Abstract
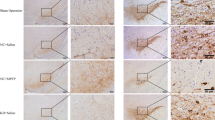
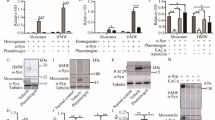
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) plays important roles in protecting the damaged or dying dopamine neurons in the animal models of Parkinson’s disease (PD). This study was to determine the effect and mechanisms of GDNF on the apoptosis of neurons in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induced Parkinson’s disease model of rats. Healthy male Sprague–Dawley rats (220–240 g) were randomly divided into six groups (n = 10). 6-OHDA was used to establish the PD rat model. Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunohistochemistry was used to assess the neuron loss in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. TUNEL and western blot were used to identify the effects and mechanisms of GDNF in the rat model of PD. The numbers of TH-positive neurons in the 6-OHDA-injected lesioned substantia nigra (SN) decreased significantly compared with the Sham group. GDNF treatment effectively ameliorated the apoptosis of neuronal cells in SN induced by 6-OHDA. In addition, GDNF significantly increased serine protein kinase B (Akt) and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) phosphorylation induced by 6-OHDA. In contrast, application of LY294002 or triciribine reversed the roles of GDNF in PD models. The results implicated that the anti-apoptosis effects of GDNF in neurons might be mediated through PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Therefore, GDNF may be a promising agent for PD treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Shimohama S, Sawada H, Kitamura Y, Taniguchi T (2003) Disease model: Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med 9:360–365
Zhu G, Wang X, Wu S, Li X, Li Q (2014) Neuroprotective effects of puerarin on 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine induced Parkinson’s disease model in mice. Phytother Res 28:179–186
Perier C, Bové J, Wu DC, Dehay B, Choi DK, Jacksonlewis V, Rathkehartlieb S, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Schulz JB (2007) Two molecular pathways initiate mitochondria-dependent dopaminergic neurodegeneration in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8161–8166
Nikam S, Nikam P, Ahaley SK, Sontakke AV (2003) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Indian J Clin Biochem 24:98–101
Adams JD (2012) Parkinson’s disease-apoptosis and dopamine oxidation. Open J Apoptosis 1:1–8
Airaksinen MS, Saarma M (2002) The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:383–394
Lin LF, Doherty DH, Lile JD, Bektesh S, Collins F (1993) GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 260:1130–1132
Revishchin A, Moiseenko L, Kust N, Bazhenova N, Teslia P, Panteleev D, Kovalzon V, Pavlova G (2016) Effects of striatal transplantation of cells transfected with GDNF gene without pre- and pro-regions in mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. BMC Neurosci 17:1–15
Aron L, Klein R (2011) Repairing the parkinsonian brain with neurotrophic factors. Trends Neurosci 34:88–100
Drinkut A, Tillack K, Meka DP, Schulz JB, Kügler S, Kramer ER (2016) Ret is essential to mediate GDNF’s neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effect in a Parkinson disease mouse model. Cell Death Dis 7:e2359
Grondin R (2002) Chronic, controlled GDNF infusion promotes structural and functional recovery in advanced parkinsonian monkeys. Brain 125:2191–2201
Kitagishi Y (2014) Dietary regulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 6:35–35
Chen L, Wei X, Hou Y, Liu X, Li S, Sun B, Liu X, Liu H (2014) Tetramethylpyrazine analogue CXC195 protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis through PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway in rats. Neurochem Int 66:27–32
Qi Z, Xu Y, Liang Z, Li S, Wang J, Wei Y, Dong B (2015) Baicalein alters PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway in rats with diabetes-associated cognitive deficits. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:1993–2000
Sestito S, Nesi G, Daniele S, Martelli A, Digiacomo M, Borghini A, Pietra D, Calderone V, Lapucci A, Falasca M (2015) Design and synthesis of 2-oxindole based multi-targeted inhibitors of PDK1/Akt signaling pathway for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Eur J Med Chem 105:274–288
Fayard E, Xue G, Parcellier A, Bozulic L, Hemmings BA (2010) Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), a key mediator of the PI3K signaling pathway. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 346:31–56
Liu F, Gong X, Zhang G, Marquis K, Reinhart P, Andree TH (2005) The inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β by a metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 mediated pathway confers neuroprotection to Aβ peptides. J Neurochem 95:1363–1372
Noël A, Barrier L, Rinaldi F, Hubert C, Fauconneau B, Ingrand S (2011) Lithium chloride and staurosporine potentiate the accumulation of phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase 3β/Tyr216, resulting in glycogen synthase kinase 3β activation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Neurosci Res 89:755–763
Luo J (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) in tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Lett 273:194–200
Yang Y, Wang H, Wang S, Xu M, Liu M, Liao M, Frank JA, Adhikari S, Bower KA, Shi X (2012) GSK3β signaling is involved in ultraviolet B-induced activation of autophagy in epidermal cells. Int J Oncol 41:1782–1788
Kim SN, Kim ST, Doo AR, Park JY, Moon W, Chae Y, Yin CS, Lee H, Park HJ (2011) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway mediates acupuncture-induced dopaminergic neuron protection and motor function improvement in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Neurosci 121:562–569
Yang Y, Gehrke S, Haque ME, Imai Y, Kosek J, Yang L, Beal MF, Nishimura I, Wakamatsu K, Ito S (2005) Inactivation of Drosophila DJ-1 leads to impairments of oxidative stress response and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13670–13675
Lundblad M, Andersson M, Winkler C, Kirik D, Wierup N, Cenci MA (2002) Pharmacological validation of behavioural measures of akinesia and dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 15:120–132
Migliore MM, Vyas TK, Campbell RB, Amiji MM, Waszczak BL (2010) Brain delivery of proteins by the intranasal route of administration: a comparison of cationic liposomes versus aqueous solution formulations. J Pharm Sci 99:1745–1761
Cheng YF, Zhu GQ, Wang M, Cheng H, Zhou A, Wang N, Fang N, Wang XC, Xiao XQ, Chen ZW (2008) Involvement of ubiquitin proteasome system in protective mechanisms of Puerarin to MPP+-elicited apoptosis. Neurosci Res 63:52–58
Stanwood GD, Leitch DB, Savchenko V, Wu J, VAF, Anderson DJ, Stankowski JN, Aschner M, Mclaughlin BA (2009) Manganese exposure is cytotoxic and alters dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons within the basal ganglia. J Neurochem 110:378–389
Ossola B, Kääriäinen TM, Raasmaja A, Männistö PT (2008) Time-dependent protective and harmful effects of quercetin on 6-OHDA-induced toxicity in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicology 250:1–8
Simola N, Morelli M, Carta AR (2007) The 6-Hydroxydopamine model of parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 11:151–167
Virgone-Carlotta A, Uhlrich J, Akram MN, Ressnikoff D, Chrétien F, Domenget C, Gherardi R, Despars G, Jurdic P, Honnorat J (2013) Mapping and kinetics of microglia/neuron cell-to-cell contacts in the 6-OHDA murine model of Parkinson’s disease. Glia 61:1645–1658
Thiele SL, Warre R, Nash JE (2012) Development of a unilaterally-lesioned 6-OHDA mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Vis Exp 60:e3234–e3234
Jing X, Shi H, Zhang C, Ren M, Han M, Wei X, Zhang X, Lou H (2014) Dimethyl fumarate attenuates 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells and in animal model of Parkinson’s disease by enhancing Nrf2 activity. Neuroscience 286:131–140
Li Z, Hu Y, Zhu Q, Zhu J (2008) Neurotrophin-3 reduces apoptosis induced by 6-OHDA in PC12 cells through Akt signaling pathway. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:635–640
Bezard, Zhao (2005) Protective effect of green tea polyphenols on the SH-SY5Y cells against 6-OHDA induced apoptosis through ROS-NO pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 39:682–695
Mazumder S, Plesca D, Almasan A (2015) Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol 414:13–21
Porter AG, Jänicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104
Kim M, Cho KH, Shin MS, Lee JM, Cho HS, Kim CJ, Shin DH, Yang HJ (2014) Berberine prevents nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuronal loss and suppresses hippocampal apoptosis in mice with Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Med 33:870–878
Hartmann A, Hunot S, Michel PP, Muriel MP, Vyas S, Faucheux BA, Mouatt-Prigent A, Turmel H, Srinivasan A, Ruberg M (2000) Caspase-3: a vulnerability factor and final effector in apoptotic death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2875–2880
Zong WX, Lindsten T, Ross AJ, Macgregor GR, Thompson CB (2001) BH3-only proteins that bind pro-survival Bcl-2 family members fail to induce apoptosis in the absence of Bax and Bak. Genes Dev 15:1481–1486
Xu H, An D, Yin SM, Chen W, Zhao D, Meng X, Yu DQ, Sun YP, Zhao J, Zhang WQ (2015) The alterations of apoptosis factor Bcl-2/Bax in the early Parkinson’s disease rats and the protective effect of scorpion venom derived activity peptide. Chin J Applied Physiol 31:225–229
Arenas E, Trupp M, Åkerud P, Ibáñez CF (1995) GDNF prevents degeneration and promotes the phenotype of brain noradrenergic neurons in vivo. Neuron 15:1465–1473
Sharma HS (2006) Post-traumatic application of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glia-derived neurotrophic factor on the rat spinal cord enhances neuroprotection and improves motor function. Acta Neurochir Suppl 96:329–334
Clarkson ED, Zawada WM, Freed CR (1996) GDNF reduces apoptosis in dopaminergic neurons in vitro. Neuroreport 7:145–149
Tsybko AS, Il’Chibaeva TV (2015) The effects of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) on the levels of mRNA of apoptotic genes Bax and Bcl-xl in the brain of mice genetically predisposed to pathological behavior. Russ J Genet 5:407–412
Barre B, Perkins ND (2010) The Skp2 promoter integrates signaling through the NF-kappaB, p53, and Akt/GSK3beta pathways to regulate autophagy and apoptosis. Mol Cell 38:524–538
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, Birnbaum MJ, Yao R, Cooper GM, Segal RA, Kaplan DR, Greenberg ME (1997) Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt. Science 275:661–665
Dal-Cim T, Molz S, Egea J, Parada E, Romero A, Budni J, Saavedra MDMD, Barrio LD, Tasca CI, López MG (2012) Guanosine protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against mitochondrial oxidative stress by inducing heme oxigenase-1 via PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Neurochem Int 61:397–404
Gong L, Zhang QL, Zhang N, Hua WY, Huang YX, Di PW, Huang T, Xu XS, Liu CF, Hu LF (2012) Neuroprotection by urate on 6-OHDA-lesioned rat model of Parkinson’s disease: linking to Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway. J Neurochem 123:876–885
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81501109, U1504813).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, P., Gao, L., Wang, X. et al. Intranasal Administration of GDNF Protects Against Neural Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease Through PI3K/Akt/GSK3β Pathway. Neurochem Res 42, 1366–1374 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2184-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2184-1