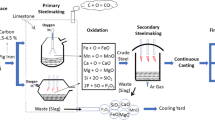
Reduce, reuse, and recycle are important techniques for waste management. These become significant for improving environmental and economic condition of industries. Integrated steel industries are generating huge amounts of steel slag as waste through the blast furnace and Linz–Donawitz (LD) process. Presently, these wastes are disposed by dumping in an unplanned manner, which causes many environmental problems. The generation rate of slag produced from steel industries is found to be in the range of 150–200 kg per ton of steel production. The LD slag generated by the basic oxygen converter, is one of the waste which can be reused due to the presence of a considerable amount of valuable minerals. In order to recycle and reuse the waste, assessment of their physicochemical, mineralogical and geotechnical characterization is imperative. This paper addresses the characterization and possible utilization of LD slag.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Das, S. Prakash, P. S. R. Reddy, and V. N. Mishra, “An overview of utilisation of slag and sludge from steel industries,” Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 50, 40–57 (2007).
J. Alexandre and J. Y. Boudonnet, “Les laitiers d'aciérie LD et leurs utilisations routières,” Laitier sidérurgiques, 75, 57–62 (1993).
S. Wu, Y. Xue, Q. Ye, and Y. Chen, “Utilisation of steel slag as aggregates for stone mastic asphalt (SMA) mixtures,” Build Environ., 42, 2580–5 (2007).
D. H. Shen, C. M. Wu, and J. C. Du, “Laboratory investigation of basic oxygen furnace slag for substitution of aggregate in porous asphalt mixture,” Constr. Build Mater., 23, 453–61(2009).
U. S. Yadav, B. K. Das, A. Kumar, and H. S. Sandhu, “Solid waste recycling through sinter status at Tata Steel,” Proc. Int. Environment and Waste Management., NML, Jamshedpur, India (2002), pp. 81–94.
T. Umadevi, S. P. Rao, Pankaj. Roy, et al., “Influence of LD slag on iron ore sinter properties and productivity,” 6th International Seminar on Mineral Processing Technology, NML Jamshedpur, 747–757 (2010).
An Overview of Steel Sector, http://steel.gov.in/Annual%20Report%20(201314)/English/Annual%20Report%20(English).pdf.
J. Pal, P. N. Chaudhary, and M. C. Goswami, “Utilisation of LD slag – An overview,” J. Met. Mater. Sci., 45, No. 2, 61–72 (2003).
H. Kolb and W. Leipold, “Slag for the building industry,” Redex Rundschau, No. 1–2, 261–9 (1993).
H, Schoenberger, “Final draft: best available techniques reference document on the production of iron and steel,” Publications of EC: European Commission, Joint Research Centre, IPTS, European IPPC Bureau, (2001).
D. Brandt and J. C. Warner (3rd ed.), Metallurgy Fundamentals, Goodheart-Willcox, Tinley Park, Ill, USA (2005).
I. Z. Yildirim and M. Prezzi, “Chemical, mineralogical, and morphological properties of steel slag,” Adv. Civ. Eng., 13 (2011).
S. Seetharaman, Fundamentals of Metallurgy, Woodhead Publishing and CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA (2005).
J. Waligora, D. Bulteel, P. Degrugilliers, et al., “Chemical and mineralogical characterisations of LD converter steel slag: A multi-analytical techniques approach,” Mater. Charact., 61, 39–48 (2010).
D. C. Goldring and L. M. Juckes, “Petrology and stability of LD slag,” Iron Making Steel Making, 24, No. 6, 447–56 (1997).
J. N. Murphy, T. R. Meadowcroft, and P. V. Barr, “Enhancement of the cementitious properties of steelmaking slag,” Can. Metall. Q., 36, 315–331(1997).
A. Monshi and M. K. Asgarani, “Producing Portland cement from iron and steel slags and limestone,” Cem. Concr. Res., 29, 1373–1377(1999).
W. Xuequan, Z. Hong, H. Xinkai, and L. Husen, “Study on steel slag and fly ash composite Portland cement,” Cem Concr Res., 29, No. 7, 1103–1106 (1999).
Y. S. Li, “The use of waste basic oxygen furnace slag and hydrogen peroxide to degrade 4-chlorophenol,” Waste Manage., 19, 495–502 (1999).
H. Motz and J. Geiseler, "Products of steel slags an opportunity to save natural resources,” Waste Manage., 21, 285–293 (2001).
S. K. Kawatra, S. J. Ripke, “Pelletising steel mill desulphuurisation slag,” Int. J. Miner. Process., 65, 165–175 (2002).
I. A. Altun and I. Yilmaz, “Study on steel furnace slags with high MgO as additive in Portland cement,” Cem. Concr. Res., 32, 1247–1249 (2002).
K. Morita, M, Guo, N, Oka, and N, Sano, “Resurrection of the iron and phosphorous resource in steel-making slag,” J. Mater. Cycles. Waste Manage., 4, 93–101 (2002).
L. M. Juckes, “The volume stability of modern steelmaking slags,” Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 112, No. 3, 177–197 (2003).
H. Shen and E. Forssberg, “An overview of recovery of metals from slags,” Waste Manage., 23, 933–949 (2003).
Y. Topkaya, N. Sevinc, and A. Gunaydin, “Slag treatment at Kardemir integrated iron and steel works,” Int. J. Miner. Process., 74, 31–40 (2004).
C. Shi, “Steel slag–its production, processing, characteristics, and cementitious properties,” J. Mater. Civ. Eng., 16, No. 3, 230–236 (2004).
H. Y. Poh, G. S. Ghataora, and N. Ghazireh, “Soil stabilisationusing basic oxygen steel slag fines,” J. Mater. Civ. Eng., 18, No. 2, 229–240 (2006).
M. Tossavainen, F. Engstrom, Q. Yang, et al., “Characteristics of steel slag under different cooling conditions,” Waste Manage., 27, No. 10, 1335–1344 (2007).
P. Y. Mahieux, J. E. Aubert, and G. Escadeillas, “Utilisation of weathered basic oxygen furnace slag in the production of hydraulic road binders,” Construct. Build. Mater., 23, 742–747 (2009).
N. Menad, M. Save, and M. Gamet, “Broyage et tris des laitiers d'aciérie de conversion,” Technical Report, BRGM, Orléans, France, 33 (2010).
M. Aarabi-Karasgani, F. Rashchi, N. Mostoufi, and E. Vahidi, “Leaching of vanadium from LD converter slag using sulphuric acid,” Hydromettallurgy, 102, 14–21 (2010).
N. P. Mahural, N. Pradhan, N. C. Mohanta, et al., “Dephosphorisation of LD slag by phosphorus solubilising bacteria,” Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 65, 404–409 (2011).
D. Wang, M. Jiang, C. Liu, et al., “Enrichment oe Fe-containing phases and recovery of iron and its oxides by magnetic separation from BOF slags,” Steel Res. Int., 83, No. 2, 189–196 (2012).
R. Singh, A. K. Gorai, and R. G. Segaran, “Characterisation of LD slag of Bokaro Steel Plant and its feasibility study of manufacturing commercial fly ash-LD slag bricks,” Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manage., 16, No. 1/2, 129–145 (2013).
N. Menad, N. Kanari, and M. Save, “Recovery of high grade iron compounds from LD slag by enhanced magnetic separation techniques,” Int. J. Miner. Process., 126, 1–9 (2014).
M. Nicolae, I. Vılciu, and F. Zaman, “x-Ray diffraction analysis of steel slag and blast furnace slag viewing their use for road construction,” UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. B, 69, No. 2, 99–108 (2007).
A. S. Reddy, R. K. Pradhan, and S. Chandra, “Utilisation of Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) slag in the production of a hydraulic cement binder,” Int. J. Miner. Process., 79, No. 2, 98–105 (2006).
F. Wachsmuth, J. Geiseler, W. Fix, et al., “Contribution to the structure of BOF-slags and its influence on their volume stability,” Can. Metall. Q., 20, No. 3, 279–284 (1981).
J. Geiseler, “Use of steel works slag in Europe,” Waste Manage., 16, No. 1–3, 59–63 (1996).
“Recycling of steel waste materials,” Steel Today and Tomorrow (Japan), 124, 11–12 (in English) (1993).
X. Huang and F. Wang, An overview of steel slag processing and utilisation, Manganese Ore of China 3 (in Chinese) (2001).
V. Ghai and W. H. Noseworthy, “Resource recovery programs at Lake Erie Steel,” Iron Steel Eng., (USA), 75, No. 5, 24–29 (1998).
K. M. Goodson and N. Donaghy, R. O. Russsel, Steelmaking Conference Proc., ISS (1995), p. 481.
C. J. Liu, X. Zhuy, and M. F. Jiang, Iron Steelmaking, 36 (2003).
T. Emi, “Molten slags, fluxes and salts,” Proc. 6th Int. Conf., Stockholm (2000), p. 001.
R. Dippenaar, “Industrial uses of slag (the use and re-use of iron and steelmaking slags),” Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 32, No. 1, 35–46 (2005).
T. M. Miller, J. Jimenez, A. Sharan, and D. A. Goldstein, “In Making, shaping and treating of steel," Steelmaking and Refining, 514, AISE Steel Foundation (1998).
D. M. Proctor, K. A. Fehling, E. C. Shay, et al.,“Physical and chemical characteristics of blast furnace, basic oxygen furnace, and electric arc furnace steel industry slags,” Environ. Sci. Technol., 34, No. 8, 1576–1582 (2000).
O. Negim, M. Mench, C. Bes, et al.,“In situ stabilisation of trace metals in a copper-contaminated soil using P-spiked Linz–Donawitz slag,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. R., 19, 847–857 (2012).
M. Pinto, M. Rodrigvez, and G. Besga, “Effects of Linz–Donawitz (LD) slag as soil properties and pasture production in the Basque country (Northern Spain),” New Zealand J. Agri. Res., 38, 143–155 (1995).
N. Pradhan, R. N. Kar, L. B. Sukla, et al., “Use of steel plant waste (LD Slag) as soil conditioner,” Proc. International Seminar on Downsizing Technology for Rural Development (2003), pp. 224–229.
M. Mench, V. Didier, M. Löffler, et al., “A mimicked in-situ remediation study of metal-contaminated soils with emphasis on cadmium and lead,” J. Environ. Qual., 23, 58–63 (1994a).
D. M. Proctor, E. C. Shay, K. A. Fehling, and B. L. Finley, “Assessment of human health and ecological risks posed by the uses of steel industry slags in the environment,” Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess., 8, 681–711 (2002).
C. S. Gahan, M. L. Cunha, and A. Sandstrom, “Comparative study on different steel slags as neutralising agent in bioleaching,” Hydrometallurgy, 95, 190–197 (2009).
D. Yilmaz, L. Lassabatere, R. Angulo-Jaramillo, et al., “Hydrodynamic characterisation of basic oxygen furnace slag through an adapted BEST method,” Vadose Zone J., 9, 107–116 (2010).
G. S. Basu, R. P. Sharma, and A. S. Dhilon, “Solid waste management in steel plants challenges and opportunities,” Tata Search., 39–42 (2002).
“Promoting effective utilisation of steel making slag,” NKK Monthly, Dec. 25, 2000.
F. A. Lopez Gomez, R. Aldecoa, M. A. Fernandez Prieto, et al., “Preparation of NPK fertilisers from ferrous-metallurgy,” Simoes. C. Eur. Commun. [Rep.], 18616, 1–57 (1999).
M. Maslehuddin, A. M. Alfarabi, M. Sharif, et al., “Comparison of properties of steel slag and crushed limestone aggregate concretes,” Construct. Build. Mater., 17, No. 2, 105–12 (2003).
S. Ozeki, “Properties and usage of steel plant slag. Encosteel: steel for sustainable development,” International Iron and Steel, Stockholm, Sweden (1997), pp. 16–17.
A. K. Mukherjee and T. K. Chakraborty, “Towards zero waste concept and possibilities in Indian iron and steel industry,” Proc. Int. Environment and Waste Management, NML, Jamshedpur, India (2000), pp. 37–49.
R. P. Sharma, G. S. Basu, M. D. Maheshawari, et al., “Utilisation of LD-slag in cementmaking-experience at Tata Seel,” Proc. ASIA Steel Int. Conf., Jamshedpur, India (2003), pp. 1.i.7.1–1.i.7.7.
H. N. Banerjee (ed.), The Technology of Portland Cement and Blended Cement, A.H. Wheeler and Co., Bengalore (1980), pp. 8–15.a.
H. Suito, Y. Hayashida, and Y. Takahashi “Minaralogical study of LD converter slags,” Tetsu-to-Hagane., 63, No. 8, 1252–1259 (1977).
B. Das, S. Prakash, P. S. R. Reddy, et al., “Effective utilisation of blast furnace flue dust of integrated steel plants,” Eur. J. Miner. Process. Environ. Prot., 2, No. 2, 61–7 (2002b).
S. Shiomi, N. Sano, and Y. Matsushita, “Removal of phosphorus in BOF slag,” Tetsu-to-Hagane., 63, No. 9, 1520–1528 (1977).
M. Dziarmagowski, M. Karboniczek, M. Pyzalsky, and J. Okon, “Reduction of converter slag in electric arc furnace,” Ironmaking and Steelmaking., 19, No. 1, 45–49 (1992).
Z. Guo, D. Wang, and Z. Xu, “Fundamental research on phosphorus removal in the smelting reduction process,” Steel Res., 65, No. 2, 47–52 (1994).
T. K. Roy, B. B. Sinha, B. Singh, and A. K. Das, “The metallurgy of solid waste recycling in integrated steel plant,” Tata Search., 123–126 (1998).
E. Fregeau-Wu, S. Pignolet-Brandom, and I. Iwasaki, “Liberation analysis of slow cooled steel making slags: implications for phosphorus removal," Proc. 1st International Conference on Processing Materials for Properties, sponsored by TMS, MMIJ Punl by Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS) (1993), pp. 153–6.
G. H. Thomas, “Investigations on LD slag with particular reference to its use for road construction (pamphlet),” Commission of the European Communities, Boite Postale, Luxembourg, 1003, 75 (1983).
N. Pradhan, B. Das, S. Acharya, et al., “Removal of phosphorus from LD slag using a heterotrophic bacterium,” Miner. Metall. Process., 3, No. 21, 149–52 (2005).
R. Panda, R. N. Kar, and C. R. Panda, “Dephosphorisation of LD slag by penicillium citrinum,” The Ecoscan: Int. Quart. J. Envir. Sci., 3, 247–250 (2013).
H. S. Park, B. C Ban, and K. S. Cho, “Smelting reduction for vanadium-recovery from LD-slag (I),” J Korean Inst. Met. Mater., 32, No. 8, 982–8 (1994).
F. J. Weiss, M. A. Goksel, J. L. Coburn, G. E. Metius, “The recycling of steel plant waste oxides using the PTC (Pellet Technology Corporation) cold bond carbon bearing pellet technology,” Disposal, Recycling and Recovery of Electric Furnace Exhaust Dust, Iron and Steel Society, AIME, 410, Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, Pennsylvania 15086, USA (1987), pp. 115–20.
K. K. Sharma, S. Swaroop, and D. S Thakur, “Recycling of LD slag through sinter route on direct charging in blast furnace at Bhilai Steel Plant,” Proc. National Seminar on Pollution Control in Steel Industries (1993), pp. 72–9.
Y. D. Shi, J. Wang, and P. G. Tan, “Study on the Treatment of Mercury in Sea Water with Steel Slag,” J. Qingdao. Univ. Technol. (in Chinese), 32, No. 3, 80–3 (2011).
C. Oh, S. Rhee, M. Oh, J. Park, “Removal characteristics of As(III) and As(V) from acidic aqueous solution by steel making slag,” J. Hazard. Mater., 213–214, 147–155 (2012).
D. H. Kim, M. C. Shin, H. D. Choi, et al., “Removal mechanisms of copper using steel-making slag: adsorption and precipitation,” Desalination, 223, 283–289 (2008).
J. M. Duan, J. M. Lin, H. D. Fang, et al., “Adsorption characteristic of modified steel-making slag for simultaneous removal of phosphorus and ammonium nitrogen from aqueous solution,” Chin. J. Environ. Eng. (in Chinese), 6. No. 1, 201–4 (2012).
A. N. Shilton, I. Elmetri, A. Driz, et al., “Phosphorus removal by an ‘active’ slag filter-a decade of full scale experience,” Water Res., 40, 113–8 (2006).
J. Gao, S. Y. Liu, Y. J. Yang, et al., “Study on adsorptive removal of phenol by steel slag,” Chin. J. Environ. Eng. (in Chinese), No. 2(4), 323–6 (2010).
Y, Sun, M. S. Yao, J. P. Zhang, and G. Yang, “Indirect CO2 mineral sequestration by steelmaking slag with NH4Cl as leaching solution,” Chem. Eng. J., 173, 437–445 (2011).
S. Eloneva, S. Tei, J. Salminen, et al., “Fixation of CO2 by carbonating calcium derived from blast furnace slag,” Energy, 33, 1461–7 (2008).
C. Kunzler, N. Alves, E. Pereira, et al., “CO2 storage with indirect carbonation using industrial waste,” Energy Procedia, 4,1010-7 (2011).
J. H. Feng, J. S. Wang, and S. H. Ke, “The basic study on desulfurisation of agglomeration gas by using converter steel sediment,” Hebei Polytech. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) (in Chinese), No. 1(32), 6–9 (2010).
X. L. Ding, Y. C. Guo, S. W. Tang, et al., “Experimental study on wet flue gas desulfurisation with scrap slag powder residue,” Environ Eng. (in Chinese), No. 3(27), 99–102 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chand, S., Paul, B. & Kumar, M. Sustainable Approaches for LD Slag Waste Management in Steel Industries: A Review. Metallurgist 60, 116–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-016-0261-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-016-0261-3