Abstract
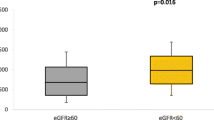
Our purpose was to determine whether the VEGF −152 G/A polymorphism could be associated with chronic kidney disease and endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive patients. There were 100 healthy volunteers enrolled into the control group. The group of patients was constituted by 99 consecutively admitted hypertensive patients referred to our Institution by their general practitioner. All patients were treated with anti-hypertensive polytherapy. Presented study revealed that the hypertensive patients bearing the GG genotype were characterized by the highest values of diastolic blood pressure and markers of endothelial damage such as Angiogenin, Endostatin, CRP as well as von Willebrandt factor. In addition, higher number of immature endothelial progenitor cells with CD34+CD133+, CD34+CD133- markers was observed in GG hypertensive carriers while in normotensive individuals no differences were found. Such phenomenon may indicate an increased mobilization of bone-marrow derived endothelial progenitors. It may testify to the preserved compensatory mechanism in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients until the G3a stage of the disease. Moreover, patients with higher estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) level had lower of vWf and Endostatin values, and higher level of VEGF. Taken together our findings clearly indicate the −152 GG hypertensive carriers as more prone to develop CKD. We can suspect that the VEGF −152 GG genotype is strongly associated with hypertension-dependent CKD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noble LE, Ferdinand AC, Stassen Frank RM, Hacking Wim JG, Boudier Struijker Harry AJ (1998) Angiogenesis and hypertension. J Hypertens 16:1563–1572
Antonios TF, Singer DR, Markandu ND, Mortimer PS, MacGregor GA (1999) Rarefaction of skin capillaries in borderline essential hypertension suggests an early structural abnormality. Hypertension 34:655–658
Ciuffetti G, Pasqualini L, Pirro M, Lombardini R, De Sio M, Schillaci G, Mannarino E (2002) Blood rheology in men with essential hypertension and capillary rarefaction. J Hum Hypertens 16:533–537
Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T (1997) The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev 18:4–25
Khakoo AY, Finkel T (2005) Endothelial progenitor cells. Annu Rev Med 56:79–101
Coban E, Timurağaoğlu A, Ozdoğan M (2004) Endothelial dysfunction in patients with white coat hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 18:71–72
Mandraffino G, Sardo MA, Riggio S, Loddo S, Imbalzano E, Alibrandi A, Saitta C, Cinquegrani M, Mormina EM, Saitta A (2011) Circulating progenitor cells are increased in newly diagnosed untreated hypertensive patients with arterial stiffening but normal carotid intima-media thickness. Hypertens Res 34:876–883
Palmirotta R, Ferroni P, Ludovici G, Martini F, Savonarola A, D’Alessandro R, Raparelli V, Proietti M, Scarno A, Riondino S, Basili S, Guadagni F (2010) VEGF-A gene promoter polymorphisms and microvascular complications in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Biochem 43:1090–1095
Hamedian AA, Esteghamati A, Noshad S, Mozafari M, Moin-Tavakkoli H, Nakhjavani M, Mahmoudi T, Nikzamir M, Safary R, Nikzamir A (2012) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) +405 C/G polymorphism is associated with essential hypertension in a population from Tehran of Iran. Mol Biol Rep 39:6213–6218
Rajnoch J, Viklický O (2004) Angiogenesis and organ transplantation. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 49:499–505
Reiterová J, Obeidová H, Lenícek M, Stekrová J, Merta M, Maixnerová D, Vítek L, Viklický O, Tesar V (2008) Influence of VEGF polymorphism on progression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Blood Press Res 31:398–403
Yang JW, Hutchinson IV, Shah T, Fang J, Min DI (2011) Gene polymorphism of vascular endothelial growth factor −1154 G > A is associated with hypertensive nephropathy in a Hispanic population. Mol Biol Rep 38:2417–2425
Lee S-H, Jeung IC, Park TW, Lee K, Lee DG, Cho Y-L, Lee TS, Na H-J, Park Y-J, Lee HG, Jeong MS, Bae K-H, Lee SC, Lee HJ, Kwon Y-G, Hong HJ, Kim J-S, Min J-K (2015) Extension of the in vivo half-life of endostatin and its improved anti-tumor activities upon fusion to a humanized antibody against tumor-associated glycoprotein 72 in a mouse model of human colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget 6:7182–7194
Skrzypkowska M, Myśliwska J, Słomiński B, Siebert J, Gutknecht P, Ryba-Stanisławowska M (2014) Quantitative and functional characteristics of endothelial progenitor cells in newly diagnosed hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens. doi:10.1038/jhh.2014.85
Zhang K, Yin F, Lin L (2014) Circulating endothelial cells and chronic kidney disease. Biomed Res Int 2014:364738
Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, Verschuren M, Albus C, Benlian P, Boysen G, Cifkova R, Deaton C, Ebrahim S, Fisher M, Germanò G, Hobbs R, Hoes A, Karadeniz S, Mezzani A, Prescott E, Ryden L, Scherer M, Syvanne M, Scholte Op Reimer WJM, Vrints C, Wood D, Zamorano JL, Zannad F (2012) Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: the fifth joint task force of the european society of cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice constituted by re. Eur Heart J 2012(33):1635–1701
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of diet in renal disease study group. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Mula-Abed W-AS, Al-Rasadi K, Al-Riyami D (2012) Estimated glomerular filtration rate (egfr): a serum creatinine-based test for the detection of chronic kidney disease and its impact on clinical practice. Oman Med J 27:108–113
Kirsztajn GM, Filho NS, Draibe SA, de Netto MVP, Thomé FS, Souza E, Bastos MG (2012) Fast reading of the KDIGO guidelines for evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease in clinical practice. J Bras Nefrol'orgão Of Soc Bras e Lat-Am Nefrol 36:63–73
Rodríguez-Carrio J, de Paz B, López P, Prado C, Alperi-López M, Ballina-García FJ, Suárez A (2014) IFNα serum levels are associated with endothelial progenitor cells imbalance and disease features in rheumatoid arthritis patients. PLoS One 9:e86069
Summers AM, Coupes BM, Brennan MF, Ralph SA, Short CD, Brenchley PEC (2005) VEGF -460 genotype plays an important role in progression to chronic kidney disease stage 5. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2427–2432
Chen J, Hamm LL, Kleinpeter MA, Husserl F, Khan IE, Chen C-S, Liu Y, Mills KT, He C, Rifai N, Simon EE, He J (2012) Elevated plasma levels of endostatin are associated with chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol 35:335–340
Zhai Y-L, Zhu L, Shi S-F, Liu L-J, Lv J-C, Zhang H (2014) Elevated soluble VEGF receptor sFlt-1 correlates with endothelial injury in IgA nephropathy. PLoS ONE 9:e101779
Domingueti CP, Dusse LM, Fóscolo RB, Reis JS, Annichino-Bizzacchi JM, Orsi FL, Mazetto Bde M, Carvalho Md, Gomes KB, Fernandes AP (2015) Von Willebrand Factor, ADAMTS13 and d-dimer are correlated with different levels of nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. PLoS One 10:e0132784
Acknowledgments
The paper was subsided by the grant of National Science Centre Nr 2011/01/B/NZ5/00345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Małkiewicz, A., Skrzypkowska, M., Słomiński, B. et al. The GG genotype of the −152 G/A vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) polymorphism predisposes to hypertension-related chronic kidney disease. Mol Biol Rep 43, 967–975 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4035-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4035-6