Abstract
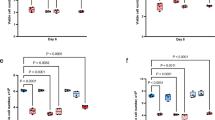
We studied the effects of phosphates on the expression of the human tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) gene and phosphate-regulating genes in short-term cultures of human osteoblastic osteosarcoma cell lines. When human osteosarcoma cell lines, SaOS-2, MG-63, and U2OS were cultured with 10 mM inorganic sodium dihydrogenphosphate, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 250 μM pyridoxal phosphate, or 100 μM inorganic pyrophosphate, enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase began to increase at 72 h after addition of sodium dihydrogenphosphate and β-glycerophosphate in SaOS-2 cells. Pyridoxal phosphate and pyrophosphate did not induce alkaline phosphatase activity. U2OS cells slightly reacted to β-glycerophosphate, but MG-63 cells did not react on exposure to phosphates. In SaOS-2 cells, TNSALP mRNA measured by real-time RT-PCR reached a peak level at 72 h after the addition of β-glycerophosphate. PHEX and MEPE mRNAs were also induced by β-glycerophosphate. These results suggest that TNSALP, PHEX and MEPE were concordantly induced by β-glycerophosphate on mineralisation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris H: The human alkaline phosphatases: What we know and what we don't know. Clin Chim Acta 186: 133–150, 1989
Whyte MP: Hypophosphatasia: Nature's window on alkaline phosphatase function in man. In: J. P. Bilezikian, L. G. Raisz, G. A. Rodan (eds). Principles of Bone Biology, 2nd ed., Vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, 2002, pp 1229–1248
Hui M, Tenenbaum HC: New face of an old enzyme: alkaline phosphatases may contribute to human tissue aging by inducing tissue hardening and calcification. Anat Rec 253: 91–94, 1998
Johnson K, Moffa A, Chen Y, Protzker K, Goding J, Terkeltaub R: Matrix vesicle plasma cell membrane glycoprotein-1 regulates mineralization by murine osteoblastic MC3T3 cells. J Bone Miner Res 14: 883–892, 1999
Ho AM, Johnson MD, Kingsley DM: Role of the mouse ank gene in control of tissue calcification and arthritis. Science 289: 265–270, 2000
Terkeltaub RA: Inorganic pyrophosphate generation and disposition on pathophysiology. Am J Physiol 281: C1–C11, 2001
Hessle L, Johnson KA, Anderson HC, Narisawa S, Sali A, Goding JW, Terkeltaub R, Millán JL: Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase and plasma cell membrane glycoprotein-1 are central antagonistic regulators of bone mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 9445–9449, 2002
Harmey D, Hessle L, Narisawa S, Johnson KA, Terkeltaub R, Millán JL: Concerted regulation of inorganic pyrophosphate and osteopontin by Akp2, Enpp1, and Ank. Am J Pathol 164: 1199–1209, 2004
Di Mauro S, Manes T, Hessle L, Kozlenkov A, Pizauro JM, Hoylaerts MF, Millán JL: Kinetic characterization of hypophosphatasia mutations with physiological substrates. J Bone Miner Res 17: 1383–1391, 2002
Weiss MJ, Cole DEC, Ray K, Whyte MP, Lafferty MA, Mulivor RA, Harris H: A mis sense mutation in the human liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase gene causing a lethal form of hypophosphatasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 7666–7669, 1988
Henthorn PS, Raducha M, Fedde KN, Lafferty MA, Whyte MP: Different missense mutations at the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene locus in autosomal recessively inherited forms of mild and severe hypophosphatasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 9924–9928, 1992
Orimo H, Hayashi Z, Watanabe A, Hirayama T, Hirayama T, Shimada T: Novel missense and frameshift mutations in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene in a Japanese patients with hypophosphatasia. Hum Mol Genet 3: 1683–1684, 1994
Orimo H, Goseki-Sone M, Sato S, Shimada T: Detection of deletion 1154–1156 hypophosphatasia mutation using TNSALP exon amplification. Genomics 42: 364–366, 1997
Mornet E: Hypophosphatasia: the mutations in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene. Hum Mutat 15: 309–315, 2000
Orimo H, Girschick HJ, Goseki-Sone M, Ito M, Oda K, Shimada T: Mutational analysis and functional correlation with phenotype in German patients with childhood-type hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res 16: 2313–2319, 2001
Russell RGG, Bisaz S, Donath A, Morgan DB, Fleisch H: Inorganic pyrophosphate in plasma in normal persons and in patients with hypophosphatasia, osteogenesis imperfecta, and other disorders of bone. J Clin Invest 50: 961–969, 1971
Fedde KN, Blair L, Silverstein J, Coburn SP, Ryan LM, Weinstein RS, Waymire K, Narisawa S, Millán JL, MacGregor GR, Whyte MP: Alkaline phosphatase knock-out mice recapitulate the metabolic and skeletal defects of infantile hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res 14: 2015–2026, 1999
Anderson HC, Sipe JB, Hessle L, Dhamyamraju R, Atti E, Camacho NP, Millán JL: Impaired calcification around matrix vesicles of growth plate and bone in alkaline phosphatase-deficient mice. Am J Pathol 164: 841–847, 2004
Scheibe RJ, Moeller-Runge I, Mueller WH: Retinoic acid induces the expression of alkaline phosphatase in P19 teratocarcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 266: 21300–21305, 1991
Kyeyune-Nyombi E, Lau K-HW, Baylink DJ, Strong DD: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 stimulates both alkaline phosphatase gene transcription and mRNA stability in human bone cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 291: 316–325, 1991
Orimo H, Shimada T: Regulation of the human tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene expression by all-trans-retinoic acid in SaOS-2 osteosarcoma cell line. Bone 36: 866–876, 2005
McQuillan DJ, Richardson MD, Bateman JF: Matrix deposition by a calcifying human osteogenic sarcoma cell line (SAOS-2). Bone 16: 415–426, 1995
Quarles LD: FGF23, PHEX, and MEPE regulation of phosphate homeostasis and skeletal mineralization. Am J Physiol 285: E1–E9, 2003
Collins JF, Bai L, Ghishan FK: The SLC20 family of proteins: Dual functions as sodium-phosphate cotransporters and viral receptors. Pflugers Arch-Eur J Physiol 447: 647–652, 2004
San Miguel SM, Goseki-Sone M, Sugiyama E, Watanabe H, Yanagishita M, Ishikawa I: The effects of retinoic acid on alkaline phosphatase activity and tissue-non-specific alkaline phosphatase gene expression in human periodontal ligament cells and gingival fibroblasts. J Periodont Res 33: 428–433, 1998
Lipman ML, Panda D, Bennett HPJ, Henderson JE, Shane E, Shen Y, Goltzman D, Karaplis AC: Cloning of human PEX cDNA. J Biol Chem 273: 13729–13737, 1998
Argiro L, Desbarats M, Glorieux FH, Ecarot B: MEPE, the gene encoding a tumor-secreted protein in oncogenic hypophosphatemic osteomalacia, is expressed in bone. Genomics 74: 342–351, 2001
Kehlen A, Lauterbach R, Santos AN, Thiele K, Kabisch U, Weber E, Riemann D, Langner L: IL-1β- and IL-4-induced down-regulation of autotoxin mRNA and PC-1 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clin Exp Immunol 123: 147–154, 2001
Reichenberger E, Tiziani V, Watanabe S, Park L, Ueki Y, Santanna C, Baur ST, Shiang R, Grange DK, Beighton P, Gardner J, Hamersma H, Sellars S, Ramesar R, Lidral AC, Sommer A, Raposo do Amaral CM, Gorlin RJ, Mulliken JB, Olsen BR: Autosomal dominant craniometaphyseal dysplasia is caused by mutations in the transmembrane protein ANK. Am J Hum Genet 68: 1321–1326, 2001
Jono S, McKee MD, Murry CE, Shioi A, Nishizawa Y, Mori K, Morii H, Giachelli CM: Phosphate regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ Res 87: e10–e17, 2000
Kaubisch A, Ward M, Schoetz S, Hesdorffer C, Bank A: Up-regulation of amphotrophic retroviral receptor expression in human peripheral blood CD34+ cells. Am J Hematol 61: 243–253, 1999
Shui C, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL, Khosla S: Changes in Runx2/Cbfa1 expression and activity during osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res 18: 213–221, 2003
Owen TA, Aronow M, Shalhoub V, Barone LM, Wilming L, Tassinari MS, Kennedy MB, Pockwinse S, Lian JB, Stein GS: Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: Reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol 143: 420–430, 1990
Mansfield K, Teixeira CC, Adams CS, Shapiro IM: Phosphate ions mediate chondrocyte apoptosis through a plasma membrane transporter mechanism. Bone 28: 1–8, 2001
Tenenhouse HS, Sabbagh Y: Novel phosphate-regulating genes in the pathogenesis of renal phosphate wasting disorders. Pflugers Arch–Eur J Physiol 444: 317–326, 2002
HYP Consortium: A gene (PEX) with homologies to endopeptidases is mutated in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Nat Genet 11: 130–136, 1995
Ecarot B, Desbarats M: 1,25-(OH)2D3 down-regulates expression of Phex, a marker of the mature osteoblast. Endocrinology 140: 1192–1199, 1999
Siggelkow H, Schmidt E, Hennies B, Hüfner M: Evidence of downregulation of matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein during terminal differentiation in human osteoblasts. Bone 35: 570–576, 2004
Rowe PSN, Garrett IR, Schwarz PM, Carnes DL, Lafer EM, Mundy GR, Gutierrez GE: Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) confirms that MEPE binds to PHEX via the MEPE-ASARM motif: a model for impaired mineralization in X-linked rickets (HYP). Bone 36: 33–46, 2005
Kavanaugh MP, Miller DG, Zhang W, Law W, Kozak SL, Kabat D, Miller AD: Cell-surface receptors for gibbon ape leukemia virus and amphotropic murine retrovirus are inducible sodium-dependent phosphate symporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 7071–7075, 1994
Beck Jr GR, Zerler B, Moran E: Phosphate is a specific signal for induction of osteopontin gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 8352–8357, 2000
Goseki-Sone M, Yamada A, Asahi K, Hirota A, Ezawa I, Iimura T: Phosphate depletion enhances tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene expression in a cultured mouse marrow stromal cell line ST2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265: 24–28, 1999
Oka T, Sugitatsu H, Nordin H, Thakur MK, Aoyama M, Sasagawa T, Suzuki I, Tsuji H: Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate inhibits DNA binding of HNF1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1568: 189–196, 2001
Matsubara K, Matsumoto H, Mizushima Y, Lee JS, Kato N: Inhibitory effect of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate on endothelial cell proliferation, replicative DNA polymerase and DNA topoisomerase. Int J Mol Med 12: 51–55, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orimo, H., Shimada, T. Effects of phosphates on the expression of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene and phosphate-regulating genes in short-term cultures of human osteosarcoma cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem 282, 101–108 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-1520-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-1520-6