Abstract
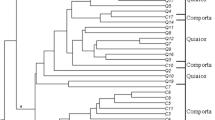
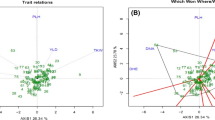
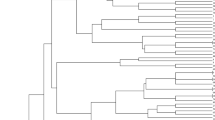
Aegilops tauschii Coss. is a diploid (2n = 2x = 14,DD) goat grass species which has contributed the D genome in common wheat. Genetic variations in 28 accessions of Aegilops tauschii belonged to different provinces of Iran, were evaluated using 16 morphological traits and 19 SSR markers. In number of spikelet per spike and plant height, there was a high variation in ssp. tauschii and ssp. strangulata respectively and for days to mature a low variation in both subspecies was found. Discriminant function analysis showed that 67.9% of original grouped cases correctly classified. Factor analysis indicated that three factor explain 66.49% of total variation. The three clusters revealed by the cluster analysis were not consistent with their geographical distributions. We determined 208 alleles using 19 microsatellites. Average of alleles for every locus was 10.94. The total average of PIC was 0.267. 2261 bands produced for total of genotypes and Chinese Spring had the highest bands (95 alleles). The range of similarity coefficients was between 0.23 and 0.73. Genotypes were clustered using UPGMA method. The accessions did not match according to morphological cluster and geographical regions. 51.2% of total variations were related to 9 principle components.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaharieva M, Dimov A, Stankova P, David J, Monnereux P (2003) Morphological diversity and potential interest for wheat improvement of three Aegilops L. species from Bulgaria. Genet Resour Crop Ev. 50:507–517
Dvorak J, Luo MC, Yang ZL, Zhang HB (1998) The structure of Aegilops tauschii genepool and the evaluation of hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 97:657–670
van Slageren MN (1994) Wild wheat: a monograph of Aegilops L.and Amblyopyrom (Jaub.&Spach) Eig. Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Nakai Y (1979) Isosyme variation in Aegilops and Triticum, IV the origin of the common wheat revealed from the study on esterase isozymes in synthesized wheats. Jpn J Genet 54:175–189
Kihara H, Tanaka M (1958) Morphological and physiological variation among Aegilops squarrosa strains collected in Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran. Preslia 30:241–251
Eig A (1929) Monographisch-kritisch Ubersicht der Gattung Aegilops. Verlag des Repertoriums, Dahlem bei Berlin
Pestsova E, Korzun V, Gncharov NP, Hammer K, Ganal MW, Roder MS (2000) Microsatellite analysis of Aegilops tauschii germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 101:100–106
Knaggs P, Ambrose MJ, Reader SM, Miller TE (2000) Morphological characterization and evaluation of the subdivision of Aegilops tauschii Coss. Wheat Inform Serv 91:15–19
Cox TS, Raupp WJ, Wilson DL, Gill BS, Leath S, Bockus WW, Browder LE (1992) Resistance to foliar diseases in a collection of Triticum-tauschii germ plasm. Plant Dis 76:1061–1064
Lagudah ES, Halloran GM (1988) Phylogenetic relationships of Triticum tauschii the D genome donor to hexaploid wheat. 1: Variation in HMW subunits of glutenin and gliadins. Theor Appl Genet 75: 592–598
Le HT, Reikosky DA, Olien CR, Cress CE (1986) Freezing hardiness of some accessions of Triticum tauschii and Triticum turgidum var. durum. Can J Plant Sci 66:893–899
Limin AE, Fowler DB (1981) Cold hardiness of some relatives of hexaploid wheat. Can J Bot 59:572–573
Orth RA, Bushuk W (1973) Studies of glutenin: III. Identification of subunits coded by the D-genome and their relation to bread making quality. Cereal Chem 50:80–687
Schachtman DP, Lagudah ES, Munns R (1992) The expression of salt tolerance from Triticum tauschii in hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84:714–719
Hammer K (1980) Vorarbeiten zur monographischen Darstellung von Wildpflanzensortimenten :Aegilops L.Kulturpflanze 28:33–180
Naghavi MR, Amirian R (2005) Morphological characterization of accessions of Aegilops tauschii. Int J Agric Biol 7:392–394
Goncharov NP, Chikida NN (1995) Genetics of growth habit in Aegilops squarrosa L. Russ J Genet 3:343–346
Konarev VG (1980) Ae.squarrosa. In: Konarev VG (ed) Proteins of wheat (in Russian). Moscow, Kolos, pp 227–241
Jasska V (1981) Aspartate aminotransferas and alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes:intraspecific differentiation in Aegilops tauschii and origin of the Dgenome polyploids in the wheat group. Plant Syst Evol 137:259–273
Nishikawa K, Furuta Y, Wada T (1980) Genetic studies on alpha-amylase isozymes in wheat. III. Intraspecific variation in Aegilops squarrosa and the birthplace of hexaploid wheat. Jpn J Genet 55:325–336
Lubbers EL, Gill KS, Cox TS, Gill BS (1991) Variation of molecular markers among geographically diverse accessions of Triticum tauschii. Genome 34:354–361
Saeidi H, Rahiminejad MR, Vallian S, Heslop-Harison JS (2006) Biodiversity of diploid D-genome Aegilops tauschii Coss. In Iran measured using microsatellites. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:1477–1484
Naghavi MR, Mardi M, Pirseyedi SM, Kazemi M, Potki P, Ghaffari MR (2007) Comparison of genetic variation among accessions of Aegilops tauschii using AFLP and SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:237–240
Fahima T, Roder M, Grama A, Vnero E (1998) Microsatellite DNA polymorphism divergence in triticum dicoccoides accessions highly resistance to yellow rust. Theor Appl Genet 96:187–195
Roder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetice 149:2007–2023
Saghai maroof MA, Blyashefve RM, Yang GP, Zhang G, Allera RM (1994) Extraordinary polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barely species diversity chromosomal location and accession dynamic. Proceeding of the national academy of science USA 91:5466–5470
Roder MS, Pluschke J, Konig SU, Borner A, Sorrells ME (1995) Abundance, variability and chromosomal location of microsatellites in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 246:327–333
Zhang LQ, Liu DC, Yan ZH, Lan XJ, Zheng YL, Zhou YH (2004) Rapid changes of microsatellite flanking sequence in the allopolyploidization of new synthesized hexaploid wheat. Sci China Ser C 47:553–561
Kihara H, Yamashita K, Tanaka M (1965). Morphological, physiological, genetical and cytological studies in Aegilops and Triticum collected in Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran. In: Yamashita K (Ed), Cultivated plants and their relatives. Results of the Kyoto University Scientific Expedition to the Korakoram and Hindukush, 1955.Vol. 1. Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, pp 41–48
Kim WK, Innes RL, Kerber ER (1992) Ribosomal DNA repeat unit polymorphism in six Aegilops species. Genome 35:510–514
Vojdani P, Meybodi M (1993) Distribution and genetic diversity of primitive bread wheat in Iran. In: Damanina AB (ed) Biodiversity and wheat improvement. Wiley, Chichester, UK, pp 409–415
Nevo E (1988) Genetic resources of wild emmer wheat revisited: genetic evolution conservation and utilization. In: Miller TE, Kobner RMD (eds) Proc 7th International wheat genetics Symposium, Cambridge, UK, pp 121–126
Semagn K (2002) Genetic relationships among ten endod types as revealed by a combination of morphological, RAPD and AFLP markers. Heredity 137:149–156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahernezhad, Z., Zamani, M.J., Solouki, M. et al. Genetic diversity of Iranian Aegilops tauschii Coss. using microsatellite molecular markers and morphological traits. Mol Biol Rep 37, 3413–3420 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9931-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9931-6