields, Ph.D. dissertation, University of Maryland USA (1999)
Yu, Y.: On decomposing the proximal map. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst 1, 91–99 (2013)
Jia, S., Qian, Y.: Spectral and spatial complexity-based hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 45(12), 3867–3879 (2007)
Jia, S., Qian, Y.: Constrained nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 47(1), 161–173 (2009)
Zhu, F., Wang, Y., Xiang, S., Fan, B., Pan, C.: Structured sparse method for hyperspectral unmixing, ISPRS. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 88 (2), 101–118 (2014)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Xile Zhao at School of Mathematics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China for his useful comments and suggestions. We also thank Professor Heng-Chao Li at the School of Information Science and Technology, Southwest Jiaotong University for fruitful discussions. Besides, We are grateful to the two anonymous referees and the Editor-in-Chief Prof. Claude Brezinski for their constructive and helpful suggestions on improving the quality of the paper. The work of Longfei Ren was supported by the China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Funding
The work of Peipei Tang was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China under Grant LY19A010028 and the Science and Technology Development Project of Hangzhou, China under Grant 20170533B22, 20162013A08.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Wang, C., Tang, P. et al. A dual symmetric Gauss-Seidel alternating direction method of multipliers for hyperspectral sparse unmixing. Numer Algor 87, 719–754 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-020-00985-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-020-00985-8