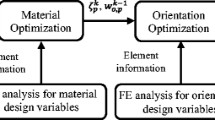
In practice, the problems connected with the fatigue of composites are intricate because of their complex structure and the fatigue loading. Fatigue tests under different fiber orientation angles are time-consuming and also very expensive. Therefore, it is important to establish a technique to consider the fatigue damage at any fiber orientation angle without having to perform excessive amounts of testing. The general purpose is to elaborate a methodology for finding a globally optimum design of composite laminates subjected to in-plane loads. In this part of the study, the Fawaz–Ellyin model of fatigue life prediction is presented and further validated. The results obtained show that the model can be applied to optimization problems of composites.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. T. Hahn and R. Y. Kim, “Fatigue behavior of composite laminate,” J. Compos. Mater., 10, 156–180 (1976).
B. Harris, Fatigue in Composites: Science and Technology of the Fatigue Response of Fibre-Reinforced Plastics. University of Bath, UK: Woodhead Publ. Limited (2008).
S. Sihn and J. W. Park “MAE: An Integrated Design Tool for Failure and Life Prediction of Composites,” J. Compos. Mater., 42, 1–22 (2008).
K. L. Reifsnider, Fatigue of Composite Materials, Elsevier Sci. Publ. B. V. (1991).
O. O. Ochoa and J. N. Reddy, Finite Element Analysis of Composite Laminates, Kluwer Academic Publishers (1992).
Z. Fawaz and F. Ellyin, “A new methodology for the prediction of fatigue failure in multidirectional fiber-reinforced laminates,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 53, No. 1, 47–55 (1995).
Z. Fawaz and F. Ellyin, “Fatigue failure model for fiber-reinforced materials under general loading conditions,” J. Compos. Mater., 28, No. 15, 1432–1451 (1994).
W. Hwang, K. S. Han, “Fatigue of composites-fatigue modulus concept and life prediction,” J. Compos. Mater., 20, 154–165 (1986).
Z. Hashin and A. Rotem, “Fatigue failure criterion for fiber-reinforced materials,” J. Compos. Mater., 7, 448–464 (1973).
I. J. Toth, “Creep and fatigue behavior of unidirectional and cross-plied composites. Composite Materials: Testing and Design,” 1969, ASTM STP 460, pp. 236–253.
J. Awerbuch and H. T. Hahn, “Off-axis fatigue of graphite/epoxy composite. Fatigue of Fibrous Composite Materials,” 1981, ASTM STP 723, pp. 243–273.
H. El-Kadi and F. Ellyin, “Effect of stress ratio on the fatigue of unidirectional glass-fiber epoxy composite laminae,” Composites, 25, No.10, 917–924 (1994).
E. W. Smith, “Cyclic Biaxial Deformation and Failure of a Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Composites,” Ph.D. Thesis, Cambridge University Press, 1976.
A. Rotem and H.G. Nelson, “Failure of a laminated composite under tension-compression fatigue loading,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 36, No.1, 46–62 (1989).
15 W. Fuqiang and Y. Weixing, “A model of the fatigue life distribution of composite laminates based on their static strength distribution,” Chinese J. Aeronaut., 21, 241–246 (2008).
W. F. Wu, L. J. Lee, and S. T. Choi, “A study of fatigue damage and fatigue life of composite laminates,” J. Compos. Mater., 30, No.1, 123–137 (1996).
U. Icardi, S. Locatto, and A. Longo, “Assessment of recent theories for predicting failure of composite laminates,” Appl. Mech. Rev., 1–6, 76–86 (2007).
M. Quaresimin, L. Susmel, and R. Talreja, “Fatigue behaviour and life assessment of composite laminates under multiaxial loadings,” Int. J. Fatigue, 32, No. 1, 2–16 (2010).
J. Kennedy and R.C. Eberhart, “Particle swarm optimization,” Proc. the fourth IEEE Int. Conf. on Neural Networks, 1995. p. 1942–1948.
F. Ellyin and H. El-Kadi, “A fatigue failure criterion for fiber-reinforced composite laminae,” Compos. Struct., 15, 61–74 (1990).
A. P. Mouritz, “A simple fatigue life model for three-dimensional fiber-polymer composites,” J. Compos. Mater., 40, No.5, 455–469 (2006).
V. M. Harik and T. A. Bogetti, “Low cycle fatigue of composite laminates: A damage-mode-sensitive model,” J. Compos. Mater., 37, No.7, 597–610 (2003).
M. Shokrieh and L.B. Lessard, “Progressive fatigue damage modeling of composite materials, part I: Modeling”, J Compos Mater, 34, No. 13, 1056–1080 (2000).
M. Shokrieh and L.B. Lessard, “Multiaxial fatigue behavior of unidirectional plies based on uniaxial fatigue experiments-I. modeling,” Int. J. Fatigue, 19, No.3, 201–207 (1997).
J. Noda, M. Nakada, and Y. Miyano, “Fatigue life prediction under variable cyclic loading based on statistical linear cumulative damage rule for CFRP laminates,” J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., 26, No.7, 665–680 (2007).
Z.-M. Huang, “Micromechanical life prediction for composite laminates,” Mech. Mater., 33, 185–199 (2001).
J. A. Epaarachchi and P. D. Clausen, “An empirical model for fatigue behavior prediction of glass fibre-reinforced plastic composites for various stress ratios and test frequencies,” Compos. Part A- Appl. S, 34, 313–326 (2003).
C. Kassapoglou, “Fatigue life prediction of composite structures under constant amplitude loading,” J. Compos. Mater., 41, No.22, 2737–2754 (2007).
Z. Hashin, “Failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composites,” J. Appl. Mech.-T ASME, 47, 329–335 (1980).
R. Apinis, “Acceleration of fatigue tests of polymer composite materials by using high-frequency loadings,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 40, No. 2, 107–118 (2004).
P. P. Oldyrev and R. P. Apinis, “On the influence of loading frequency on the multicycle fatigue of organoplastics,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 4, 629–633 (1983).
W. Van Paepegem and J. Degrieck, “Experimental set-up for and numerical modeling of bending fatigue experiments on plain woven glass/epoxy composites,” Compos. Struct., 51, No. 1, 1–8 (2001).
V. A. Limonov, V. G. Perevozchikov, and V. P. Tamuzh, “Fatigue of laminated composites with various reinforcement systems. 1. Experimental results,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 24, No. 5, 585–594 (1988).
Acknowledgment
This paper is based on the work supported by TUBITAK, The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, with code number 112M023. The author wishes to express his thanks to Professors V. Tamuzs and J. Jansons for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 48, No. 6, pp. 1011–1028, November-December, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ertas, A.H. Optimization of fiber-reinforced laminates for a maximum fatigue life by using the particle swarm optimization. Part I. Mech Compos Mater 48, 705–716 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-013-9314-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-013-9314-x