Abstract
Soil erosion is a natural process causing grave land degradation problems. In Tunisia, soil erosion represents a serious environmental problem. Both man-made and natural phenomenon is reducing acres of agricultural land. The problem of soil erosion by water is very critical in Lebna watershed. In fact, Lebna is a town in the northeast of Tunisia and it seems high time to protect water and ground resources and to prevent the Lebna dam situated in the downstream from silting. In this context, the application of geographic RUSLE model using the techniques of geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing has made it possible to assess the estimation of the soil erosion risk at the targeted watershed. This model is composed of several factors associated with climate, topography, soil and vegetation. The spatial distribution of annual average rate of soil loss resulting of this methodology shows an average of 24 ton/ha/year. Consequently, this method based on a combination of RUSLE as erosion model gave very similar results with bathymetric measures performed by Institute of Research for Development. It was about 29 ton/ha/year. Accordingly, Lebna watershed belongs to a zone of rather a steep erosive potential knowing that the maximum acceptable limit value of the erosive potential estimated is 12 ton/ha/year (Roose in Introduction à la gestion conservatoire de l’eau, de la biomasse et de la fertilité des sols (GCES). FAORome, 1994). The results have shown that Lebna watershed has a serious risk on soil erosion on sloping land. The highest values are mainly associated with the steep slopes, poor conservation practices, low vegetation cover and high rainfall. The final soil loss map can be thus a base to plan appropriate strategies for decision-makers to avoid soil erosion risks and consequently to lengthen dam life.

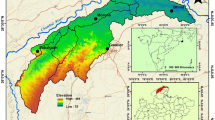
Source: Base map of Arcgis











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achouri M (1995) La conservation des eaux et du sol en Tunisie : bilan et perspectives, Centre Internationale de Hautes Études Agronomiques Méditerranéenne et l’Institut Agronomique Méditerranéen de Zaragoza, Tunisie, pp 35–45
Adediji A, Tukur AM, Adepoju KA (2010) Assessment of Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in Katsina area, Katsina state of Nigeria using remote sensing (RS) and geographic information system (GIS). Iran J Energy Environ 1(3):255–264
Ajmi M, Hamza MH, Labiadh M, Yermani M, Ben Khatra N, Al-Thubaiti AS, I Moharrem A, El Arrim A (2014) Setting up a spatial data infrastructure (SDI) for the ROSELT/OSS network. J Geogr Inf Syst 6:150–161. doi:10.4236/jgis201462016
Archambault J, Burrolet P, Schoeller H, Arnould M, Berkaloff E (1949) Carte géologique de la Tunisie au 1/50 000, Feuille 22, Menzel Bouzelfa, Edition S.g.d.l.d.d.t.p.d., Tunis, Tunisie
Arekhi S, Niazi Y, Kalteh AM (2012) Soil erosion and sediment yield modeling using RS and GIS techniques: a case study, Iran. Arab J Geosci 5:285–296. doi:10.1007/s12517-010-0220-4
Aronica G, Ferro V (1997) Rainfall erosivity over Calabrian region. Hydrol Sci J 42(1):35–48
Ashiagbor G, Forkuo EK, Laari P, Aabeyir R (2013) Modeling soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS tools. Int J Remote Sens Geosci 2(4):2013
Banasik K, Gorski D (1994) Rainfall erosivity for South-East Poland. In: Rickson RJ (ed) Conserving soil resources, European perspectives, lectures in soil erosion control. Silsoe College, Cranfield University, Cranfield, pp 201–207
Benkadja R, Boussag F, Benkadja A (2015) Identification et evaluation du risque d’erosion sur le bassin versant du K’sob (Est Algerien). Bull Eng Geol Environ. doi:10.1007/s10064-014-0611-y
Bensalem H (1989) Carte géologique de la Tunisie au 1/50 000, Feuille 15, Tazoghrane, Edition Office National des Mines, Tunis, Tunisie
Bergsma E (1980) Provisional rain-erosivity map of The Netherlands. In: De Boodt M, Gabriels D (eds) Assessment of erosion. Wiley, Chichester
Bhandari KP, Aryal J, Darnsawasdi R (2015) A geospatial approach to assessing soil erosion in a watershed by integrating socio-economic determinants and the RUSLE mode. Nat Hazards 75:321–334. doi:10.1007/s11069-014-1321-2
Bhattarai R, Dutta D (2008) Comparative analysis of sediment yield simulation by empirical and process-oriented models in Thailand. Hydrol Sci J 53(6):1253–1269. doi:10.1623/hysj.53.6.1253
Bolinne A, Laurant A, Rosseau P (1980) Provisional rain-erosivity map of Belgium. In: De Boodt M, Gabriels D (eds) Assessment of erosion. Wiley, Chichester, pp 111–120
Bonill CA, Reyes JL, Magri A (2010) Water erosion prediction using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, central Chile. Chil J Agric Res 70(1):159–169. doi:10.4067/S0718-58392010000100017
Bracken LJ, Kirkby MJ (2005) Differences in hillslope runoff and sediment transport rates within two semi-arid catchments in southeast Spain. Geomorphology 68:183–200
Breiby T (2006) Assessment of soil erosion risk within a subwatershed using GIS and RUSLE with a comparative analysis of the use of STATSGO and SSURGO soil databases, resource analysis, vol 8, p 22
Chadli K (2016) Estimation of soil loss using RUSLE model for Sebou watershed (Morocco). Model Earth Syst Environ. doi:10.1007/s40808-016-0105-y
Chaibi N (2001) Modélisation du transport solide arrivant au lac collinaire de Kamech, spatialisation des paramètres de l’équation universelle de pertes en terre, DEA, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis, Tunisie, pp 42–45
Chen T, Niu R, Wang Y, Li P, Zhang L, Du B (2011) Assessment of spatial distribution of soil loss over the upper basin of Miyun reservoir in China based on RS and GIS techniques. Environ Monit Assess 179:605–617. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1766-z
Demirci A, Karaburun A (2012) Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in a GIS framework: a case study in the Buyukcekmece Lake watershed, northwest Turkey. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1300-9
El Aroussi O, Mesrar L, El Garouani A, Lahrach A, BeaabidaL t, Akdi B, Jabrane R (2011) Predicting the potential annual soil loss using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in the oued El Malleh catchment (Prerif, Morocco). Present Environ Sustain Dev 5(2):5–16
Fagnano M, Diodato N, Alberico I, Fiorentino N (2012) An overview of soil erosion modelling compatible with RUSLE approach. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 23:69–80. doi:10.1007/s12210-011-0159-8
Ferreira V, Panagopoulos T (2014) Seasonality of soil erosion under Mediterranean conditions at the Alqueva dam watershed. Environ Manag 54(2014):67–83. doi:10.1007/s00267-014-0281-3
Ferro V, Giordano G, Lovino M (1991) Isoerosivity and erosion risk map for Sicily. Hydrol Sci J 36(6):549–564
Fu B, Newham LT, Ramos-Sharrón CE (2010) A review of surface erosion and sediment delivery models for unsealed roads. Environ Model Softw 25(2010):1–14
Gao H, Zhanbin Z, Li P, Jia L, Zhang X (2012) Quantitative study on influences of terraced field. J Geogr Sci 5:946–960. doi:10.1007/s11442-012-0975-5
Hamza MH, Added A, Rodrigue R, Abdeljaoued S, Ben Mammou A (2007) A GIS-based DRASTIC vulnerability and net recharge reassessment in an aquifer of a semi-arid region (Metline-Ras Jebel-Raf Raf Aquifer, Northern Tunisia). J Environ Manag 84:12–19. doi:10.1016/jjenvman200604004
Hussein MH (1986) Rainfall erosivity in Iraq. J Soil Water Conserv 58(1986):336–338
Jinghu P, Yan W (2014) Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in Caijiamiao watershed, China. Nat Hazards 71:2187–2205. doi:10.1007/s11069-013-1006-2
Kefi M, Yoshino K, Setiawan Y, Zayani K, Boufaroua M (2011) Assessment of the effects of vegetation on soil erosion risk by water: a case of study of the Batta watershed in Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0891-x
Kefi M, Yoshino K, Setiawan Y (2012) Assessment and mapping of soil erosion risk by water in Tunisia using time series MODIS data. Paddy Water Environ 10(2012):59–73. doi:10.1007/s10333-011-0265-3
Kouli M, Soupios P and Vallianatos F (2008) Soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete, Greece. Springer, Berlin, pp 483–497. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1318-9
Kumar A, Devi M, Deshmukh B (2014) Integrated remote sensing and geographic information system based RUSLE modelling for estimation of soil loss in western Himalaya, India. Water Resour Manag 28:3307–3317. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0680-5
Lal R (1990) Erosion in the tropics: principles and management. McGraw-Hil, New York, p 1990
Li X, Wu B, Zhang L (2013) Dynamic monitoring of soil erosion for upper stream of Miyun Reservoir in the last 30 years. J Mt Sci 10:801–811. doi:10.1007/s11629-013-2559-y
Lu D, Li G, Valladares GS, Batistella M (2004) Mapping soil erosion risk in Rondonia, Brazilian Amazonia: using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS. Land Degrad Dev 15:499–512. doi:10.1002/ldr634
Mansouri T (2001) Modélisation spatialisée des écoulements et du transport solide des bassins versants des lacs collinaires et de la dorsale tunisienne et du Cap Bon, Thèse de doctorat, FST, pp 286–300
Markose VJ, Jayappa KS (2016) Soil loss estimation and prioritization of sub-watersheds of Kali River basin, Karnataka, India, using RUSLE and GIS. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-016-5218-2
Masson JM (1971) L’érosion des sols par l’eau en climat méditerranéen, Méthodes expérimentales pour l’étude de quantités érodées à l’échelle du champ, Thèse DocIng, UnivSc et Tech du Languedoc, Montpellier , p 213
Mellouli M, Abid M (2007) Analyse sommaire de la gestion du barrage Lebna. Ministère de l’agriculture et des ressources hydrauliques, Tunisie, p 2007
Millward AA, Mersey JE (1999) Adapting the RUSLE to model soil erosion potential in a mountainous tropical watershed. Catena 1999:109–129. doi:10.1016/S0341-8162(99)00067-3
Mitasova H, Hofierka J, Zlocha M, Iverson LR (1996) Modeling topographic potential for erosion and deposition using GIS. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 10(5):629–641
Morgan RPC (1994) Soil erosion and conservation. Cranfield University, College, p 1994
Naqvi HR, Mallick J, Devi LM, Siddiqui MA (2013) Multi-temporal annual soil loss risk mapping employing revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model in Nun Nadi watershed, Uttarakhand (India). Arab J Geosci 6:4045–4056. doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0661-z
Nekhay O, Arriaza M, Boerboom LGJ (2009) Evaluation of soil erosion risk using analytic network process and GIS: a case study from Spanish mountain olive plantations. J Environ Manag 90(10):3091–3104. doi:10.1016/jjenvman200904022
Ozsoy G, Aksoy E, Dirim MS, Tumsavas Z (2012) Determination of soil erosion risk in the Mustafakemalpasa River Basin, Turkey, using the revised universal soil loss equation, geographic information system, and remote sensing. Environ Manag 50(2012):679–694. doi:10.1007/s00267-012-9904-8
Pan J, Wen Y (2013) Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in Caijiamiao watershed, China. Nat Hazards. doi:10.1007/s11069-013-1006-2
Pradeep GS, Ninu Krishnan MV, Vijith H (2014) Identification of critical soil erosion prone areas and annual average soil loss in an upland agricultural watershed of Western Ghats, using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and RUSLE techniques. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-014-1460-5
Prasannakumar V, Vijith H, Geetha N, Shiny R (2011) Regional scale erosion assessment of a sub-tropical highland segment in the Western Ghats of Kerala, South India. Water Resour Manag 25(2011):3715–3727. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9878-y
Prasannakumar V, Vijith H, Abinod S, Geetha N (2012) Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci Front 3(2):209–215. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2011.11.003
Priess JA, Schweitzer C, Batkhishig O, Koschitzki T, Wurbs D (2013) Impacts of agricultural land-use dynamics on erosion risks and options for land and water management in Northern Mongolia. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3380-9
Rango A, Arnoldus HMJ (1987) Aménagement des bassins versants. Cahiers techniques de la FAO
Renard KG, Freimund JR (1994) Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R factor in the revised USLE. J Hydrol 157(1994):287–306
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). U.S. Departement of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook, No. 703, 404 pp
Renschler CS, Harbor J (2002) Soil erosion assessment tools from point to regional scales—the role of geomorphologists in land management research and implementation. Geomorphology 47(2002):189–209. doi:10.1016/S0169-555X(02)00082-X
Roose E (1994) Introduction à la gestion conservatoire de l’eau, de la biomasse et de la fertilité des sols (GCES), Bulletin pédologique de la FAO, No 70, FAORome, p 420
Rozos D, Skilodimou HD, Loupasakis C, Bathrellos GD (2013) Application of the revised universal soil loss equation model on landslide prevention. An example from N Euboea (Evia) Island, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 70(2013):3255–3266. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2390-3
Saygın SD, Ozcan AU, Basaran M, Timur OB, Dolarslan M, Yılman FE, Erpul G (2014) The combined RUSLE/SDR approach integrated with GIS and geostatistics to estimate annual sediment flux rates in the semi-arid catchment, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 71(2014):1605–1618. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2565-y
Shi ZH, Cai CF, Ding SW, Wang TW, Chow TL (2004) Soil conservation planning at the small watershed level using RUSLE with GIS: a case study in the Three Gorge Area of China. Catena 2004:33–48. doi:10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00088-2
Shieferaw A (2011) Estimating soil loss rates for soil conservation planning in the borena woreda of South Wollo Highlands, Ethiopia. J Sustain Dev Africa 13(3):1520–5509
Tang Q, Xu Y, Bennett SJ, Li Y (2014) Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: a case study of the Yangou watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3523-z
Teh SH (2011) Soil erosion modeling using RUSLE and GIS on Cameron highlands, Malaysia for hydropower development, Master’s thesis, The School for Renewable Energy Science in affiliation with University of Iceland and University of Akureyri, pp 13–43
Terranova O, Antronic L, Coscarelli R, Iaquinta P (2009) Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: an application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 112(2009):228–245. doi:10.1016/jgeomorph200906009
Van Rompaey AJJ, Viellefont V, Jones RJA, Montanarella L, Verstraeten G, Bazzoffi P, Dostal T, Krasa J, DeVente J and Poesen J (2003) Validation of soil erosion estimates at European scale European Commission. Joint Research Center, EUR, p 20827
Van R, Hamilton M, Hickey R (2001) Estimating the LS factor for RUSLE through iterative slope length processing of digital elevation data. J Cartogr 30(1):27–35
Vrieling A, De Jong SM, Sterk G, Rodrigues SC (2008) Timing of erosion and satellite data: a multi-resolution approach to soil erosion risk mapping. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 10:267–281
Walling DE, Collins AL, Sichingabula HM (2003) Using unsupported lead-210 measurements to investigate soil erosion and sediment delivery in a small Zambian catchment. Geomorphology 52:193–213
Williams JR (1975) Sediment yield prediction with universal equation using runoff energy factor In Present and prospective technology for predicting sediment yields and sources. Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture, Washington, pp 244–252
Wischmeier WH (1959) A rainfall erosion index for a universal soil-loss equation. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 23(1959):246–249
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1965) Predicting rainfall-erosion losses from ropland east of the Rocky Mountains guide for selection of practices for soil and water conservation, Agric, handbook, vol 282. US Gov Print Office, Washington, p 1965
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses—a guide to conservation planning, Agriculture Handbook, No 537. US Department of Agriculture Science and Education Administration, Washington, p 163
Wordofa G (2011) Soil erosion modeling using GIS and RUSLE on the Eurajoki watershed Finland. Master’s thesis, Tampere University of Applied Sciences, Department of Environmental Engineering, pp 8–31
Wu L, Long T, Liu X, Mmereki D (2012) Simulation of soil loss processes based on rainfall runoff and the time factor of governance in the Jialing River Watershed, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:3731–3748. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2220-6
Xu Y, Luo D, Peng J (2011) Land use change and soil erosion in the Maotiao River watershed of Guizhou Province. J Geogr Sci 21:1138–1152. doi:10.1007/s11442-011-0906-x
Yu B, Rosewell CJ (1996a) An assessment of a daily rainfall erosivity model for New South Wales. Aust J Soil Res 34:139–152
Yu B, Rosewell CJ (1996b) Erosivity estimation using daily rainfall amounts for South Australia. Aust J Soil Res 34:287–306
Yu B, Rosewell CJ (1996c) A robust estimator of the R factor for the universal soil loss equation. Trans Am Soc Agric Eng 39(2):559–561
Zante P, Collinet J, Leclerc G (2003) Cartographie des risques érosifs sur le bassin-versant de la retenue collinaire d’Abdessadock (Dorsale Tunisienne). Tunis : direction de la Conservation des Eaux et des Sols, Institut de recherche pour le développement (IRD, mission Tunis)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
I. Gaubi and A. Chaabani have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaubi, I., Chaabani, A., Ben Mammou, A. et al. A GIS-based soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) (Lebna watershed, Cap Bon, Tunisia). Nat Hazards 86, 219–239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2684-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2684-3