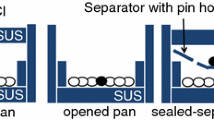
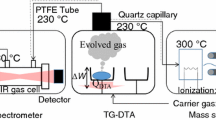
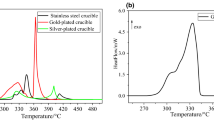
Abstract
Raman spectra of ammonium nitrate (AN) above its melting point of 443 K and decomposition temperature of 533 K were acquired, and the thermal properties of AN were assessed using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) so as to obtain a better understanding of the condensed phase decomposition. The Raman spectra of molten AN at both 443 and 533 K exhibited a strong peak at 1043 cm−1, assigned to the ν1 vibrational stretching mode of the NO −3 group, and a 710 cm−1 peak attributed to the δ4 bending mode of the NO −3 group, whereas no peak was observed at approximately 940 cm−1 due to the O′–NO2 stretching mode of HNO3. Chemical equilibrium calculations based on the reaction NO −3 + NH +4 ⇌ HNO3 + NH3 demonstrated that the concentration of HNO3 gradually increases with temperature, although the HNO3 to NO −3 ratio was still only approximately 0.0034, even at 533 K. Thus, molten AN was found to contain primarily NO −3 and only a minor amount of liquid HNO3 over the temperature range analyzed. The heat flow associated with condensed phase decomposition was simulated based on the assumption that the decomposition rate of AN is given by \( - {\text{d}}C_{\text{AN}} /{\text{d}}t = 10^{9.4} { \exp }\left( { - 125520/{RT}} \right)C_{{{\text{NH}}_{4}^{ + } }} C_{{{\text{HNO}}_{3} }} \) and that \( C_{{{\text{NH}}_{4}^{ + } }} \) and \( C_{{{\text{HNO}}_{3} }} \) are constant due to chemical equilibrium. The heat flow curves thus calculated were in good agreement with the experimental DSC data acquired at 5.1 MPa.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oommen C, Jain SR. Ammonium nitrate: a promising rocket propellant oxidizer. J Hazard Mater. 1999;67:253–81.
Oxley JC, Smith JL, Wang W. Compatibility of ammonium nitrate with monomolecular explosives. Part II. Nitroarenes. J Phys Chem. 1994;98:3901–7.
Marlair G, Kordek M. Safety and security issues relating to low capacity storage of AN-based fertilizers. J Hazard Mater. 2005;A123:13–28.
Dechy N, Bourdeaux T, Ayrault A, Kordek M, Coze JL. First lessons of the Toulouse ammonium nitrate disaster, 21st September 2001, AZF plant, France. J Hazard Mater. 2004;111:131–8.
Sinditskii VP, Egorshev VY, Levshenkov AI, Serushkin VV. Ammonium nitrate: combustion mechanism and the role of additives. Propellants Explos Pyrotech. 2005;30:269–80.
Sinditskii VP, Egorshev VY, Serushkin VV, Filatov SA. Combustion of energetic materials controlled by condensed-phase reactions. Combust Explos Shock Waves. 2012;48:81–99.
Kajiyama K, Izato Y, Miyake A. Thermal characteristics of ammonium nitrate, carbon, and copper(II) oxide mixtures. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:1475–80.
Izato Y, Miyake A, Echigoya H. Influence of the physical properties of carbon on the thermal decomposition behavior of ammonium nitrate and carbon mixtures. Sci Technol Energ Mater. 2009;70:101–4.
Izato Y, Date S, Miyake A. Combustion characteristics of ammonium nitrate and carbon mixtures based on a thermal decomposition mechanism. Propellants Explos Pyrotech. 2013;38:129–35.
Izato Y, Kajiyama K, Miyake A. Thermal decomposition mechanism of ammonium nitrate and copper(II) oxide mixtures. Sci Technol Energ Mater. 2014;75:128–33.
Miyake A, Izato Y. Thermal decomposition behaviors of ammonium nitrate and carbon mixtures. Int J Energ Mater Chem Propuls. 2010;9:467–75.
Matsunaga H, Habu H, Miyake A. Thermal behavior of new oxidizer ammonium dinitramide. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:1183–8.
Matsunaga H, Habu H, Miyake A. Influences of aging on thermal decomposition mechanism of high performance oxidizer ammonium dinitramide. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:1387–94.
Oxley JC, Smith JL, Rogers E, Yu M. Ammonium nitrate: thermal stability and explosivity modifiers. Thermochim Acta. 2002;384:23–45.
Brower KR, Oxley JC, Tewari MP. Evidence for hemolytic decomposition of ammonium nitrate at high temperature. J Phys Chem. 1989;93:4029–33.
Manelis GB, Nazin GM, Rubtsov YI, Strunin VA. Thermal decomposition and combustion of explosives and propellants. New York: Taylor & Francis; 2003. p. 175–83.
Ratcliffe CI, Irish DE. Vibrational spectral studies of solutions at elevated temperatures and pressures. VII. Raman spectra and dissociation of nitric acid. Can J Chem. 1985;63:3521–5.
Lucas H, Petitet J. High pressure Raman spectroscopy of nitric acid. J Phys Chem A. 1999;103(45):8952–8.
Wagman DD, Evans WH, Parker VB, Schumm RH, Halow I, Bailey SM, Churney KL, Nuttall RL. The NBS tables of chemical thermodynamic properties. J Phys Chem Ref Data. 1982;11(supl.2):67–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Izato, Yi., Miyake, A. Thermal decomposition of molten ammonium nitrate (AN). J Therm Anal Calorim 122, 595–600 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4762-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4762-2