Abstract
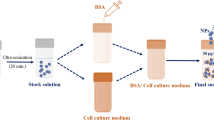
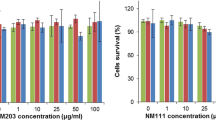
Here, we show that key physicochemical parameters of commercial Silicon Carbide nanoparticles, such as the primary particles of about 53 nm in size, the agglomerates size, and the surface composition, are considerably modified with respect to the pristine conditions, during in vitro assessment. The use of sample conditioning stages, such as the pre-dispersion in aqueous media and the subsequent dispersion in a culture medium specific to the in vitro assay, produce modifications as the absorption of N, C, and O, from the culture medium, in the nanoparticles surface. Our results show that the sedimented dose, fraction of sedimented NPs during incubation and consequently in contact with cells seeded at the bottom, of Silicon Carbide nanoparticles can be measured from the particle size distribution obtained using a centrifugal liquid sedimentation technique. It is underlined that the variations observed in the physicochemical properties are related to the in vitro assay conditions. Culture medium and incubation time are found to influence the most the sedimented dose and consequently the cells dose uptake.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora S, Rajwade JM, Paknikar KM (2012) Nanotoxicology and in vitro studies: the need of the hour. YTAAP 258(2):151–165. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2011.11.010
ATCC Cultures and Products (2011) http://www.lgcstandards-atcc.org/. Accessed 10 June 2012
Barillet S, Jugan M-L, Simon-Deckers A, Leconte Y, Herlin-Boime N, Mayne-l’Hermite M, Reynaud C, Carriere M (2009) SiC nanoparticles cyto- and genotoxicity to Hep-G2 cells. J Phys Conf Ser 170:012016
Barillet S, Jugan ML, Laye M, Leconte Y, Herlin-Boime N, Reynaud C, Carrière M (2010a) In vitro evaluation of SiC nanoparticles impact on A549 pulmonary cells: cyto-, genotoxicity and oxidative stress. Toxicol Lett 198(3):324–330
Barillet S, Simon-Deckers A, Herlin-Boime N, Mayne-L’Hermite M, Reynaud C, Cassio D, Gouget B, Carrière M (2010b) Toxicological consequences of TiO, SiC nanoparticles and multi-walled carbon nanotubes exposure in several mammalian cell types: an in vitro study. J Nanopart Res 12(1):61–73. doi:10.1007/s11051-009-9694-y
Bihari P, Vippola M, Schultes S, Praetner M, Khandoga A, Reichel C, Coester C, Tuomi T, Rehberg M, Krombach F (2008) Optimized dispersion of nanoparticles for biological in vitro and in vivo studies. Part Fibre Toxicol 5(1):14
Bruch J, Rehn B, Song W, Gono E, Malkusch W (1993) Toxicological investigations on silicon carbide. 2. In vitro cell tests and long term injection tests. Br J Ind Med 50(9):807–813
Christian P, Kammer F, Baalousha M, Hofmann T (2008) Nanoparticles: structure, properties, preparation and behaviour in environmental media. Ecotoxicology 17(5):326–343. doi:10.1007/s10646-008-0213-1
Cohen J, DeLoid G, Pyrgiotakis G, Demokritou P (2012) Interactions of engineered nanomaterials in physiological media and implications for in vitro dosimetry. Nanotoxicology 7(4):1–15. doi:10.3109/17435390.2012.666576
Dhawan A, Sharma V (2010) Toxicity assessment of nanomaterials: methods and challenges. Anal Bioanal Chem 398(2):589–605
Dickson MA, Hahn WC, Ino Y, Ronfard V, Wu JY, Weinberg RA, Louis DN, Li FP, Rheinwald JG (2000) Human keratinocytes that express hTERT and also bypass a p16INK4a-enforced mechanism that limits life span become immortal yet retain normal growth and differentiation characteristics. Mol Cell Biol 20(4):1436–1447. doi:10.1128/mcb.20.4.1436-1447.2000
Fubini B, Ghiazza M, Fenoglio I (2010) Physico-chemical features of engineered nanoparticles relevant to their toxicity. Nanotoxicology 4(4):347–363
Guevara-Lora I, Czosnek C, Smycz A, Janik J, Kozik A (2009) SiC nanoparticles as potential carriers for biologically active substances. J Phys: Conf Ser 146(1):012022
Hinderliter P, Minard K, Orr G, Chrisler W, Thrall B, Pounds J, Teeguarden J (2010) ISDD: a computational model of particle sedimentation, diffusion and target cell dosimetry for in vitro toxicity studies. Part Fibre Toxicol 7(1):36
Iolitec (2007) Silicon(IV)carbide–Technical data sheet. http://www.nanomaterials.iolitec.de/prod_ca_e.htm. Accessed 5 Aug 2012
Jiang J, Oberdörster G, Biswas P (2009) Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nanopart Res 11(1):77–89
Jones CF, Grainger DW (2009) In vitro assessments of nanomaterial toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(6):438–456
Kato H, Fujita K, Horie M, Suzuki M, Nakamura A, Endoh S, Yoshida Y, Iwahashi H, Takahashi K, Kinugasa S (2010) Dispersion characteristics of various metal oxide secondary nanoparticles in culture medium for in vitro toxicology assessment. Toxicol In Vitro 24(3):1009–1018
Laloy J, Robert S, Marbehant C, Mullier F, Mejia J, Piret J-P, Lucas S, Chatelain B, Dogné J-M, Toussaint O, Masereel B, Rolin S (2012) Validation of the calibrated thrombin generation test (cTGT) as the reference assay to evaluate the procoagulant activity of nanomaterials. Nanotoxicology 6(2):213–232. doi:10.3109/17435390.2011.569096
Limbach LK, Li Y, Grass RN, Brunner TJ, Hintermann MA, Muller M, Gunther D, Stark WJ (2005) Oxide nanoparticle uptake in human lung fibroblasts: effects of particle size, agglomeration, and diffusion at low concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 39(23):9370–9376. doi:10.1021/es051043o
Lison D, Thomassen LCJ, Rabolli V, Gonzalez L, Napierska D, Seo JW, Kirsch-Volders M, Hoet P, Kirschhock CEA, Martens JA (2008) Nominal and effective dosimetry of silica nanoparticles in cytotoxicity assays. J Toxicol Sci 104(1):155–162. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfn072
Lozano O, Mejia J, Masereel B, Toussaint O, Lison D, Lucas S (2012a) Development of a PIXE analysis method for the determination of the biopersistence of SiC and TiC nanoparticles in rat lungs. Nanotoxicology 6(3):263–271. doi:10.3109/17435390.2011.572301
Lozano O, Mejia J, Tabarrant T, Masereel B, Dogné J-M, Toussaint O, Lucas S (2012b) Quantification of nanoparticles in aqueous food matrices using particle-induced X-ray emission. Anal Bioanal Chem 403(10):2835–2841. doi:10.1007/s00216-012-5895-9
Maiorano G, Sabella S, Sorce B, Brunetti V, Malvindi MA, Cingolani R, Pompa PP (2010) Effects of cell culture media on the dynamic formation of protein-nanoparticle complexes and influence on the cellular response. ACS Nano 4(12):7481–7491
Mejia J, Tichelaar F, Saout C, Toussaint O, Bernard M, Mekhalif Z, Lucas S, Delhalle J (2011) Effects of the dispersion methods in Pluronic F108 on the size and the surface composition of MWCNTs and their implications in toxicology assessment. J Nanopart Res 13(2):655–667
Mejia J, Valembois V, Piret J-P, Tichelaar F, Bernard M, Toussaint O, Delhalle J, Mekhalif Z, Lucas S (2012) Are stirring and sonication pre-dispersion methods equivalent for the in vitro toxicology evaluation of SiC and TiC? J Nanopart Res 14(4):815–833. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-0815-7
Merkus HG (2009) Particle size measurements–fundamentals, practice, quality. Particle technology series, vol 17. Springer Netherlands, Netherlands, pp 329–334. doi:978-1-4020-9016-5
Monopoli MP, Walczyk D, Campbell A, Elia G, Lynch I, Baldelli Bombelli F, Dawson KA (2011) Physical-chemical aspects of protein corona: relevance to in vitro and in vivo biological impacts of nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 133(8):2525–2534
Piret JP, Detriche S, Vigneron R, Vankoningsloo S, Rolin S, Mejia Mendoza J, Masereel B, Lucas S, Delhalle J, Luizi F, Saout C, Toussaint O (2010) Dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in biocompatible dispersants. J Nanopart Res 12(1):75–82
Pourchez J, Forest V, Boumahdi N, Boudard D, Tomatis M, Fubini B, Herlin-Boime N, Leconte Y, Guilhot B, Cottier M, Grosseau P (2012) In vitro cellular responses to silicon carbide nanoparticles: impact of physico-chemical features on pro-inflammatory and pro-oxidative effects. J Nanopart Res 14(10):1–12. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1143-7
Singh B, Jena J, Besra L, Bhattacharjee S (2007) Dispersion of nano-silicon carbide (SiC) powder in aqueous suspensions. J Nanopart Res 9(5):797–806
Stone V, Johnston H, Schins RPF (2009) Development of in vitro systems for nanotoxicology: methodological considerations. Crit Rev Toxicol 39(7):613–626. doi:10.1080/10408440903120975
Svensson I, Artursson E, Leanderson P, Berglind R, Lindgren F (1997) Toxicity in vitro of some silicon carbides and silicon nitrides: whiskers and powders. Am J Ind Med 31(3):335–343. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0274(199703)31:3<335:AID-AJIM10>3.0.CO;2-1
Teeguarden JG, Hinderliter PM, Orr G, Thrall BD, Pounds JG (2007) Particokinetics in vitro: dosimetry considerations for in vitro nanoparticle toxicity assessments. J Toxicol Sci 95(2):300–312. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfl165
Vankoningsloo S, Piret J-P, Saout C, Noel F, Mejia J, Zouboulis CC, Delhalle J, Lucas S, Toussaint O (2010) Cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in three skin cellular models: effects of sonication, dispersive agents and corneous layer of reconstructed epidermis. Nanotoxicology 4(1):84–97. doi:10.3109/17435390903428869
Vankoningsloo S, Piret J-P, Saout C, Noel F, Mejia J, Coquette A, Zouboulis CC, Delhalle J, Lucas S, Toussaint O (2011) Pro-inflammatory effects of different MWCNTs dispersions in p16INK4A-deficient telomerase-expressing human keratinocytes but not in human SV-40 immortalized sebocytes. Nanotoxicology 6(1):1–17
Wittmaack K (2011) Novel dose metric for apparent cytotoxicity effects generated by in vitro cell exposure to silica nanoparticles. Chem Res Toxicol 24(2):150–158
Zouboulis CC, Seltmann H, Neitzel H, Orfanos CE (1999) Establishment and characterization of an immortalized human sebaceous gland cell line (SZ95). J Invest Dermatol 113(6):1011–1020
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the “Direction Générale des Technologies de la Recherche et de l’Energie” (DGTRE) of the Walloon Region of Belgium (Nanotoxico Project, RW/FUNDP research convention No. 516252). O. Toussaint is a Research Associate of the Belgian FRS/FNRS. The authors acknowledge financial support from the European Union under the Framework 7 program, Qnano (INFRASTRUCTURE-2010-1-262163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mejia, J., Piret, JP., Noël, F. et al. Dose assessment of SiC nanoparticle dispersions during in vitro assays. J Nanopart Res 15, 1875 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1875-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1875-z